Key takeaways:
- Traditional data analysis in Excel requires mastering a dozen complex functions like
VLOOKUP,SUMIFS, andTRIM, leading to hours of manual work and hard-to-maintain spreadsheets. - Excel AI tools like Excelmatic replace this complexity, allowing you to clean, merge, and analyze data by simply describing your goals in plain language.
- Using an AI agent significantly cuts down analysis time, reduces formula-related errors, and provides the flexibility to answer ad-hoc questions without rebuilding your entire report.
Problem Background & Pain Points
Imagine it's Monday morning. You have a raw data export of the latest sales figures. In a separate file, you have a list of employees and the regions they belong to. Your manager wants a summary report by noon, breaking down sales performance by region and identifying any data inconsistencies.
For most Excel users, this scenario triggers a familiar sense of dread. You know you're about to embark on a multi-step battle with Excel functions.
Your mental checklist probably looks something like this:
- Clean the data: The "Region" column from a web form has extra spaces (" North " instead of "North"), and some sales figures are formatted as text, not numbers.
- Combine data sources: You need to pull the "Region" information from the employee file into your main sales data sheet.
- Summarize the results: You have to calculate total sales and the number of transactions for each region.
- Handle errors: What happens when an employee name in the sales data has a typo and doesn't match the employee list?
Each of these steps is a potential roadblock, a rabbit hole of nested formulas, and a source of potential errors that could compromise your entire analysis. You're not just analyzing data; you're fighting the tool itself.
The Traditional Excel Solution: A Stack of Functions
To solve this, a seasoned Excel user would typically rely on a toolkit of powerful but complex functions. The process is logical but incredibly manual and prone to error.
Step 1: Data Cleaning with TRIM and VALUE
First, you need to fix the messy data. You'd likely create "helper columns" to clean the original data.
- To remove leading and trailing spaces from the region names, you'd use the
TRIMfunction.=TRIM(A2) - To convert sales figures stored as text back into numbers that you can sum up, you'd use the
VALUEfunction.=VALUE(B2)
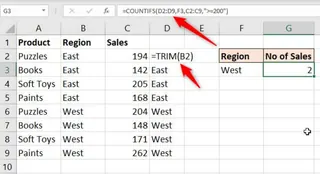
The Limitation: This creates a bloated spreadsheet with original and cleaned columns. If new data is pasted in, you have to remember to drag the formulas down again.
Step 2: Merging Data with VLOOKUP
Next, to bring the region information into your sales table, you'd use the classic VLOOKUP function.
=VLOOKUP(B2, $G$2:$H$12, 2, FALSE)
This formula looks for the employee's name (in cell B2) within the employee table (G2:H12), returns the value from the second column (Region), and requires an exact match (FALSE).
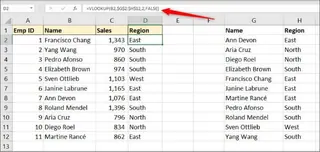
The Limitations:
- Complexity: You must remember the four arguments in the correct order. What does the
2mean? What doesFALSEdo? It's not intuitive. - Brittleness: If an employee's name has a typo or they aren't in the lookup table,
VLOOKUPreturns an ugly#N/Aerror. You then need to wrap it in anIFERRORfunction to make your report look clean, making the formula even longer:=IFERROR(VLOOKUP(...), "Name not found"). - Rigidity:
VLOOKUPcan only look to the right. If the region was to the left of the employee name in your source table, it wouldn't work at all.
Step 3: Conditional Summaries with SUMIFS and COUNTIFS
Once your data is cleaned and merged, you can finally start summarizing. To get total sales by region, you'd use SUMIFS.
=SUMIFS(C2:C9, B2:B9, E3)
This sums the values in the sales column (C2:C9) where the corresponding region in column B matches the region name in cell E3. COUNTIFS works similarly to count transactions.
The Limitation: These formulas are static. If your manager suddenly asks, "Great, now can you show me the breakdown by product category within each region?", you have to go back and manually edit the formula, adding another criteria range and criterion. Every new question requires a new or modified formula.
Step 4: Reporting with UNIQUE, SORT, and FILTER
For users with modern versions of Excel (Microsoft 365 or 2021+), dynamic array functions like UNIQUE, SORT, and FILTER have made reporting easier. You could combine them to create a sorted, unique list of products and then sum their sales.
=SORT(UNIQUE(B2:B15))
The Limitation: This creates a collaboration barrier. If you send your super-sleek report to a colleague who has Excel 2019, the dynamic array formulas will break, showing a #SPILL! or #NAME? error. Your advanced solution becomes unusable for others.
The New Solution: Using an Excel AI Agent (Excelmatic)
Instead of memorizing dozens of functions and their limitations, what if you could just tell Excel what you want? That's the promise of Excel AI agents like Excelmatic. You upload your file and use plain language to get the same, or even better, results in a fraction of the time.

Step-by-Step: Solving the Same Problem with Excelmatic
Here's how you'd tackle the exact same reporting challenge using a conversational approach.
1. Upload Your Data File(s)
First, you just upload your raw Excel or CSV files to Excelmatic. You can even upload multiple files at once, like your sales_data.xlsx and employee_regions.xlsx. Excelmatic will recognize them as separate data sources.
2. Describe What You Want in Plain Language
Instead of writing formulas, you simply type your requests into the chat. The AI understands the context of your data and your intent.
Here are some prompts you could use to solve the problem:
To clean the data:
In the sales data, please clean the 'Region' column to remove any extra whitespace. Also, ensure the 'Sales Amount' column is formatted as a number.
To merge the two files (the
VLOOKUPtask):I uploaded a second file with employee regions. Can you add a 'Region' column to my main sales data table by matching the 'Employee Name' from both files?
To summarize the results (the
SUMIFStask):Create a pivot table that shows the total sales and the count of transactions for each region. Please sort the table to show the region with the highest sales on top.
To filter for specific insights (the
FILTERtask):Show me all the sales records from the 'North' region where the sale amount was over $500.
3. Review and Iterate on the Results
Excelmatic won't just give you a final answer. It will show you the resulting table, pivot table, or chart and wait for your feedback. This is where the real power of conversational AI shines. You can continue the dialogue to refine your analysis.
- "That's great. Now, can you add a column to that summary table calculating the average sale value per transaction for each region?"
- "Could you visualize the total sales by region as a bar chart?"
- "Remove 'South' region from this view."
This iterative process is impossible with traditional formulas, where each change requires a significant rework.
4. Export Your Finalized Work
Once you're satisfied, you can download the results as a new, clean Excel file. You can get the cleaned data, the final report, the pivot table, or even ask Excelmatic to give you the exact Excel formula it would have used, which is a great way to learn.
Dialogue Example
Here’s how a full conversation with Excelmatic might look:
User: I've uploaded two files: sales_export.csv and employee_regions.xlsx. The sales data is messy. First, please clean the 'Sales Amount' column to be a number and trim any extra spaces from the 'Sales Rep' names.
Excelmatic: Done. I have cleaned the 'Sales Amount' and 'Sales Rep' columns in sales_export.csv. The data is now ready for analysis. What's next?
User: Now, use the employee_regions.xlsx file to add a new 'Region' column to the sales data by matching the 'Sales Rep' name with the 'Employee' column in the other file.
Excelmatic: I have successfully merged the data. The sales_export.csv table now includes a 'Region' column. I found 3 names that did not have a match. Would you like to see a list of them?
User: Yes, show me. And then, create a pivot table summarizing the total sales for each region. Sort it from highest to lowest sales.
Excelmatic: Here are the 3 unmatched names: [...]. I have also created the pivot table you requested, showing total sales by region, sorted in descending order. You can view it below or download the updated Excel file.
Traditional Formulas vs. Excelmatic: A Quick Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Method (Formulas) | Excelmatic (AI Agent) |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Result | 30-60 minutes, depending on complexity. | 2-5 minutes. |
| Required Skill | Deep knowledge of VLOOKUP, SUMIFS, TRIM, IFERROR, etc. |
Ability to describe a business need in language skills. |
| Flexibility | Low. New questions require new formulas. | High. Ask follow-up questions in a conversation. |
| Error Handling | Manual. Requires IFERROR and debugging #N/A. |
Proactive. The AI can flag mismatches for you. |
| Collaboration | Risky if colleagues have different Excel versions. | Easy. Share the final, clean Excel file that works for everyone. |
FAQ
1. Do I need to know any Excel functions to use Excelmatic? No. The entire point is to replace formula syntax with natural language. You just need to be able to describe the outcome you want, not the steps to get there.
2. Is my company's data safe if I upload it? Excelmatic is designed with data privacy in mind. Data is processed securely, and you retain ownership of your files. For specific compliance details, always refer to the official privacy policy on the website.
3. What if my data is really messy with inconsistent column names? The AI is trained to understand common variations in column headers (e.g., 'Sales Amount', 'sale_value', 'Revenue'). For more complex cases, you can simply tell the AI which columns to use, for example: "My sales column is called 'Total Rev'. Use that to sum the sales."
4. Can Excelmatic handle analysis that involves multiple steps? Absolutely. That's one of its main strengths. You can chain commands together in a single conversation, just as you would instruct a human data analyst. It maintains the context of your previous requests.
5. Can I get the actual Excel formulas from Excelmatic? Yes. You can ask Excelmatic to provide the formula it used to generate a result. This is a fantastic way to learn how to perform complex tasks in Excel or to reuse the formula in your own spreadsheets.
Take Action: Upgrade Your Excel Workflow Today
Stop spending your valuable time wrestling with formula syntax and debugging #N/A errors. The hours spent on manual data prep and reporting could be spent uncovering insights and making decisions.
Continuing with the traditional, function-heavy approach means more time wasted, a higher risk of error, and rigid reports that are difficult to adapt. By embracing an Excel AI agent, you transform your relationship with your data. You become a director, not a laborer.
Ready to see for yourself? Try Excelmatic today. Upload one of the messy spreadsheets you've been avoiding, and ask your first question. You might be surprised how much you can accomplish in just a few minutes.






