Key Takeaways:
- Applying superscripts in Excel for units, exponents, or footnotes is tedious, requiring multiple clicks, complex custom formats, or VBA knowledge
- Excelmatic provides the simplest solution by applying superscript formatting instantly using plain language instructions—no manual editing or technical skills needed
- Compared to traditional methods that risk breaking calculations, Excelmatic intelligently chooses the right approach to preserve numeric values while delivering perfect visual formatting
- For business professionals who need professional-looking reports quickly, using AI tools like Excelmatic means faster document preparation and more time for meaningful analysis
When working in Excel, you often need to express square units (m²), mathematical exponents (2³), ordinal numbers (1st), footnotes, or trademark symbols (™ and ®). But unlike Microsoft Word, which has a simple toolbar button, applying superscripts in Excel requires a little more effort.
Don't worry. In this guide, I'll show you the best workarounds, from traditional manual methods to a cutting-edge AI solution that handles it for you.
Before we dive in, it's important to remember: Superscript formatting in Excel is purely visual; it does not alter the actual value in the formula bar or impact calculations.
This guide is divided into two parts: one focused on formatting text and the other on numbers. Let's explore the traditional ways first, then see how an AI tool can revolutionize this task.
The Traditional Way: Superscripting Text in Excel
Excel allows you to manually apply superscript to text using several methods.
Method 1: The Format Cells Dialog Box
This is the most common method for applying superscript formatting to text.
- Select the cell containing the text you want to format.
- Double-click the cell or press F2 to enter edit mode.
- Highlight only the specific characters you want to superscript.
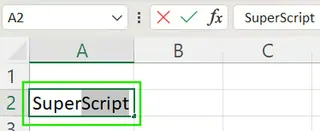
- Press Ctrl + 1 to open the Format Cells dialog box.
- In the Font tab, check the "Superscript" box under the Effects section.
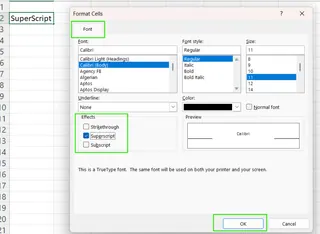
- Click OK to apply the formatting.
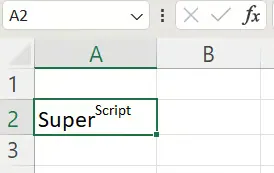
Method 2: Keyboard Shortcut Path
While Excel lacks a dedicated superscript shortcut, you can use this fast keystroke sequence:
- Select the text you want to format in edit mode.
- Press Ctrl + 1 to open the Format Cells dialog box.
- Press Alt + E to select the Superscript option.
- Press Enter to apply the formatting and close the dialog.
This sequence is quicker than using a mouse if you're a keyboard enthusiast.
Method 3: Add Superscript to the Quick Access Toolbar (QAT)
For frequent use, add the command to your QAT for one-click access.
- Go to File → Options.
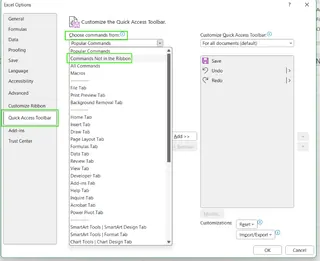
- In the Quick Access Toolbar tab, under "Choose commands from," select Commands Not in the Ribbon.
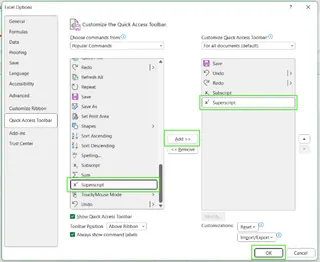
- Find Superscript, click Add >>, and hit OK.
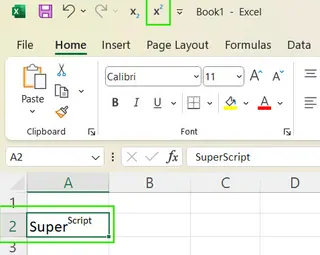
Now, you can select text and click the new icon in your QAT.
You can also add the command to the Excel Ribbon by right-clicking the ribbon and selecting Customize the Ribbon, which follows a similar process.
The Modern Way: Using an AI Agent like Excelmatic

The manual methods work, but they are repetitive, especially for large datasets. What if you could skip the clicks, shortcuts, and customizations entirely?
This is where AI tools like Excelmatic come in. Excelmatic is an Excel AI Agent that understands plain English instructions to perform tasks instantly. Instead of you figuring out how to apply superscripts, you just tell Excelmatic what you want.
Here’s how you would handle the same task with Excelmatic:
- Upload Your File: Drag and drop your Excel file into Excelmatic.
- State Your Request: In the chat box, type your formatting goal in simple language.
- Get Instant Results: Excelmatic analyzes your request and applies the formatting for you.
For example, you could ask:
- "In column B, for all cells containing 'm2', format the '2' as a superscript."
- "Find all ordinal numbers like 1st, 2nd, and 3rd in column D and make the letters superscript."
- "Add a trademark symbol ™ as superscript to the company names in column A."

Excelmatic intelligently handles these requests, saving you from the tedious process of editing cells one by one or setting up custom toolbars.
Manual vs. AI: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Manual Methods (Format Cells, Shortcuts) | Excelmatic (AI Agent) |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Requires memorizing steps or shortcuts. | Intuitive; just type what you want. |
| Speed | Slow, especially for multiple cells. | Extremely fast, applies to all relevant cells at once. |
| Learning Curve | Moderate; involves navigating menus. | Virtually none. |
| Scalability | Poor for large datasets. | Excellent; handles thousands of rows effortlessly. |
| Flexibility | Rigid; you perform the exact same steps each time. | High; understands context and applies logic. |
Superscripting Numbers in Excel
Superscripting numbers is trickier because Excel often converts the formatted number into a text string, which can break formulas. Here are the traditional approaches and how AI simplifies them.
Traditional Methods for Numbers
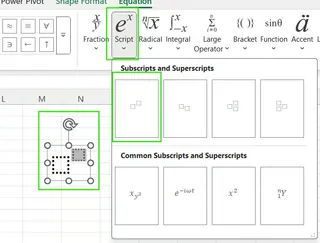
Using the Equation Tool: Go to Insert → Equation → Script to create a visual superscript. However, this creates a floating object, not content within a cell, so it's only useful for titles or visual aids.
Using Alt Codes: You can type ¹ (Alt+0185), ² (Alt+0178), and ³ (Alt+0179) using the numeric keypad. This is limited to these three numbers and converts the cell to text.
Using the CHAR() Function: The formula
=A1 & CHAR(178)appends a superscript 2 to the value in cell A1. This also results in a text string.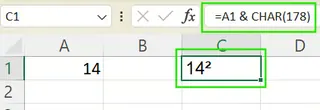
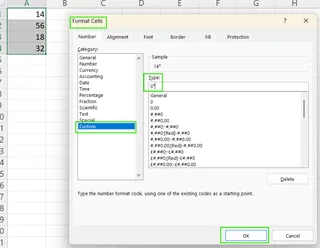
Using Custom Number Formats: This is the best manual method for preserving the number's value.
- Press Ctrl + 1 to open Format Cells.
- Go to Number → Custom.
- In the "Type" box, enter a format like
0"²". You can copy-paste other superscript characters (like ⁴, ⁵, etc.) into the format string.
The cell will display
10²but its underlying value remains10, so it can still be used in calculations.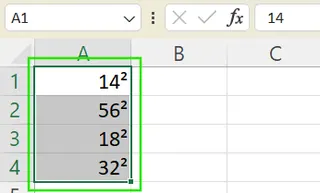
Using VBA: For automation, a VBA script can append superscript characters to a range of cells. This requires knowledge of programming.
Sub SuperscriptNumbers() Dim cell As Range For Each cell In Selection cell.Value = cell.Value & Chr(178) ' Appends superscript 2 Next cell End Sub
The Excelmatic Approach for Numbers
With Excelmatic, you don't need to choose between visual formatting and numeric functionality. Just state your goal.
- For visual display with preserved values: "For the numbers in column C, display them with a superscript 2 at the end, but keep their original numeric value for calculations." Excelmatic would correctly apply a custom number format.
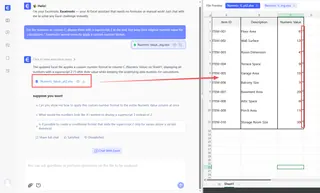
- For creating text strings: "Combine the text in column A with a superscript 3." Excelmatic would apply the equivalent of the
CHAR()function without you needing to know the formula.
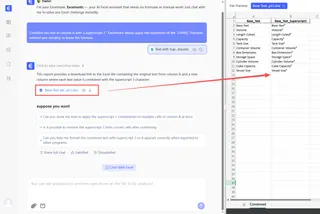
This AI-driven approach selects the best method for your specific need, saving you from the trial-and-error of traditional techniques.
Limitations and Workarounds
All manual methods have drawbacks:
- Numeric-to-String Conversion: Most methods (Alt codes,
CHAR()) convert numbers to text, breaking calculations. - Limited Character Support: Alt codes are only for ¹, ², and ³. Others must be copy-pasted.
- Complexity: Custom number formatting and VBA require technical knowledge.
AI-powered tools like Excelmatic are the ultimate workaround. They abstract away the complexity. You don't need to remember Alt codes, write VBA, or figure out custom format syntax. The AI handles the "how" so you can focus on the "what."
Conclusion
As you've seen, there are several ways to add superscripts in Excel. Manual methods like the Format Cells dialog, keyboard shortcuts, and custom number formats are valuable skills. They give you precise control over your worksheet's appearance.
However, for speed, efficiency, and ease of use, modern AI agents are a game-changer. By simply describing your goal in plain language, you can achieve in seconds what used to take minutes of clicking and typing. This shift allows you to be more productive and focus on generating insights rather than getting bogged down in formatting details.
Ready to format your Excel sheets instantly and professionally? Try Excelmatic today and transform text and number formatting from a chore into a simple command.
FAQ
How do I apply superscript to text or numbers in Excel?
The fastest manual way is to select text, press Ctrl+1, and check the "Superscript" box. The easiest way is to use an AI tool like Excelmatic and simply ask it to format the text for you.
Does superscripting affect formulas or calculations?
Usually, no. Standard superscript formatting is purely visual. However, methods that insert special characters (like Alt codes or the CHAR function) convert the cell's content to a text string, which cannot be used in calculations.
Why don’t Alt codes work on my computer?
Alt codes require a dedicated numeric keypad with Num Lock enabled. They typically do not work on laptops using the number row above the letters.
How can I automate superscripting for many cells?
The traditional way is to write a VBA macro. The modern, simpler way is to upload your file to an AI agent like Excelmatic and describe the formatting rule you want to apply.
What fonts support superscript characters?
Common fonts like Calibri, Arial, and Times New Roman have good support for superscript characters. Be aware that some custom or decorative fonts may not display them correctly.