Key Takeaways:
- The
#NAME?error in Excel is a common but disruptive problem for business users, often caused by typos, forgotten syntax, or version incompatibilities that stall critical analysis. - Excelmatic eliminates the root cause of these errors by allowing users to describe their goals in natural language, bypassing the need to write and debug complex formulas entirely.
- For non-technical professionals, this AI-powered approach translates to immediate, error-free results, freeing up time to focus on insights and decisions rather than technical troubleshooting.
- Adopting tools like Excelmatic represents a strategic shift from wrestling with software mechanics to achieving business outcomes with speed and confidence.
Have you ever meticulously typed a formula into Excel, only to be greeted by the frustrating #NAME? error? This message means Excel doesn’t recognize something you’ve typed. It could be a small typo, a missing named range, or a function syntax that Excel can't understand. Whatever the cause, it's a headache that can bring your analysis to a halt.
In this guide, we’ll explore the common causes of the #NAME? error and walk through traditional ways to fix it. We'll also introduce a modern, AI-powered approach that can help you bypass these formula-based errors altogether, saving you time and effort.
What Is the #NAME? Error in Excel?
The #NAME? error appears when Excel encounters something in a formula that it cannot interpret. Formulas follow a strict syntax, and every element—whether a function name, named range, or text string—must be something Excel recognizes. When a component is undefined, misspelled, or improperly formatted, Excel raises the #NAME? error. It's not a simple warning you can ignore; it's a signal that part of your formula is unresolvable within Excel's language.
Common Causes of the #NAME? Error
Let's look at why you might see a #NAME? error in your spreadsheet, comparing the manual fix with an AI-powered solution.
Misspelled Function Names
One of the most common causes is a simple typo. One wrong letter can break your formula. For example, if you write CONTIF() instead of the correct COUNTIF(), Excel won’t recognize it and will return the #NAME? error.

The AI-Powered Alternative
Instead of memorizing and typing function names, an AI agent like Excelmatic allows you to state your goal in plain language commands. You can simply upload your file and ask, "Count how many cells in column C are 'Pass'." Excelmatic interprets your request and delivers the answer, completely bypassing the need to write a formula and eliminating the risk of typos.
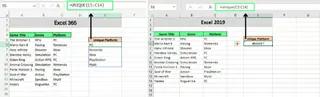
Using New Functions in Older Excel Versions
Sometimes, the error occurs because you’re using a function that’s only available in newer Excel versions, like Excel 365. For example, FILTER(), XLOOKUP(), and UNIQUE() won’t work in Excel 2019 or earlier, leading to a #NAME? error.
Note: To check your Excel version, go to File > Account > About Excel.
The AI-Powered Alternative
Version compatibility issues disappear with an AI tool. Excelmatic operates in a consistent, up-to-date environment. You can ask it to perform a task that would normally require XLOOKUP() or FILTER(), and it will execute it flawlessly, regardless of the Excel version installed on your computer.
Invalid or Misspelled Named Ranges
Named ranges are custom names for cell groups. If you misspell the name or if the named range has been deleted, Excel will show the #NAME? error.
Note: Go to the Formulas tab and open Name Manager to confirm the range name and its scope (local to a sheet or global to the workbook).
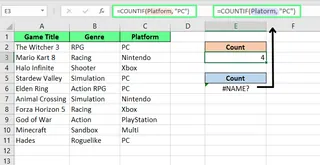
The AI-Powered Alternative
With Excelmatic, you don't need to worry about the exact syntax for named ranges. You can refer to your data more naturally, such as "Calculate the total profit from the 'Sales2024' table." The AI understands the context from your uploaded file and finds the correct data without you needing to manage or type named ranges perfectly.
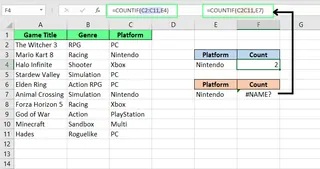
Incorrect Range References
Excel also shows the #NAME? error for improperly formatted range references. For example, typing C2C11 instead of C2:C11 (missing the colon) will confuse Excel.
A good manual habit is to use your mouse to select the range when building a formula to avoid such typos.
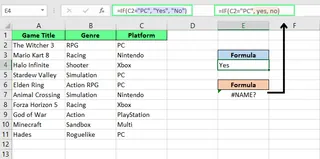
Missing Quotation Marks Around Text
When using text strings in a formula, you must wrap them in straight double quotes (e.g., "Apples"). If you forget the quotes, Excel assumes the text is a function or a named range. If it can't find a match, you get the #NAME? error.
For example:
- This works:
=IF(A1="Apple", "Yes", "No") - This won’t:
=IF(A1=Apple, Yes, No)
Also, watch out for "smart quotes" (like “ or ”) often copied from websites or Word documents, as they won't work in Excel formulas.
The AI-Powered Alternative for Reference and Text Errors
Both incorrect ranges and missing quotes are syntax errors that are eliminated when using a tool like Excelmatic. By describing your goal—"If the value in column A is 'Apple', put 'Yes' in column B, otherwise put 'No'"—the AI handles the correct syntax, including colons for ranges and quotes for text, automatically.
Missing Add-ins or Custom Functions
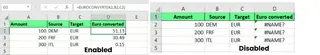
Some functions require specific add-ins to be enabled. For example, EUROCONVERT() only works if the Euro Currency Tools add-in is active. If it's not, you'll see a #NAME? error. The same applies to custom functions created with VBA that are specific to one workbook.
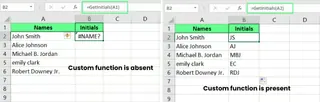
If you try to use a custom VBA function like =GetInitials(A1) in a workbook where the code doesn't exist, Excel won't recognize it.
How to Fix the #NAME? Error in Excel
Now that we know the causes, let's look at the solutions.
The Traditional Method: Manual Debugging
Fixing a single #NAME? error involves careful inspection.
- Use Autocomplete: As you type a formula, Excel suggests functions. Press
Tabto insert the correct one and avoid typos. - Check Name Manager: If using a named range, go to Formulas > Name Manager to verify its spelling and scope.
- Fix Quotes: Ensure all text in formulas is wrapped in
"straight double quotes". - Use Your Mouse for Ranges: Select ranges with your mouse instead of typing them to prevent errors like
C2C11. - Verify Excel Version: Ensure your Excel version supports the function you're using.
- Enable Add-ins: Go to File > Options > Add-ins to enable any required add-ins.
- Refresh Formulas: Press
F9to force a recalculation of the entire workbook.
Finding and Fixing All #NAME? Errors in a Workbook
If your sheet is full of errors, here are two ways to find them all:
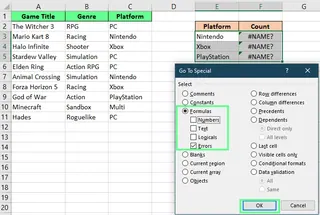
Use Go To Special
- Go to Home > Find & Select > Go To Special (or press
F5, thenSpecial...). - Select Formulas and check only the Errors box.
- Click OK. Excel will highlight all cells containing formula errors.
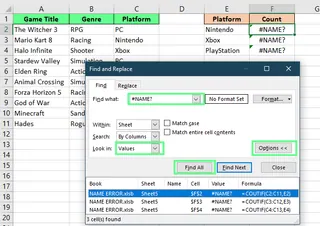
Use Find and Replace
- Press
Ctrl + Fto open the Find dialog. - Type
#NAME?in the "Find what" box. - Click Find All to see a list of every cell with that error.
The AI-Powered Method: Forget Debugging, Just Get the Answer
Instead of hunting for and fixing each #NAME? error, you can take a more direct route with an AI agent.

With Excelmatic, the process is different. You don't fix the broken formula; you simply tell the AI what you were trying to achieve in the first place.
- Upload your spreadsheet to Excelmatic.
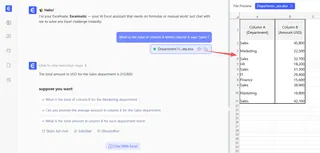
- State your original goal in plain language. For example, instead of fixing a broken
=SUMMIF(A1:A50, "Sales", B1:B50), you just ask, "What is the total of column B where column A says 'Sales'?"
- Get the correct result instantly. Excelmatic analyzes the raw data and calculates the answer, ignoring any existing errors in your sheet.
This approach shifts the focus from debugging a process (fixing the formula) to achieving an outcome (getting the correct number).
How to Prevent #NAME? Errors
The best way to deal with errors is to prevent them from happening.
The Traditional Way: Use the Formula Wizard
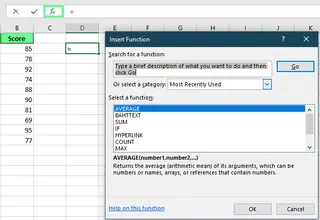
If you're unsure how to write a formula, Excel's Formula Wizard can guide you. Click the fx button next to the formula bar to open it, search for a function, and fill in the arguments with help from Excel's prompts.
The AI Way: Use Natural Language
The ultimate prevention tool is one that doesn't require you to write formulas at all. With an AI agent like Excelmatic, your instructions are the formula. By asking questions in plain language, you eliminate syntax errors, typos, and version issues before they can even occur. It's like having an expert sitting next to you, translating your questions into accurate results.
Additional Tips and Best Practices
A few good habits can save you from running into the #NAME? error again:
Don’t Hide the Error: Fix It
Functions like IFERROR() can hide errors by displaying a custom message, but they don't solve the underlying problem. The incorrect calculation is still there, just hidden. Always aim to fix the root cause first.
Keep an Eye on Named Ranges
In large or shared workbooks, named ranges can be accidentally deleted or changed. Periodically check the Name Manager to ensure everything is in order.
Final Thoughts
And that’s the #NAME? error in Excel. While it may seem daunting, it usually points to a simple mistake like a typo, a missing quote, or a broken reference. By knowing what to look for, you can manually fix these issues with a bit of patience.
However, as we've seen, modern AI tools offer a fundamentally different and often faster workflow. Instead of getting bogged down in formula syntax and debugging, you can use an AI agent like Excelmatic to focus on your questions and let the technology handle the execution. This not only prevents #NAME? errors but also accelerates your entire data analysis process.
Ready to skip the errors and get straight to answers? Try Excelmatic today and transform how you work with data. Simply upload your spreadsheet, ask your question, and get results—no formulas required.
Does Excel differentiate between uppercase and lowercase in function names?
No, Excel functions are not case-sensitive. Typingsum() or SUM() works the same. However, spelling must be exact.
Can protected sheets or locked cells contribute to #NAME? errors?
No, protection does not directly cause #NAME? errors, but it can prevent fixing them if you can’t edit the formula cell.






