Key Takeaways:
- Automating repetitive Excel tasks can save countless hours, but traditional methods like VBA require significant programming knowledge and a steep learning curve.
- Excelmatic offers a revolutionary alternative by allowing you to automate complex workflows using simple language commands—no coding, macros, or technical expertise needed.
- For business professionals who need results fast, Excelmatic bridges the gap between high automation needs and low technical skills, turning intricate data tasks into simple instructions.
- While VBA remains powerful for deep customization, AI-driven automation is the superior choice for speed, accessibility, and handling everyday business data challenges.
In Excel, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is a powerful programming language that allows users to automate repetitive tasks and extend functionality beyond standard features. Whether you are a beginner looking to boost productivity or an advanced user seeking to streamline complex workflows, VBA can make things easier.
However, with the advancement of artificial intelligence, the way we automate Excel tasks is undergoing a transformation. In this guide, I will explain the fundamentals and advanced concepts of VBA while comparing it with modern AI tools like Excelmatic. This will help you choose the best solution for your needs.
What is Excel Automation? Tradition vs. Modernity
The core goal of automating Excel is to reduce manual effort while increasing efficiency and accuracy. Traditionally, this has been primarily achieved through VBA.
Traditional Method: Excel VBA
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is a programming language used to automate tasks in Microsoft Office applications. Although it can be used with programs like Word and Access, its most widespread application is creating custom macros in Excel.
I first used VBA to automate a weekly report that used to take hours to compile manually. With a few lines of code, I simplified the entire process into a single button click, saving significant time. From that moment, I knew that investing time to master VBA would yield huge returns in productivity. However, it undeniably requires a considerable time investment to learn programming.
Modern Method: Excel AI Agent

With the development of AI technology, Excel AI Agents like Excelmatic have emerged. These tools are designed to perform tasks through natural language understanding. You don't need to write any code; simply upload your file and describe what you need in simple language—be it Chinese, English, or others—and the AI can handle various tasks for you, including data analysis, chart generation, data cleaning, and automation.
For example, for that time-consuming weekly report, using Excelmatic, I would simply say: "Please consolidate the weekly sales data, calculate total sales and profit margin, and generate a summary chart." The AI would complete this instantly, with no programming knowledge required.
Preparations Before Starting with VBA
Before diving deep into VBA, you must understand its key terms and concepts. These are common terms you will encounter when starting to automate tasks and build custom solutions.
- Modules: Containers that store VBA code. Procedures and functions are saved here.
- Objects: The building blocks of VBA, representing elements like workbooks, worksheets, and cells.
- Procedures: Blocks of code that perform specific tasks, usually divided into Sub procedures or Functions.
- Statements: Instructions within a procedure that tell Excel what operation to perform.
- Variables: Store data that can be used and manipulated within the code.
- Logical Operators: Compare values and make decisions based on the results, including
And,Or, andNot.
In contrast, using AI tools like Excelmatic requires no understanding of these programming concepts. Your "instructions" are your everyday language, which significantly lowers the barrier to entry.
How to Get Started with VBA
To start using VBA, you need to access the VBA Editor, where you write and edit your code.
Enabling the "Developer" Tab
The first step is to enable the Developer tab, which is usually hidden in the ribbon.
- Right-click anywhere on the ribbon.
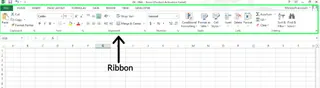
- Select the Customize the Ribbon... option.
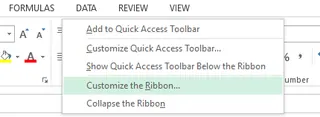
- In the dialog box that appears, check the Developer option, then click OK.
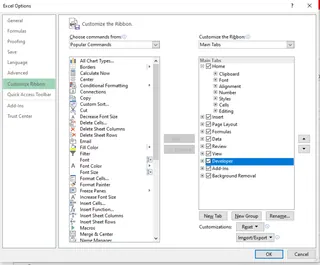
Now you can see the "Developer" tab at the top of the ribbon.
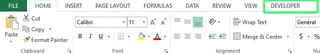
Opening the VBA Editor
Once the "Developer" tab is enabled, click on it and select Visual Basic. You can also use the shortcut ALT + F11 to open the VBA Editor directly.
Navigating the VBA Interface
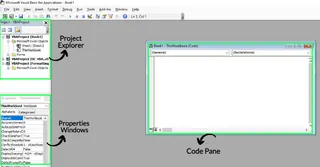
The VBA Editor might look intimidating at first, but its key areas are easy to understand:
- Code Pane: Where you write and edit VBA code.
- Project Explorer: Shows a hierarchical view of the projects and modules in your workbook.
- Properties Window: Displays the properties of the selected object, used to customize its settings.
Writing Code: VBA vs. AI Instructions
Now, let's compare the implementation methods of VBA and AI tools through some practical examples.
Example 1: Displaying a Simple Message
VBA Method
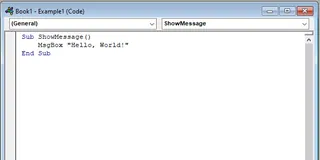
In the VBA Editor, select Insert > Module to create a new module. Then, enter the following code in the Code Pane:
Sub ShowMessage()
MsgBox "Hello, World!"
End Sub
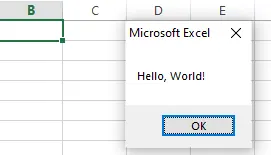
Press F5 or run this macro via Developer > Macros, and you'll see a message box.
AI Method (Excelmatic)
For this kind of simple interaction, VBA is very straightforward. But for more complex data manipulation, the advantages of AI begin to show. Let's look at a more practical example.
Example 2: Renaming a Worksheet
VBA Method
To rename the currently active worksheet to "Sales Report," you need to write the following code:
Sub RenameActiveSheet()
' Renames the active sheet to "Sales Report".
ActiveSheet.Name = "Sales Report"
End Sub
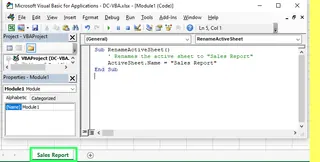
After running, the worksheet name will be changed.

AI Method (Excelmatic)
Using Excelmatic, you don't need to open any editor or write code. Simply upload your Excel file and enter a simple instruction:
Rename the current worksheet to 'Sales Report'.
Excelmatic immediately understands and performs the action. The advantage of this method lies in its intuitiveness and speed, especially for users unfamiliar with the VBA object model (like ActiveSheet.Name).
Example 3: Formatting a Cell Range
VBA Method
Suppose you want to change the background color of the cell range F3 to I3 to green. The VBA code would be:
Sub FormatRange()
' Selects the range from F3 to I3
Range("F3:I3").Select
' Changes the background color of the selected range to Green
Selection.Interior.Color = RGB(101, 255, 143)
End Sub
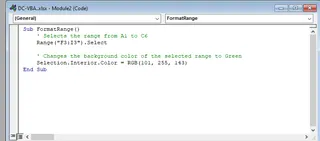
The result is as follows:
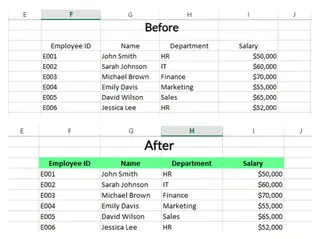
AI Method (Excelmatic)
Similarly, using Excelmatic, you just need to describe the outcome you want:
Change the background color of cells F3 to I3 to green.
The AI can not only accomplish this task but also handle more complex formatting requests, such as: "Highlight the background of all rows with sales below 500 in red," without you needing to write VBA code with loops and conditional statements.
Using Macros for Automation: Recording vs. Smart Instructions
Macros are sequences of instructions created in VBA to perform repetitive tasks.
Recording an Excel Macro
For users who don't know programming, recording a macro is a great starting point.
- Go to Developer > Record Macro.
- Name the macro, set a shortcut key (e.g., Ctrl+S), then click OK.
- Perform the actions you want to automate (e.g., formatting a table).
- When finished, click Stop Recording.
Afterward, you can apply the same formatting to other data with one click via the shortcut key or the macro menu.
While recorded macros are convenient, the generated code is often verbose and inflexible. For example, it always acts on a fixed cell range, and if the data range changes, the macro may fail. You often need to manually edit the code to enhance its generality.
Writing Custom Macros vs. AI Instructions
In some cases, recording a macro is insufficient, and you must write code from scratch.。
VBA Method: Copying Data
Suppose you want to copy data from Sheet1 to Sheet2. A custom VBA macro would look like this:
Sub CopyData()
Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B1:E21").Copy Destination:=Sheets("Sheet2").Range("B1")
End Sub
This requires you to know the exact syntax for worksheet and cell range references.
AI Method (Excelmatic)
Using Excelmatic, this task becomes as simple as a conversation:
Copy the data from cells B1 to E21 on Sheet1 to cell B1 on Sheet2.
The advantage of AI lies in its flexibility. You can easily modify the instruction, for example: "Copy all data rows containing 'Completed' status from Sheet1 to Sheet2," which would require writing more complex logic in VBA. The AI understands your intent, not just mechanically executing recorded steps.
Conclusion: Which Tool to Choose?
Both VBA and AI tools like Excelmatic offer powerful solutions for Excel automation, but they cater to different users and scenarios.
Choose VBA if you:
- Enjoy programming and want complete control over every detail of automation.
- Need to build complex, deeply integrated custom applications with Excel.
- Work in an environment that restricts the use of external AI tools.
- Don't mind investing time in learning a new programming language.
Choose Excelmatic if you:
- Want to solve problems quickly without learning to program.
- Need to handle everyday data cleaning, report generation, formatting, and analysis tasks.
- Prioritize efficiency and want to complete work with simple natural language instructions.
- Need to flexibly handle dynamically changing data and requirements.
Mastering VBA is undoubtedly a valuable skill, but for most Excel users looking to simplify daily tasks, AI tools offer a faster, more intuitive path. The key is to understand the strengths and weaknesses of both approaches and choose the one that best enhances your productivity.
Ready to automate your Excel tasks without writing a single line of code? Try Excelmatic today and experience the power of AI-driven productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the purpose of the Explicit statement in VBA?
The Option Explicit statement forces all variables to be explicitly declared before use. This helps reduce bugs caused by typos and makes code easier to maintain.
2. How can I protect my VBA code with a password?
In the VBA Editor, go to Tools > VBAProject Properties > Protection tab. Check Lock project for viewing and set a password.
3. What is the difference between ActiveWorkbook and ThisWorkbook in VBA?
ActiveWorkbook refers to the workbook currently active (the one being operated on by the user), which may not contain the running VBA code. ThisWorkbook always points to the workbook where the VBA code resides, regardless of which workbook is active.
4. What are UserForms in VBA and how are they used?
UserForms are custom dialog boxes in VBA that allow users to input data or interact with the program. They can be used to create data entry forms, option selection interfaces, or any scenario that requires a custom user interface.






