Key Takeaways:
- Using π in Excel calculations, from simple areas to complex trigonometry, traditionally requires memorizing and correctly writing formulas like
PI(), which is prone to errors and time-consuming for non-technical users. - Excelmatic revolutionizes this process by allowing you to simply describe your calculation in natural language (e.g., “calculate the area of these circles”), delivering precise results instantly without any formulas.
- The AI-powered approach shines with advanced scenarios, automatically handling complex equations and unit conversions that would require intricate, error-prone manual formulas.
- For business professionals who need accurate geometric or trigonometric results without the math headache, Excelmatic is the fastest and most reliable way to incorporate π into your data analysis.
If you've ever needed to calculate the area of a circle or work with trigonometric formulas in Excel, you've probably wondered how to get π (pi) into your spreadsheet. Manually typing 3.14159… works, but it lacks the precision required for accurate results and opens the door to manual errors.
Traditionally, the solution is to use Excel's built-in PI() function. It's a reliable method that has served users for decades. But what if there was a faster, more intuitive way that didn't require you to remember any formulas at all?
In this article, we'll cover both methods. First, we'll do a refresher on the classic PI() function. Then, we'll introduce a modern, AI-powered approach using Excelmatic to show you how you can get the same, or even more complex, results just by asking.
The Traditional Method: Understanding the Excel PI() Function
The PI() function is Excel’s built-in way of returning the value of the mathematical constant π, which is approximately 3.14159. Pi is fundamental in calculations involving circles and spheres, but it shows up in many unexpected places, as we'll see in the examples.
What does the PI() function do?
You might be wondering what sets PI() apart from simply typing 3.14 into a cell. The answer is precision. When you use PI(), Excel returns π to 15 significant digits (3.141592653589793), which is more than enough for almost any calculation you’ll encounter. Using a less precise, hardcoded number can lead to inaccuracies, especially in scientific and engineering calculations.
The PI() function syntax
The syntax is as simple as it gets:
=PI()
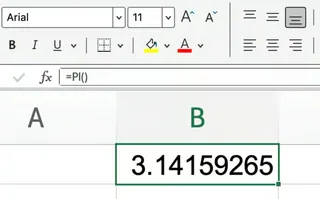
There are no arguments or options to adjust. If you try to enter any arguments inside the parentheses, Excel will return an error.
Applying Pi in Formulas: The Manual Way vs. The AI Way
Now that you know what PI() is, let’s see it in action. Below, we’ll compare how to solve common problems using traditional Excel formulas versus using an AI agent like Excelmatic.
Calculating the Area of a Circle
The formula to calculate the area of a circle from its radius is Area = π × r².
The Traditional Way:
If your circle’s radius is in cell A2, you would enter this formula:
=PI() * (A2^2)

This multiplies pi by the radius squared, giving you the area. If you have a list of radii, you'd drag this formula down the column.
The Excelmatic Way:

Forget formulas. Simply upload your spreadsheet to Excelmatic and ask in plain language:
Calculate the area of a circle for each radius listed in column A.
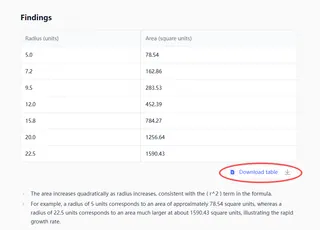
Excelmatic understands your request, performs the calculation with full precision, and returns the results in a new column for you. No formulas to remember, no dragging cells.
Finding the Circumference of a Circle
The circumference of a circle is given by the formula 2 × π × r.
The Traditional Way:
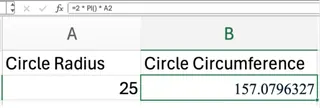
With the radius in cell A2, the Excel formula is:
=2 * PI() * A2
The Excelmatic Way:
Again, just state your goal:
Find the circumference for the circles using the radii in column A.
Excelmatic processes the request and delivers the answers instantly.
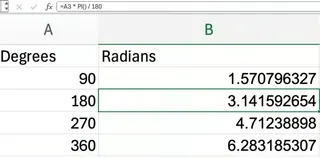
Converting Degrees to Radians
Excel’s trigonometric functions like SIN() and COS() use radians, not degrees. To convert degrees to radians, the formula is: Degrees × π / 180.
The Traditional Way:
If the degree value is in A2, the formula is:
=A2 * PI() / 180
The Excelmatic Way:
Simplify the process by asking directly:
Convert the angles in column A from degrees to radians.
This is not only easier to remember but also less prone to error than typing the conversion formula by hand.
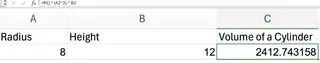
Calculating the Volume of a Cylinder
The volume of a cylinder is π × r² × h. This requires two variables: radius (r) and height (h).
The Traditional Way:
With the radius in cell A2 and the height in B2, you would use:
=PI() * (A2^2) * B2
The Excelmatic Way:
Just describe the data and what you need:
Calculate the volume of a cylinder using the radius from column A and the height from column B.
Excelmatic correctly maps the columns to the variables and computes the volume for your entire dataset.
The True Power of AI: Handling Complex Formulas
The benefits of an AI approach become undeniable when formulas get complicated. PI() often appears in advanced scientific, engineering, and financial equations that are difficult to write and even harder to debug.
Consider the spherical law of cosines, which calculates the shortest distance between two points on a sphere (like Earth).
The Traditional Way:
To calculate the distance between Denver (latitude/longitude in B2/C2) and Edinburgh (latitude/longitude in B3/C3), you'd need to write this monstrous formula:
=3958*ACOS(SIN(B2*PI()/180)*SIN(B3*PI()/180)+COS(B2*PI()/180)*COS(B3*PI()/180)*COS((C3-C2)*PI()/180))
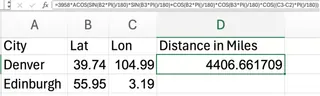
One misplaced parenthesis or an incorrect cell reference, and the entire formula breaks. It's powerful but extremely fragile. The result, 4,400.4 miles, is very close to Google's official distance of 4,405 miles.
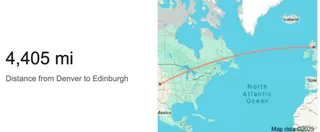
As the original author notes, using a truncated value for pi (like 3.14) in this formula yields a less accurate result of 4,418.3 miles. Precision is key.
The Excelmatic Way:
Instead of wrestling with that formula, you can simply tell Excelmatic your objective:
My file has latitudes in column B and longitudes in column C. Calculate the distance in miles between Denver (row 2) and Edinburgh (row 3).
Excelmatic handles the complex trigonometry, the degree-to-radian conversions, and the final calculation behind the scenes. You get the accurate answer without the headache, saving time and eliminating the risk of formula errors.
Conclusion: Choose the Right Tool for the Job
Mastering Excel's PI() function is a valuable skill for anyone who regularly works with mathematical formulas. It ensures your calculations are precise and professional.
However, the landscape of data analysis is evolving. For simple, one-off calculations, a quick formula might suffice. But for complex tasks, repetitive calculations, or situations where you can't afford a formula error, an AI agent like Excelmatic offers a clear advantage. It allows you to focus on the what—your business goal—rather than the how—the complex syntax of a formula.
Becoming an advanced Excel user today means knowing both the traditional methods and when to leverage smarter tools to solve problems, automate processes, and find insights others might miss.
Ready to calculate with π and other complex formulas without the complexity? Try Excelmatic today and get precise answers to your mathematical questions in seconds.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use PI() with other Excel functions?
Yes, definitely. Combine it with functions likeSIN(), COS(), SQRT(), or even with basic arithmetic to build more complex formulas.
How many decimal places does PI() return in Excel?
PI() returns π to 15 significant digits: 3.14159265358979.
What happens if I type a value inside PI(), like PI(2)?
Excel will return a#VALUE! error. The function must always be written as PI() with nothing between the parentheses.
Is there a quick way to display π with fewer decimals?
Use Excel’s cell formatting options to limit decimal places. The underlying value in your formula will remain precise.






