Key Takeaways
- Matrix multiplication in Excel with
MMULT()is technically complex, requiring strict adherence to array dimensions and syntax rules, which is intimidating for non-technical business users and prone to errors. - Excelmatic transforms this process by allowing users to perform matrix calculations using plain language instructions, eliminating the need to remember complex formulas and array rules.
- Excelmatic makes advanced mathematical operations accessible to marketers, sales analysts, and operations professionals without technical expertise, saving time and reducing calculation errors significantly.
- For business users who need to perform complex calculations but lack advanced Excel skills, Excelmatic is the fastest and most reliable way to handle matrix multiplication and other advanced Excel operations.
You might not use matrix multiplication every day, but when the need arises for financial modeling or complex data analysis, knowing how to do it in Excel is a powerful skill. The traditional way involves the MMULT() function, a core tool for linear algebra in Excel.
However, a new approach using AI is changing the game. In this practical guide, we'll explore both methods. We'll start with the classic MMULT() function and then show you a faster, more intuitive way using an AI assistant, helping you choose the best method for your needs.
Method 1: The Classic Approach with Excel's MMULT() Function
Let’s start with Excel's built-in function. MMULT() performs matrix multiplication, which is a mathematical operation where you multiply rows of one matrix by columns of another. It’s especially helpful when you're working with things like:
- Weighted averages
- Financial forecasting
- Regression models
While dedicated tools like Python or R are great for this, MMULT() lets you stay within the Excel environment, avoiding the hassle of switching between applications.
Excel MMULT() Syntax and Arguments
The MMULT() function requires two arguments: the two matrices (or arrays) you want to multiply.
=MMULT(array1, array2)
array1: The first matrix (a range of cells).array2: The second matrix (a range of cells).
A critical rule: The number of columns in array1 must match the number of rows in array2. If this condition isn't met, Excel will return a #VALUE! error.
Important Note on Excel Versions: If you’re using Excel 365 or Excel 2021 (or later), you can just hit Enter like any normal formula. But if you’re on an older version, you must use a special key combination:
- Select the entire output range first (make sure it’s sized correctly!).
- Type in your
MMULT()formula. - Press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to enter it as an array formula.
When done correctly in older versions, Excel will surround your formula with curly braces {}.
MMULT() in Action: A Real Example
Let’s bring this to life. Imagine you have the following two matrices in your spreadsheet:
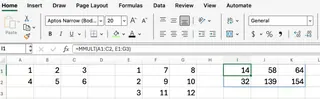
To multiply these two matrices, you would use the formula:
=MMULT(A1:C2, E1:G3)
Behind the scenes, Excel performs these calculations:
- C[1][1] = 14 = (1×1) + (2×2) + (3×3)
- C[1][2] = 58 = (1×7) + (2×9) + (3×11)
- C[1][3] = 64 = (1×8) + (2×10) + (3×12)
- C[2][1] = 32 = (4×1) + (5×2) + (6×3)
- C[2][2] = 139 = (4×7) + (5×9) + (6×11)
- C[2][3] = 154 = (4×8) + (5×10) + (6×12)
Thankfully, you don't have to do this math manually. Once you enter the formula correctly, Excel populates the result matrix for you.
Common Errors and How to Fix Them
Working with MMULT() can be tricky. Here are some common issues:
- #VALUE! error: This usually happens if your arrays have non-numeric values or if their dimensions are incompatible (columns in array1 ≠ rows in array2).
- Incorrect result size: In older Excel versions, if your selected output range is the wrong size, Excel might return a partial result or an error.
- Forgetting Ctrl + Shift + Enter: This is the most common pitfall for users on older Excel versions. Without it, the function won't work correctly.
Always double-check the dimensions of your input and output ranges before entering the formula.
Method 2: The Instant AI-Powered Approach with Excelmatic
Remembering function syntax, array rules, and special key combinations can be a chore. What if you could just ask Excel to do the multiplication for you in plain language commands? That's where AI tools like Excelmatic come in.

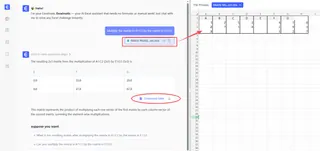
Excelmatic is an Excel AI Agent that handles complex tasks instantly. Instead of writing formulas, you simply upload your file and describe what you need.
Matrix Multiplication with Excelmatic: The Same Example
Let's use the same two matrices from before. Here’s how you’d solve it with Excelmatic in seconds:
- Upload Your File: Drag and drop your Excel file containing the two matrices into Excelmatic.
- State Your Request: Type a simple instruction in the chat box, like:
Multiply the matrix in A1:C2 by the matrix in E1:G3
- Get Your Answer: Excelmatic processes the request, performs the matrix multiplication, and delivers the resulting matrix instantly, correctly formatted and placed in your sheet.
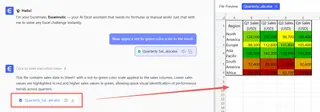
There's no need to remember the MMULT function, worry about array dimensions, or use Ctrl + Shift + Enter. The AI handles all the technical details.
MMULT() vs. Excelmatic: Which Should You Use?
| Feature | MMULT() Function (Manual) |
Excelmatic (AI-Powered) |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Moderate. Requires knowledge of syntax and array rules. | Excellent. Uses simple, plain language commands. |
| Speed | Slower. Requires typing the formula and selecting ranges. | Faster. Just type a sentence and get an instant result. |
| Error-Proneness | High. Prone to errors from incorrect syntax, dimensions, or key combinations. | Low. The AI handles technical details, minimizing user error. |
| Learning Curve | Steeper. You need to learn the function and its constraints. | Minimal. If you can describe what you want, you can use it. |
| Requirement | Built into all versions of Excel. | Requires access to the Excelmatic tool. |
For one-off calculations or for those who want to understand the mechanics, MMULT() is a valuable function to know. But for frequent, complex analysis or for users who prioritize speed and accuracy, an AI assistant like Excelmatic is a far more efficient solution.
Visualizing the Results
Whether you used MMULT() or Excelmatic, visualizing the resulting matrix can help you interpret the data. A great way to do this is with conditional formatting. You can use color scales to highlight high versus low values.
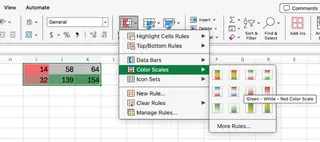
With Excelmatic, you can even ask for this as a follow-up:
Now, apply a red-to-green color scale to the result.
Conclusion
The MMULT() function is a powerful, native tool in Excel for matrix multiplication, essential for certain types of financial and statistical analysis. Mastering it is a great way to deepen your Excel expertise.
However, the landscape of data analysis is evolving. AI-powered tools like Excelmatic are streamlining these tasks, allowing you to move from question to answer almost instantly. By replacing complex formulas with simple instructions, they not only save time and reduce errors but also make powerful data analysis accessible to everyone.
Ready to transform how you handle complex calculations in Excel? Try Excelmatic today and experience the power of conversational data analysis. Simply upload your file, describe what you need in simple language, and get instant, accurate results - no formulas to memorize, no complex menus to navigate, just professional-grade calculations at your fingertips.