Key Takeaways:
- Calculating probabilities for normal distributions in Excel using
NORM.DIST()requires precise formula syntax and an understanding of statistical arguments, creating a barrier for non-technical business users. - Excelmatic removes this complexity by allowing you to simply ask your statistical question in natural language, instantly providing the probability, density, or even a chart without writing a single formula.
- Whether you need cumulative probabilities, probability densities, or visualizations, the AI-powered approach delivers accurate results faster and eliminates common formula errors.
- For professionals who need statistical insights without the statistical headache, Excelmatic is the most efficient way to leverage normal distribution analysis in your data-driven decisions.
If you often work with probabilities and statistics in Excel, you'll inevitably need to analyze normal distributions—whether you’re running quality control, assessing test scores, or digging into business data. Traditionally, this meant mastering functions like NORM.DIST() to determine the probability associated with a specific value.
But today, you have more than one way to get the job done. While the classic formula-based approach offers precision and control, modern AI tools provide a faster, more intuitive path to the same answers.
In this guide, we’ll explore both methods. We'll break down the traditional NORM.DIST() function, its syntax, and its options. Then, we'll introduce a powerful AI-driven alternative, Excelmatic, to show you how you can get the same results simply by asking a question. By the end, you’ll have a complete picture of how to handle normal distribution analysis in Excel and can choose the method that best fits your workflow.
What is a Normal Distribution Calculation?
Before we dive into the "how," let’s clarify the "what." A normal distribution calculation helps you find the probability that a value drawn from a bell-shaped data set is less than or equal to a specific number. Depending on your needs, you can get either the cumulative probability (the area under the curve up to a point) or the probability density (the height of the curve at that specific point).
So, whether you want to find out how likely it is to score below a certain number or simply need the value of the normal curve at a point, both the traditional and AI methods have you covered.
Method 1: The Traditional Formula Approach with NORM.DIST()
For users who are comfortable with Excel formulas, NORM.DIST() is the go-to function for this task. Let's look at how to use it.
NORM.DIST() Syntax and Arguments
Here’s the function’s syntax:
=NORM.DIST(x, mean, standard_dev, cumulative)
Breaking down each argument:
x: The value for which you want the distribution.mean: The mean (average) of the distribution.standard_dev: The standard deviation of the distribution.cumulative: A logical value—useTRUEfor the cumulative distribution function (CDF) orFALSEfor the probability density function (PDF).
To put this into context, imagine you want to find the probability that a value is less than or equal to 80 in a normal distribution with a mean of 70 and a standard deviation of 10. The formula would look like this:
=NORM.DIST(80, 70, 10, TRUE)
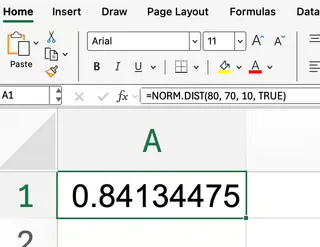
This setup returns the cumulative probability up to 80.
Cumulative vs. Probability Density
Understanding the cumulative argument is key to getting the results you want.
- Cumulative (
TRUE): When you set the last argument toTRUE,NORM.DIST()returns the probability that a value is less than or equal to x. This is the most common option for statistical analysis, as it answers questions like, “What percentage of students scored 85 or lower?” - Probability Density (
FALSE): When you chooseFALSE, the function gives you the height of the normal curve at x. This isn’t a probability itself but is useful in statistical modeling or for plotting the distribution curve.
Method 2: The Modern AI Approach with Excelmatic

What if you could skip the syntax and just ask for what you need? That’s where Excelmatic comes in. As an Excel AI Agent, it translates plain language requests into instant answers, charts, and insights.
Instead of remembering the NORM.DIST function and its four arguments, you can simply state your request. For the same scenario as above (mean=70, std dev=10, value=80), you would tell Excelmatic:
What is the cumulative probability for a value of 80 in a normal distribution with a mean of 70 and a standard deviation of 10?
Excelmatic processes this request and delivers the answer directly, without you ever typing a formula. This approach is not only faster but also less prone to errors caused by incorrect syntax or argument order.
Practical Examples: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Let’s see both methods in action to solve real-world problems.
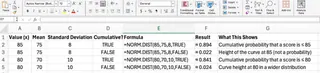
1. Finding the Cumulative Probability
Suppose you want to know the probability that a test score is less than or equal to 85, assuming test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 8.
Traditional NORM.DIST() Method:
You would type the following formula into a cell:
=NORM.DIST(85, 75, 8, TRUE)
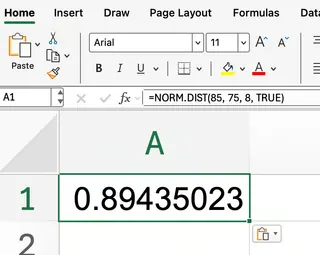
Excel will return a value close to 0.894, meaning that about 89.4% of students scored 85 or lower.
Excelmatic AI Method:
You would simply ask:
What's the probability of a test score being 85 or lower, if the scores are normally distributed with a mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 8?
Excelmatic instantly provides the same answer, 0.894, saving you the time and mental effort of constructing the formula.
2. Getting the Probability Density
Now, what if you’re interested in the height of the curve at a specific value, rather than the cumulative probability?
Traditional NORM.DIST() Method:
Here, you set the cumulative argument to FALSE:
=NORM.DIST(85, 75, 8, FALSE)
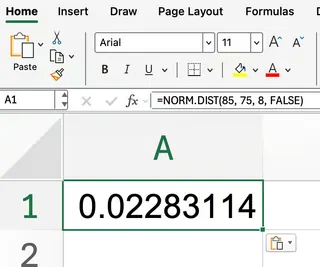
This gives you the probability density at 85. Remember, this isn’t a probability, but the value of the normal curve at that point.
Excelmatic AI Method:
Your request would be just as straightforward:
Calculate the probability density at a value of 85 for a normal distribution with a mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 8.
Again, Excelmatic handles the calculation behind the scenes and returns the correct value. The table below summarizes how the inputs affect the output for both modes.
Visualizing the Normal Distribution
Visualizing the bell curve is a great way to understand the distribution. Here too, the AI approach offers a significant shortcut.
Traditional Method: Manual Chart Creation
To create a chart in Excel, you need to first generate the data points manually:
- Create a column of
xvalues (e.g., from 60 to 90 in steps of 1). - Create a second column for the Cumulative values using the formula:
=NORM.DIST(x_cell, 75, 8, TRUE). - Create a third column for the Probability Density values:
=NORM.DIST(x_cell, 75, 8, FALSE). - Highlight all three columns.
- Go to Insert > Charts > Line Chart or Scatter with Smooth Lines to create your visual.
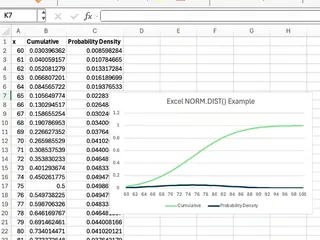
While effective, this process is multi-stepped and time-consuming.
Excelmatic Method: Instant Chart Generation
With Excelmatic, you can bypass the manual data preparation and chart formatting. Just ask:
Create a line chart showing the cumulative and probability density curves for a normal distribution with a mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 8. Use x-values from 60 to 90.
Excelmatic will generate the data and the chart for you in one step, delivering the same professional-looking visual in a fraction of the time.
Common Issues and Tips for the NORM.DIST() Function
If you choose the traditional formula path, be aware of a few common pitfalls:
- Standard deviation must be positive. Entering zero or a negative number will result in a
#NUM!error. - Mean and standard deviation flexibility. The mean can be any real number, but the standard deviation must always be positive.
- Going in reverse? If you have a probability and need to find the corresponding value, use the
NORM.INV()function instead.
Related Functions in Excel
The NORM.DIST() family includes several other useful functions for statistical analysis:
NORM.INV(): The inverse ofNORM.DIST(), it returns the value for a given cumulative probability.NORM.S.DIST(): Calculates probabilities for the standard normal distribution (mean=0, standard deviation=1).NORM.S.INV(): Returns the value for a given probability in the standard normal distribution.
While you can learn the syntax for each, remember that an AI tool like Excelmatic can also handle these tasks through simple, conversational requests (e.g., "Using a standard normal distribution, what value corresponds to a cumulative probability of 0.95?").
Conclusion
You’ve now seen how to tackle normal distribution analysis in Excel using two different but equally powerful methods. The traditional NORM.DIST() function offers granular control and is a fundamental skill for any serious Excel user. At the same time, AI agents like Excelmatic are revolutionizing data analysis by making complex statistical tasks faster, simpler, and more accessible to everyone.
Your choice of method depends on your needs. If you're building complex, interconnected dashboards, formulas may be the way to go. But for quick analysis, visualization, and getting immediate answers without getting bogged down in syntax, the AI approach is a clear winner.
Ready to simplify your statistical analysis? Stop memorizing formulas and start asking questions. Try Excelmatic today and get the probabilities and insights you need instantly.