Key Takeaways:
Predictive modeling is the key competitive edge, moving business decisions from intuition-based guesses to data-driven forecasts.
Predictive modeling sits between descriptive analytics (what happened) and prescriptive analytics (what to do), forming the critical bridge to proactive strategy.
Different models (regression, time series, tree-based, clustering) solve different problems, from forecasting sales to classifying customer risk.
A successful model follows a clear 5-step process: frame the question, prepare data, choose/train a model, evaluate results, and deploy/monitor.
Predictive modeling powers critical applications across retail (inventory), finance (fraud), healthcare (risk), and strategic planning (foresight), far beyond simple recommendations.
Have you ever wondered how Netflix seems to know your next binge-watch or how Amazon suggests the perfect product you didn't even know you needed? These aren't strokes of luck; they are the direct results of Predictive Modeling, a core capability that has quietly become the defining competitive edge in the modern economy.
For decades, strategic decisions were dominated by intuition and retrospective analysis. Today, a profound shift is underway. As articulated by researchers in the field, we are moving from an era of expert-driven, static predictions to a new paradigm of data-driven, intelligent, and systemic forecasting. This evolution is not just a technical upgrade — it's a fundamental change in how organizations perceive and prepare for the future. This article will guide you through what predictive modeling truly is, why it's indispensable, and how you can start leveraging its power.
What is Predictive Modeling? From Describing the Past to Shaping the Future
At its heart, predictive modeling is a process that uses historical data and statistical algorithms (increasingly powered by machine learning) to forecast the likelihood of future outcomes. It's the engine behind predictive analytics, transforming raw data into a forward-looking intelligence asset.
To appreciate its role, it's essential to understand the broader analytics landscape, which can be seen as a three-stage evolution:
1. Descriptive Analytics (The "What Happened?")
This is the foundation. It uses data aggregation and mining to describe past performance. Dashboards showing last quarter's sales or last month's website traffic are classic examples. It's reactive and hindsight-oriented.
2. Predictive Analytics (The "What Could Happen?")
This is where predictive modeling operates. It builds on descriptive data to identify patterns, risks, and opportunities. It answers questions like: Which customer is most likely to churn? What will demand be for this product next season? It's proactive and foresight-oriented.
3. Prescriptive Analytics (The "What Should We Do?")
This is the advanced frontier. It goes beyond prediction to recommend specific actions to achieve desired outcomes. For example, it might not only forecast a machine's failure but also prescribe optimal maintenance schedules and parts ordering.

Predictive modeling, therefore, is the critical bridge from passive observation to active strategy. A core framework for implementing this involves a continuous cycle: Data Collection & Preparation → Analysis & Insight Generation → Decision-Making & Implementation → Continuous Monitoring & Feedback. This systematic approach ensures predictions are grounded in quality data and translate into tangible actions.
The Predictive Toolbox: Core Models and Their Roles
Not all predictions are created equal, and the choice of model depends entirely on the question you're asking. Here are some of the most powerful and widely used predictive models:
Regression Models
The workhorse for forecasting continuous numerical outcomes. Want to predict next month's revenue, the price of a house, or the demand for a product? Linear or logistic regression models are often the starting point, establishing relationships between variables (e.g., marketing spend and sales).
Time Series Models
Specialized for data where time is a crucial dimension — like hourly sales, daily stock prices, or quarterly GDP figures. These models account for trends, seasonality, and cycles to forecast future values.
Tree-Based Models (Random Forest & Gradient Boosting)
These are ensemble methods that combine the power of many simple "decision trees" to create highly accurate and robust predictions. They excel at handling complex, non-linear relationships in data and are champions in tasks like customer classification and risk assessment.
Clustering Models (like K-Means)
While often used for segmentation, clustering is a powerful prelude to prediction. By uncovering hidden groups in your data (e.g., distinct customer personas), you can build more precise predictive models for each segment.
The New Frontier: AI-Enhanced Forecasting
The field is rapidly advancing with techniques like ensemble forecasting, which combines multiple models for greater stability and accuracy with complex data. Cutting-edge research is also integrating causal inference to move beyond correlation, asking "what-if" questions to make unbiased predictions even for new users with no history. Furthermore, the latest benchmarks suggest advanced AI models are approaching the forecasting accuracy of the best human "superforecasters," promising to democratize high-level strategic insight.
Your Blueprint for Action: Building a Predictive Model
The journey from concept to prediction can be demystified into a clear, actionable workflow. Modern, user-friendly platforms like Excelmatic are designed to guide you through these steps without requiring deep coding expertise.
1. Frame the Business Question
Start with clarity. Is the goal to reduce customer churn, optimize inventory, or predict equipment failure? A well-defined objective dictates everything that follows.
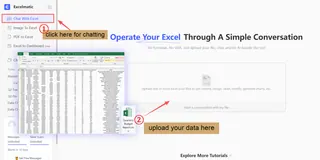
2. Prepare Your Data
This is arguably the most crucial step. Gather relevant historical data and clean it by handling missing values and outliers. In Excelmatic, you can use intuitive data wrangling tools to transform raw data into an analysis-ready format.
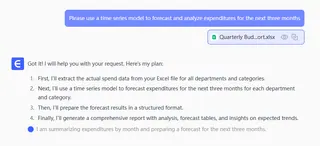
3. Choose and Train Your Model
Based on your question (e.g., classification for churn, regression for sales), select an appropriate algorithm. Excelmatic's visual interface allows you to apply different models (like Random Forest or Regression to your prepared dataset with just a few clicks.
4. Evaluate and Interpret
No model is perfect. Use key metrics (like accuracy, precision, or R-squared) provided by the platform to evaluate performance. The goal is to understand not just the prediction, but the confidence behind it and the key factors driving it.
5. Deploy and Monitor
A model's value is realized in action. Integrate the predictive insights into your business processes — whether it's a marketing automation tool or a supply chain dashboard. Crucially, continuously monitor its performance as the world changes, and periodically retrain it with new data.
Predictive Modeling in Practice: Industry Applications
The applications are as diverse as industry itself, moving far beyond product recommendations:
Retail & E-commerce
As seen with Amazon and Walmart, predictive models power dynamic pricing, personalize shopping experiences, and, most critically, optimize inventory through precise demand forecasting, dramatically reducing both stockouts and overstock.
Finance
Banks and insurers are heavy users, employing models for real-time fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and nuanced credit scoring that assesses a customer's risk profile more accurately than traditional methods.
Healthcare
This is a life-saving application. Hospitals use predictive analytics to identify patients at high risk of readmission or complications, enabling early intervention and improving outcomes while managing costs.
Strategic Planning
On a macro level, organizations and governments now use "intelligent technology foresight." By analyzing vast datasets of patents, research papers, and news, they can identify emerging technological trends and potential disruptions, informing national R&D strategy and corporate innovation pipelines.
Predict with Confidence, Start with Excelmatic
The future belongs to those who can anticipate it. Predictive modeling is no longer a complex science reserved for experts with vast resources — it's an essential, accessible tool for making smarter decisions.
This is where Excelmatic transforms the game. It removes the traditional barriers of coding and complex statistics, allowing you to go from question to forecast in a conversation. Simply ask about sales trends, customer behavior, or operational risks, and receive clear, actionable predictions directly within your workflow.
Stop wondering about what might happen and start building your strategy around what will happen. Let your data guide your next move.
Stop guessing. Start predicting. Try Excelmatic today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do I know if my predictions are reliable?
A: Don't trust a single number. Always check the confidence interval or probability score provided. A good prediction should tell you how sure it is, helping you make risk-aware decisions.
Q: How long will a predictive model stay accurate?
A: Accuracy declines over time due to changing conditions ("model drift"). To stay reliable, you must monitor performance and retrain the model with new data periodically.
Q: What's the biggest mistake when starting out?
A: Starting with the data or tool instead of the business question. Without a clear goal (e.g., "reduce churn by 10%"), projects often become technically complex but deliver no real value.






