Key Takeaways:
- Excel lookup functions like VLOOKUP and XLOOKUP require memorizing complex syntax and are prone to errors like #N/A when data changes
- Excelmatic eliminates formula complexity by letting you perform data lookups using simple language commands
- Compared to traditional functions, Excelmatic handles any lookup direction (left, right, up, down) automatically without special syntax
- For business professionals, adopting AI tools means instant answers and more time for decision-making rather than technical debugging
When you’re working with data in Excel, you'll quickly need to reference and search for information. For decades, this has meant mastering Excel's powerful lookup functions. They are the bedrock of many reports and analyses.
But what if there was a faster, more intuitive way? In this article, we’ll cover the essential Excel lookup functions and show you how to use them through examples. We'll also introduce a modern AI-powered alternative, Excelmatic, that can deliver the same results without you needing to write a single formula.
What are Excel Lookup Functions?
Lookup functions in Excel allow users to search for specific data within a dataset and return corresponding information from another column or row. They are essential in data analysis for referencing, cross-referencing, and extracting meaningful insights from large or complex datasets.
Why are Lookup Functions Important?
Lookup functions are built for efficient data retrieval. This is crucial for productivity, especially when dealing with large spreadsheets or automating reporting workflows. Using the right method reduces manual searching, ensures consistency, and enables scalable data solutions.
For example, imagine you have a sales table with thousands of rows, and you need to find the total sales for a specific product. Without a lookup method, you’d have to manually scroll and search, a process that is both time-consuming and prone to human error.
Traditional functions solve this, but modern AI tools are making it even simpler.
Types of Lookup Methods in Excel
Excel offers multiple lookup functions, each with unique strengths. However, a new class of AI tools offers a unified, simpler approach. Let’s explore the options.
1. LOOKUP

The original LOOKUP function is the most basic. It works with sorted arrays, searching for a value in a single row or column and returning a value from the same position in another. It only supports approximate matches and requires your data to be sorted.
2. VLOOKUP (Vertical Lookup)
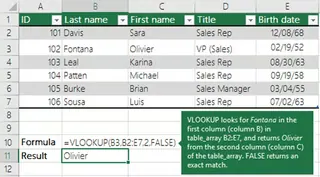
VLOOKUP is one of the most widely used functions in Excel. It searches for a value in the first column of a table and returns a value in the same row from a specified column. It has limitations, such as an inability to search to the left and performance issues with large datasets.
3. HLOOKUP (Horizontal Lookup)
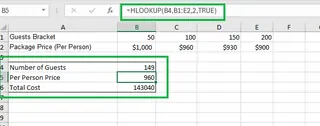
HLOOKUP is the sibling to VLOOKUP. It searches for a value in the first row of a table and returns a value from a specified row. It's useful only when your data is organized horizontally.
4. INDEX and MATCH
The INDEX and MATCH method is a powerful combination of two functions:
INDEXreturns the value of a cell based on row and column numbers.MATCHreturns the position of a value in a row or column. Used together, they are more flexible thanVLOOKUP, supporting lookups in any direction. However, the nested syntax can be complex for beginners.
5. XLOOKUP
Introduced in Excel 2019 and Microsoft 365, XLOOKUP is the modern replacement for VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP. It's versatile, allowing for searches in any direction, and has built-in error handling, making it the best traditional lookup function.
Method 1: The LOOKUP Function
Let’s start with the original.
Syntax and Parameters
=LOOKUP(lookup_value, lookup_vector, [result_vector])
- lookup_value: The value to search for.
- lookup_vector: The single row or column to search (must be sorted ascendingly).
- result_vector (optional): The range containing the value to return.
Example
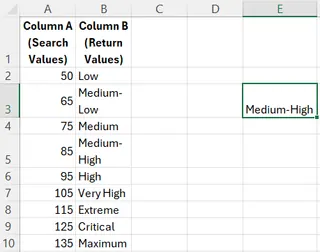
=LOOKUP(90, A2:A10, B2:B10)
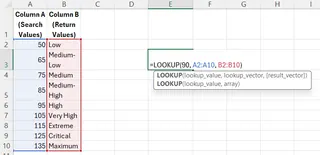
This function searches for the largest value less than or equal to 90 in A2:A10, then returns the corresponding value from B2:B10, which is "Medium-High".
The Excelmatic Alternative: A Simple Question

Instead of writing a formula and ensuring your data is sorted, you can get the answer with a simple question.
- Upload your spreadsheet to Excelmatic.
- Ask in plain language: "For a score of 90, what is the rating?"
- Excelmatic analyzes your data and instantly returns "Medium-High". It handles the underlying logic of finding the appropriate match without requiring sorted data.

Method 2: The VLOOKUP Function
VLOOKUP is an essential function to know, especially when working with older spreadsheets.
Syntax and Parameters
VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
- lookup_value: The value to search for in the first column.
- table_array: The table range to search.
- col_index_num: The column number to return a value from (e.g., 3 for the 3rd column).
- range_lookup:
FALSEfor an exact match,TRUEfor an approximate match.
Example
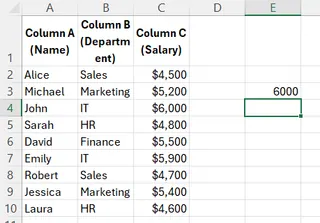
To find John's salary from the table below, you would use:
=VLOOKUP("John", A2:C10, 3, FALSE)

This searches for "John" in column A and returns the value from the third column (Salary), which is 60000.
The Excelmatic Alternative: No Formulas Needed
Why memorize the VLOOKUP syntax, count columns, and worry about #N/A errors?
- Upload your file to Excelmatic.
- Ask: "What is John's salary?"
- Excelmatic delivers the answer: 60000. It's that simple. You don't need to specify columns or worry about the formula breaking if you insert a new column.
Method 3: The HLOOKUP Function
HLOOKUP is for horizontally-arranged data.
Syntax and Parameters
HLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, row_index_num, [range_lookup])
- lookup_value: The value to search for in the first row.
- table_array: The table to search.
- row_index_num: The row number to return a value from.
- range_lookup:
TRUE(approximate) orFALSE(exact).
Example
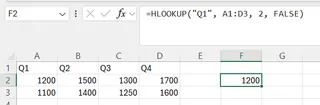
To find the Sales for "Q1", you would use:
=HLOOKUP("Q1", A1:D3, 2, FALSE)

This searches for "Q1" in the first row and returns the value from the second row (Sales), which is 1200.
The Excelmatic Alternative: Data Orientation Doesn't Matter
With a traditional approach, you have to stop and decide whether to use VLOOKUP or HLOOKUP. With an AI agent, you don't.
- Upload the file to Excelmatic.
- Ask: "What were the sales in Q1?"
- Excelmatic understands the table's structure, whether vertical or horizontal, and gives you the correct answer, 1200.
Method 4: The INDEX and MATCH Functions
This combination is a classic favorite of Excel power users for its flexibility.
Syntax
=INDEX(array, row_num, [column_num])
=MATCH(lookup_value, lookup_array, [match_type])
Using INDEX and MATCH Together
By nesting MATCH inside INDEX, you can perform powerful lookups that VLOOKUP can't handle, like looking to the left.
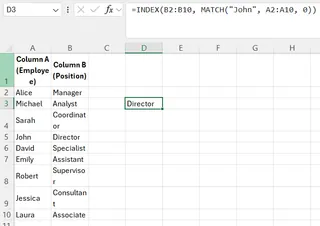
=INDEX(B2:B10, MATCH("John", A2:A10, 0))
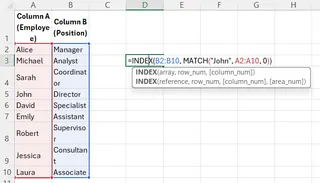
This finds the row position of "John" in column A, and INDEX returns the value from that same position in column B. The result is "Sales".
The Excelmatic Alternative: Powerfully Simple
INDEX/MATCH is flexible but requires you to write and debug a nested formula. Excelmatic delivers the same flexibility with zero complexity.
- Upload the sheet to Excelmatic.
- Ask: "What is John's department?"
- Excelmatic instantly finds "John" and returns the corresponding value "Sales," effortlessly performing a "left lookup."
Method 5: The XLOOKUP Function
XLOOKUP is the modern, superior replacement for all older lookup functions.
Syntax
XLOOKUP(lookup_value, lookup_array, return_array, [if_not_found], [match_mode], [search_mode])
Example
=XLOOKUP("John", A2:A10, B2:B10, "Not Found")
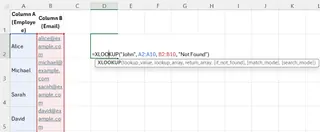
This function searches for "John" in A2:A10, returns the corresponding value from B2:B10, and returns "Not Found" if no match exists. It's clean and powerful.
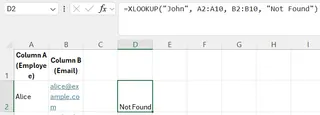
In this case, the name "John" does not exist in the employee list, so the formula correctly returns our custom "Not Found" message.
The Excelmatic Alternative: The Ultimate in Simplicity
XLOOKUP is fantastic, but it's still a formula you have to learn. Excelmatic is a conversation.
- Upload the sheet to Excelmatic.
- Ask: "What is John's department?"
- Excelmatic will check the data and respond conversationally, such as: "I could not find an employee named John." This provides the same built-in error handling with zero setup.
Comparison: Traditional Functions vs. AI Agent
Here’s how these methods stack up.
| Feature | VLOOKUP |
INDEX/MATCH |
XLOOKUP |
Excelmatic (AI Agent) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| How it Works | Formula-based | Nested Formulas | Formula-based | Natural Language Prompt |
| Ease of Use | Moderate | Difficult | Easy | Effortless |
| Lookup Direction | Right only | Any Direction | Any Direction | Any Direction (Automatic) |
| Default Match | Approximate | Exact (with 0) |
Exact | Intelligent (Context-based) |
| Error Handling | Requires IFERROR |
Requires IFERROR |
Built-in | Conversational & Built-in |
| Learning Curve | High | Very High | Moderate | None |
Conclusion
Lookup functions are essential tools in Excel. For years, mastering VLOOKUP and INDEX/MATCH was a rite of passage for any serious user. XLOOKUP has made this much easier.
However, the game is changing. AI agents like Excelmatic offer a paradigm shift. Instead of you learning the language of Excel, the tool learns to understand your language. For quick, accurate data retrieval, analysis, and reporting, asking a simple question is undeniably faster and more efficient than writing and debugging formulas.
Ready to transform how you find data in Excel? Try Excelmatic today and experience the power of conversational data lookup. Simply upload your file, ask questions in plain language, and get instant answers - no formulas to learn, no syntax to debug, just the insights you need to move your business forward.
While functions remain vital for building dynamic, in-sheet models, for the vast majority of day-to-day lookup tasks, an AI-powered approach is the smarter way to work.
FAQ
Lookup Functions in Excel FAQs
What is a lookup function in Excel?
A lookup function in Excel allows you to find specific data within a range of cells based on criteria that you specify.
What are the different types of lookup functions in Excel?
There are several types, including the legacy LOOKUP, the common VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP, the powerful INDEX/MATCH combination, and the modern XLOOKUP.
When should I use an Excel function over an AI tool like Excelmatic?
Use traditional functions when you are building complex, automated dashboards where formulas need to update dynamically as cell values change. Use an AI tool like Excelmatic for fast ad-hoc analysis, exploring a new dataset, or generating answers and charts for a report without manual formula writing.
Can I combine multiple lookup functions in one formula?
Yes, nesting functions (like INDEX and MATCH) is a common practice in Excel to create more complex and flexible formulas.
Are there any limitations to using lookup functions in Excel?
Yes. VLOOKUP can't look to its left, LOOKUP requires sorted data, and all formulas can break if the sheet structure changes. They also require you to learn and remember their specific syntax.






