Key Takeaways:
- Transposing data (flipping rows and columns) in Excel is crucial for analysis and reporting, but traditional methods require manual steps, precise formula setup, or learning complex tools
- Excelmatic offers the fastest solution by transposing data instantly with simple language instructions—no manual selection, formula writing, or tool navigation needed
- Compared to manual methods, Excelmatic handles data restructuring effortlessly, saving time and eliminating common technical errors like incorrect range sizing
- For business professionals who need to quickly reorganize data for presentations or analysis, adopting AI tools like Excelmatic means faster insights and more time for decision-making
Transposing data in Excel allows you to flip your data orientation, turning rows into columns and columns into rows. This technique is particularly useful when you need to restructure your dataset for better analysis, visualization, or reporting.
Whether you're preparing data for a PivotTable, creating a summary view, or simply need to change your data layout, Excel offers several methods to transpose your data. Traditionally, these are:
- Paste Special - A quick one-time conversion
TRANSPOSE()function - A dynamic formula-based approach- Power Query - An advanced method for larger datasets
However, a new, even faster method has emerged:
- AI-Powered Tools like Excelmatic - An intelligent approach that automates the task using plain language commands.
In this article, you'll learn step-by-step how to use each method, understand their key differences, and decide which one is best for your specific task.
Quick Answer
Need to transpose data in a hurry? Here are your fastest options:
The Absolute Quickest Way (AI-Powered): Use an AI tool like Excelmatic. Simply upload your file and ask, "Transpose the data in Sheet1 from A1 to B5." The AI handles everything instantly, with no manual steps.
The Quickest Manual Way (Paste Special):
- Select and copy your data (
Ctrl + C). - Right-click on the destination cell.
- Select "Paste Special."
- Check the "Transpose" box and click OK.
- Select and copy your data (
This immediately flips your rows to columns and columns to rows, providing a fast manual solution for most transposing needs.
What Does Transpose Mean in Excel?
Transposing in Excel means converting rows into columns and columns into rows. It's essentially rotating your data by 90 degrees, changing its orientation while preserving all the information.
When you transpose data, the first row becomes the first column, the second row becomes the second column, and so on.
For example, if you have a dataset with product names in rows and monthly sales in columns, transposing would give you product names in columns and monthly sales in rows.
Ways to Transpose in Excel
Excel offers four distinct methods to transpose data, each with its own advantages and ideal use cases. Let's explore each technique step-by-step to help you choose the right approach.
1. Using Paste Special to Transpose Data
The Paste Special method is the simplest manual way to transpose data in Excel. It creates a one-time, static copy of your data in the transposed orientation. Let's walk through an example. Imagine we have the following regional sales data in vertical format:
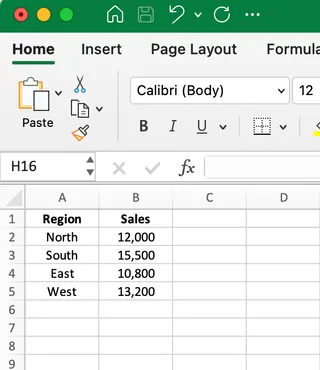
To transpose this data from a vertical to horizontal layout:
- Select all the data you want to transpose (in this case, cells A1:B5).
- Copy the data (Ctrl+C or right-click and select Copy).
- Click on the cell where you want the transposed data to appear (such as cell D1).
- Right-click and select Paste Special from the context menu.
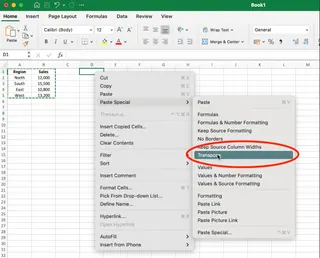
- In the Paste Special dialog box, check the Transpose box and click OK.
The result after transposing is shown below:
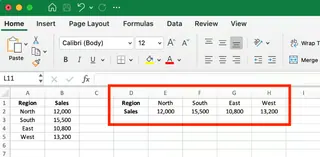
Notice how the data has been completely rotated—what was previously in rows is now in columns, and vice versa.
When to use this method:
- For quick, one-time data transformations.
- When you need a simple solution that doesn't require formulas.
- For smaller datasets that won't need frequent updating.
Advantages: Simple and quick to apply with just a few clicks. Limitations: Creates a static copy that doesn't update if your original data changes.
2. Using the TRANSPOSE() Function
The TRANSPOSE() function offers a dynamic alternative to Paste Special. Unlike the previous method, this function maintains a live link to your original data, automatically updating the transposed results whenever the source data changes.
Let's use the same regional sales data to demonstrate:
- First, you need to select the destination range. Since the original data is 5 rows by 2 columns, we'll need to select a range that is 2 rows by 5 columns to accommodate the transposed structure.
- With your destination cells selected, enter the
TRANSPOSE()formula in the formula bar:
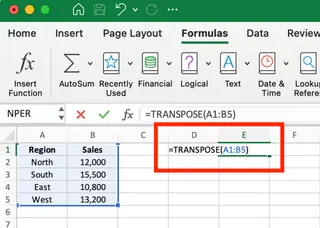
- In modern Excel (Microsoft 365 or 2021), simply press Enter. For older Excel versions, you'll need to press Ctrl+Shift+Enter, as this is an array formula.
The result will look similar to our previous example, but if you change a value in the original data, the transposed version will automatically update.
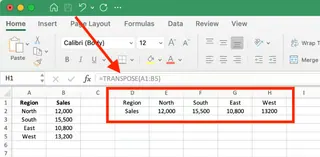
When to use this method:
- When your source data changes frequently.
- When you need to maintain a live connection between original and transposed data.
- For creating dynamic reports or dashboards.
Advantages: Creates a dynamic link that updates automatically. Limitations: Requires careful selection of the correct destination range size; can be confusing for beginners.
3. Using Power Query to Transpose Data
Power Query is Excel's most powerful data transformation tool, perfect for handling larger datasets and complex, repeatable workflows. While it requires more steps, it offers unmatched flexibility.
Let's use our same regional sales data to demonstrate:
- Select your data range, click on the Data tab, and choose From Table/Range.
- The Power Query Editor will open with your data loaded. Now, click on the Transform tab in the ribbon, and select Transpose from the menu options.
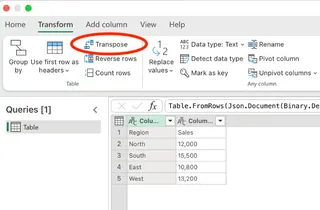
- You'll immediately see your data transposed in the preview window. The formula bar shows
Table.Transpose(Source), indicating the applied transformation.
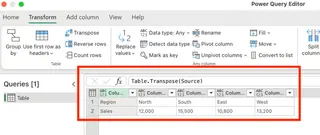
- Once you're satisfied, click Close & Load from the Home tab to send the transposed data back to your Excel worksheet.
When to use this method:
- For large datasets where other methods are slow.
- When you need to perform additional transformations (e.g., cleaning, filtering) beyond just transposing.
- For repetitive tasks that you want to automate and refresh.
Advantages: Ideal for large datasets and complex workflows; creates a refreshable query. Limitations: Has a steeper learning curve for beginners; involves more steps for a simple transpose.
4. Using an AI-Powered Approach with Excelmatic

For the ultimate in speed and simplicity, AI-powered tools like Excelmatic are changing the game. Instead of navigating menus or writing formulas, you can simply tell the AI what you want in plain language.
Excelmatic is an Excel AI Agent that handles complex tasks for you. Here’s how you would transpose the same regional sales data:
- Upload Your File: Drag and drop your Excel file into Excelmatic.
- State Your Request: In the chat interface, type a simple command like:
Transpose the data in the range A1:B5.
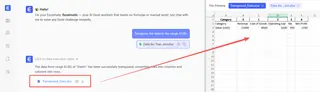
Or, more conversationally: > Flip the rows and columns for the regional sales data.
- Get Instant Results: Excelmatic processes your request, performs the transposition, and provides the correctly structured data back to you, ready to be downloaded or further analyzed. There's no need to select a destination range or worry about array formulas.
When to use this method:
- When you want the fastest and easiest solution.
- For users who aren't familiar with Excel's specific functions or menus.
- When you need to perform multiple data cleaning or analysis steps in sequence.
Advantages:
- Effortless: No learning curve. Just describe what you need.
- Extremely Fast: Automates the entire process in seconds.
- Intelligent: No need to manually define the output range or handle other technical details.
- Versatile: Can handle transposing as part of a larger analysis, like "transpose this data and then create a bar chart of the sales."
Limitations:
- Requires an internet connection and use of a third-party tool.
- The output is a new, static dataset (though you can re-run the process easily).
Method Comparison at a Glance
| Feature | Paste Special | TRANSPOSE() Function |
Power Query | Excelmatic (AI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Very Easy | Medium | Hard | Effortless |
| Speed | Fast | Fast | Medium | Fastest |
| Dynamic Updates | No | Yes (Automatic) | Yes (On Refresh) | No (Re-run query) |
| Best For | Quick, one-off tasks | Dynamic reports | Large/complex data | Speed & simplicity |
Transposing Columns, Rows, and Tables
While we've explored the four main methods, let's briefly address some specific scenarios. All four methods can achieve the following outcomes.
How to transpose columns to rows in Excel
When you have data organized in columns and need it in rows:
- Paste Special: Copy columns, right-click destination, choose Paste Special → Transpose.
TRANSPOSE()Function: Select a destination row and enter=TRANSPOSE(A1:A5).- Power Query / Excelmatic: Both tools handle this transformation seamlessly with their respective transpose features.
How to transpose rows to columns in Excel
If your data is in rows but needs to be in columns, the steps are identical. Excel's transpose tools see rows and columns as interchangeable.
- Paste Special: Copy rows, right-click destination, choose Paste Special → Transpose.
TRANSPOSE()Function: Select a destination column and enter=TRANSPOSE(A1:F1).
If you're working with larger datasets, Power Query or Excelmatic are highly effective for automating row-to-column transformations.
How to transpose tables in Excel
When working with entire tables:
- For smaller tables, Paste Special is effective.
- For larger tables, Power Query provides more control and can handle any table size efficiently.
- For the fastest result, simply ask Excelmatic to "transpose the table named 'SalesData'".
Remember that transposing a table will switch not just your data but also your headers.
Additional Things to Consider
When transposing data in Excel, keep these points in mind:
Handling blank cells
The TRANSPOSE() function may replace blanks with zeros. To avoid this, use a nested IF() statement:
=TRANSPOSE(IF(A1:F5="","",A1:F5))
This formula checks for empty cells and keeps them empty in the transposed result. Tools like Paste Special, Power Query, and Excelmatic typically preserve blank cells correctly.
Maintaining links to source data
- Paste Special creates a static copy (no link).
TRANSPOSE()creates a live, dynamic link.- Power Query creates a refreshable link.
- Excelmatic produces a static output, but the process is so fast it can be re-run instantly on updated data.
Choose the method based on how you need to handle data updates.
Using TRANSPOSE() with conditional formatting
Formatting (colors, fonts, conditional formatting) does not carry over when using the TRANSPOSE() function or Power Query. You will need to reapply formatting rules to the new, transposed range. Paste Special sometimes offers an option to paste formatting, but it can be inconsistent.
Conclusion
Transposing data is a fundamental Excel skill for restructuring datasets. We've explored four powerful methods, each with unique strengths:
- Paste Special for quick, static changes.
TRANSPOSE()function for dynamic, formula-linked results.- Power Query for robust, repeatable workflows on large datasets.
- Excelmatic for the ultimate in speed and ease-of-use, leveraging AI to eliminate manual steps.
By understanding these options, you can choose the most efficient method for any situation, from a simple data flip to a complex, automated transformation pipeline. As AI tools become more integrated with data analysis, leveraging them can save significant time and effort in your daily Excel tasks.
Ready to restructure your data instantly? Try Excelmatic today and transpose your spreadsheets with a simple, clear request.
FAQ
What does transpose mean in Excel?
Transposing in Excel means converting rows to columns and columns to rows, essentially rotating your data by 90 degrees. This restructuring maintains all your original information while changing its orientation.
How do I quickly transpose data in Excel?
The absolute fastest way is to use an AI tool like Excelmatic and ask it to "transpose the data." The fastest manual method is to select and copy your data, right-click the destination cell, select "Paste Special," and check the "Transpose" box.
Does transposed data in Excel update automatically when source data changes?
Only when using the TRANSPOSE() function, which creates a dynamic link. Paste Special creates a static copy, Power Query requires a manual refresh, and AI tools produce a new output that can be regenerated.
Can I transpose only a portion of my Excel spreadsheet?
Yes, simply select only the specific range you want to transpose before using any of the methods. This allows you to restructure certain sections while leaving others unchanged.
Why would I use Power Query or an AI tool instead of Paste Special to transpose data?
Power Query is ideal for large datasets, complex transformations, and creating reusable processes. An AI tool like Excelmatic is best when you prioritize speed and simplicity, as it requires no technical knowledge of Excel's features.
Can I keep formatting when transposing Excel data?
Generally, no. Formatting does not carry over when using the TRANSPOSE() function or Power Query. You'll need to reapply any conditional formatting, colors, or fonts to your transposed data.