Key Takeaways:
- Spacing errors in Excel are a common pain point that can ruin data analysis, requiring tedious manual fixes or complex formula combinations.
- Excelmatic offers the simplest solution by cleaning your entire dataset instantly using plain language instructions—no formulas, clicks, or technical skills needed.
- Unlike traditional methods that require constant troubleshooting, Excelmatic intelligently preserves data types, handles edge cases like non-breaking spaces, and ensures your data remains calculation-ready.
- For business professionals who need clean, reliable data quickly, using an AI tool like Excelmatic means faster reporting, fewer errors, and more time for analysis.
If you're a data analyst or a professional dealing with reports, you've likely encountered small issues that snowball into major headaches. In Excel, a common culprit is extra spaces in your data. They can mess up everything from sorting and filtering to critical lookups, causing unexpected errors. Sometimes, two values look identical but fail to match simply because of a hidden space.
Traditionally, Excel provides the TRIM() function to tackle this. But now, with AI tools, data cleaning has become easier than ever. This article will show you both approaches: the classic, manual formula method and the modern, AI-automated way.
Quick Answer
The Traditional Way: Using the TRIM() Function
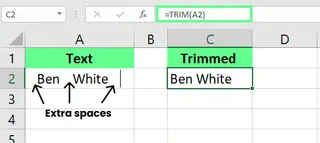
Excel's TRIM() function removes all extra leading, trailing, and in-between spaces from text, leaving only single spaces between words.
=TRIM(text)
For example, if cell A2 has a full name with extra spaces between the first and last name, you can use:
=TRIM(A2)
The AI-Powered Solution: Using Excelmatic

For a faster, smarter approach, you can use an AI tool like Excelmatic. You don't need to remember any functions.
- Upload your Excel file to Excelmatic.
- State your request in simple language, for example:
Remove all extra spaces from my entire sheet.
Excelmatic processes your data instantly, cleaning up all inconsistent spacing without you writing a single formula.
Excel TRIM() Use Cases & Examples
Let's explore specific examples of how TRIM() cleans extra spaces and fixes formatting issues, contrasting it with the AI approach.
Cleaning Imported Data
When we import data into Excel from external sources, it can sometimes get messy. Often, there are extra spaces scattered throughout, which interfere with sorting, filtering, and even simple calculations.
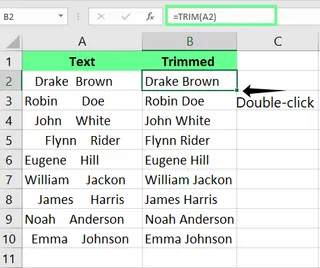
Traditional Method
Let's say I have a dataset of customer details with inconsistent spacing, and I want to remove extra spaces from cells all at once. I enter the following formula in cell C2 and then double-click the fill handle to apply it to all cells:
=TRIM(A2)
Excelmatic Solution
With Excelmatic, the process is more intuitive. You simply upload your file and tell the AI:
In the customer details column, clean up all the extra spacing.
The AI does all the work for you, without needing to create helper columns or drag fill handles. It delivers clean data directly, faster and with less room for error.
Using TRIM() on Numbers
The TRIM() function works on text only. If we use it on numbers, Excel treats them as text, which can cause issues during calculations.
Traditional Method
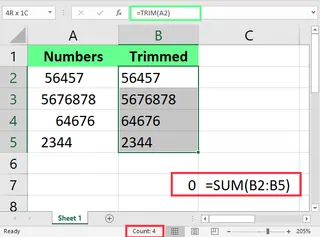
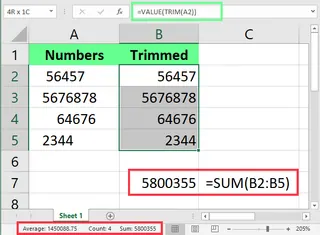
In the example above, TRIM() cleaned the spaces, but two things look wrong:
- The numbers are left-aligned instead of right-aligned.
- The
SUM()function returns zero because the values are being treated as text.
To fix this, we can nest TRIM() inside the VALUE() function:
=VALUE(TRIM(A2))
This extra step converts the trimmed text back into numbers.
Excelmatic Solution
Excelmatic understands context. When you ask it to clean a column containing numbers, it's smart enough to preserve their numeric format. You just say:
Clean the spaces in the numbers column and ensure they are still numbers.
You don't need to remember the VALUE() function or worry about data type conversion. The AI handles it automatically.
Removing Delimiters
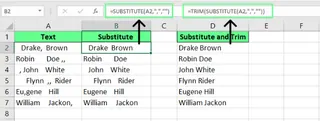
If we need to remove specific delimiters like commas from text, we can use the SUBSTITUTE() function. But on its own, it doesn't remove extra spaces that may be around the delimiter.
Traditional Method
To remove both the commas and the extra spaces, I need to combine SUBSTITUTE() with TRIM():
=TRIM(SUBSTITUTE(A2,",",""))
Excelmatic Solution
Again, no combining functions is needed here. You can accomplish everything with a single, simple instruction:
Remove all commas and extra spaces from column A.
Excelmatic handles both the delimiter and the spacing in one step, streamlining your workflow.
More Advanced Tricks with Excel's TRIM() Function
Beyond basic use, TRIM() can perform more advanced operations when combined with other Excel functions. Let's see how these become simpler with AI.
Removing Invisible Characters
Sometimes, our data might contain non-printable characters that TRIM() itself can't handle.
Traditional Method
I need to use the CLEAN() function, nested within TRIM():
=TRIM(CLEAN(A1))
Here, CLEAN() removes the invisible characters, and TRIM() cleans the extra spaces.

Excelmatic Solution
For the AI, "clean data" implies freedom from both extra spaces and hidden characters. One general instruction is all you need:
Clean my data in column A.
Excelmatic will handle both spaces and invisible characters without you having to diagnose the problem or know that the CLEAN() function exists.
Counting Words in a Cell
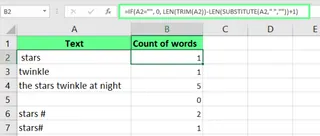
We can use TRIM() to count the number of words in a cell, but it requires a rather complex formula.
Traditional Method
Look at this formula:
=LEN(TRIM(A1)) - LEN(SUBSTITUTE(TRIM(A1), " ", "")) + 1
To handle empty cells, the formula becomes even more complex:
=IF(A2="", 0, LEN(TRIM(A2))-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(A2," ",""))+1)
Excelmatic Solution
Forget the complex formulas. Just ask the AI:
Count the number of words in each cell of column A and put the result in column B.
This approach is not only simpler and more readable but also almost impossible to get wrong.
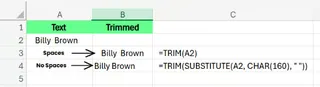
Dealing with Non-Breaking Spaces
TRIM() removes regular spaces but can't handle non-breaking spaces (CHAR(160)), which often appear in text copied from websites.
Traditional Method
You need SUBSTITUTE() and CHAR(160) to find and replace these special spaces, then TRIM() to clean up:
=TRIM(SUBSTITUTE(A1, CHAR(160), " "))
Excelmatic Solution
A good AI data-cleaning tool should recognize all types of spaces, including non-breaking ones. You don't need to be an expert in character encoding. Use the same simple instruction as before:
Fully clean up the spacing in column A, including any weird spaces from a web copy.
Excelmatic handles these nuances, letting you focus on analysis rather than troubleshooting.
Common Issues & Fixes
When using traditional functions, you might run into some problems. Let's see how to fix them and how AI avoids them from the start.
Fixing the #VALUE! Error
Traditional: If you get a #VALUE! error after using TRIM(), it's likely because the function was applied to a non-text value. You need to check data types or nest TRIM() inside VALUE() as discussed earlier.
AI Advantage: With Excelmatic, you rarely encounter formula errors like #VALUE!. Since you're not writing formulas but giving instructions, the AI ensures the correct operation is performed, avoiding this common Excel pitfall.
Fixing Performance Issues with Large Datasets
Traditional: Using TRIM() on large datasets can slow down Excel because it recalculates every row whenever the spreadsheet changes. The fix is to copy and paste the cleaned column as values (Ctrl + Alt + V > Paste as Values) after applying TRIM().
AI Advantage: Excelmatic processes data in the cloud, not in your live Excel file. This means it's often much faster with large datasets and won't slow down your computer. You get a cleaned file back, with no performance lag.
Fixing Special Character Problems
Traditional: TRIM() only handles the space character with ASCII code 32. To handle other hidden characters, you need to diagnose with functions like CODE(), LEFT(), RIGHT(), then remove them with SUBSTITUTE() and CHAR()—a tedious process.
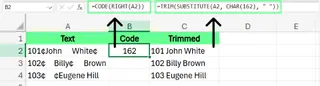
AI Advantage: You don't need to be a character encoding detective. Simply tell Excelmatic "clean my data," and it uses its powerful algorithms to identify and remove various special characters and irregular spaces, even ones you didn't know existed.
Final Thoughts
Now you know two ways to clean extra spaces in Excel.
The Traditional Path relies on the TRIM() function and its combinations with others like SUBSTITUTE(), CLEAN(), and VALUE(). It's powerful but requires you to remember multiple functions, understand their limitations, and be able to build complex nested formulas for advanced problems.
The Modern AI Path, via tools like Excelmatic, simplifies the entire process into a single step: describing what you need in natural language. This approach is faster, more intuitive, and handles all the underlying complexity for you, freeing you to focus on more important analysis.
Whichever path you choose, clean data is the foundation of reliable analysis.
Ready to clean your Excel data in seconds instead of minutes? Try Excelmatic today and turn tedious data cleaning into a simple command.
Excel Trim() FAQs
How do I check if a cell contains extra spaces before using TRIM()?
Formula Way: Use the formula =LEN(A1)-LEN(TRIM(A1)). If the number returned is greater than 0, the cell has extra spaces.
AI Way: No need to check. Just ask Excelmatic to clean the data, and it will handle all cells that need it.
How do I delete only leading spaces, keeping spaces between words?
Formula Way: You can use a more complex formula: =MID(A2,FIND(MID(TRIM(A2),1,1),A2),LEN(A2)).
AI Way: You can be more specific with Excelmatic: "Remove only the leading spaces from column A."
Can I use Excel's Find & Replace tool to remove extra spaces between words?
Yes. Select your data range, press Ctrl + H. In "Find what," enter two spaces. In "Replace with," enter one space. Click "Replace All" repeatedly until Excel says it can't find anything to replace. It's tedious but works. TRIM() or an AI tool is far more efficient.
Can I capitalize the first letter of each word and trim spaces at the same time?
Formula Way: Yes, you can use =PROPER(TRIM(A2)) to remove extra spaces while capitalizing the first letter of each word.
AI Way: Absolutely. One instruction to Excelmatic: "Clean all extra spaces and capitalize the first letter of each word in column A."






