Key Takeaways:
- Excel PivotTables don't automatically update when source data changes, leading to inaccurate business reports and missed insights
- Excelmatic eliminates the refresh problem entirely by analyzing your latest data directly and delivering instant insights through simple language commands
- Compared to manual methods, Excelmatic automatically handles new data ranges and large datasets without technical setup or configuration
- For business professionals, adopting Excelmatic means always having accurate reports and more time for decision-making rather than technical maintenance
You finally finish building your perfect report, and a neat PivotTable shows sales by region, product, and month. Everything looks great.
Then your teammate updates the data source. You open the file again, expecting the new numbers to appear, but nothing changes.
Your totals are off. The new entries are missing. And now you’re wondering if you did something wrong.
Here’s what you need to know: Excel uses a Pivot cache, which is basically a stored snapshot of your data. It helps your PivotTable load faster, but it doesn’t automatically update when the data changes. This means you need to tell it to look at the new data.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the proven methods for updating your reports—from the classic manual refresh to advanced automation, and even a new AI-powered approach that gets you answers without a single click on "Refresh."
Method 1: The Classic Approach: Manually Refreshing PivotTables
This is the most direct way to update your PivotTable in Excel. There are a few ways to do it.
Using the Ribbon
This is the standard, go-to method for most users.
- Click anywhere inside your PivotTable.
- Go to the Data tab in the top ribbon.
- Click Refresh All. If you only want to update the selected PivotTable, you can go to the PivotTable Analyze tab and click Refresh.
Tip: If you have more than one PivotTable in your workbook (even from different datasets), Refresh All updates every single one.
Using Keyboard Shortcuts
If you prefer to keep your hands on the keyboard, these shortcuts are a lifesaver:
Alt + F5: Refreshes the currently selected PivotTable.Ctrl + Alt + F5: Refreshes all PivotTables in the entire workbook.
Auto-Refresh When Opening the File
You can also make Excel do the work for you each time you open the file. This is perfect for reports you check daily.
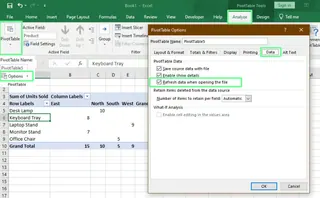
- Right-click anywhere on your PivotTable and select PivotTable Options.
- In the dialog box, go to the Data tab.
- Check the box for Refresh data when opening the file.
- Click OK.
Now, your report will be up-to-date every time you open it.
Method 2: The Power User's Toolkit: Advanced Automation in Excel
For more complex or frequently updated reports, you can set up powerful, hands-off automation. These methods require a bit more setup but save significant time in the long run.
VBA Automation
If you’re comfortable with macros, you can use VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) to create a script that refreshes all PivotTables automatically.
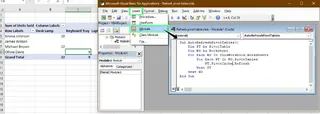
- Press
Alt + F11to open the VBA editor. - In the menu, click Insert > Module.
- Paste this simple code into the module window:
Sub AutoRefreshPivotTables()
Dim PT As PivotTable
Dim WS As Worksheet
For Each WS In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
For Each PT In WS.PivotTables
PT.PivotCache.Refresh
Next PT
Next WS
End Sub
- Close the editor. You can now run this macro to refresh everything or set it to run automatically when the workbook opens.
Power Query Refresh
If your PivotTable is built from data shaped in Power Query, you can refresh your query and PivotTable in one go.
Go to Data > Refresh All. This single command updates your query first, pulling in the latest data, and then refreshes every connected PivotTable.
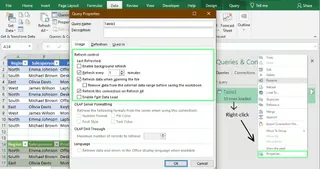
Pro tip: You can schedule automatic refreshes. In the Queries & Connections panel (under the Data tab), right-click your query and select Properties. Here, you can set the query to refresh at a regular interval (e.g., every 30 minutes).
External Data Connections
If your PivotTable pulls data from external sources like a database, CSV file, or web feed, you can set it to update automatically.
- Go to Data > Connections > Properties.
- In the Usage tab, check Refresh data when opening the file.
- For live data, you can also check Refresh every
nminutes to keep your dashboard constantly updated.
This is ideal for dashboards that need to reflect live operational data.
Method 3: The Smart Alternative: Instant Analysis with an AI Agent

What if you could skip the refresh process entirely? Instead of creating a report and then worrying about updating it, you can get instant answers from your latest data using an AI agent like Excelmatic.
Excelmatic is an Excel AI Agent that delivers instant answers, charts, and insights. It changes the workflow from "build, then refresh" to simply "ask and get."
Here’s how it works:
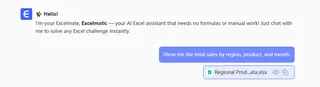
- Upload Your File: Instead of opening your old report, you upload the newly updated Excel file to Excelmatic.
- Ask Your Question: In simple language, you state what you need. For example: "Show me the total sales by region, product, and month."
- Get an Instant Answer: Excelmatic analyzes the entire new file and gives you the exact table or chart you asked for, fully updated.
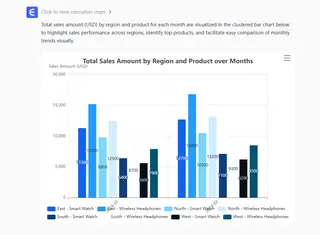
The AI Advantage vs. Manual Refreshing:
- No Pivot Cache Issues: The AI analyzes the fresh data directly. There's no outdated cache causing discrepancies.
- No Data Range Errors: Forget
Analyze > Change Data Source. Excelmatic automatically processes the entire file you provide, so new rows and columns are always included. - No Code or Complex Setup: There's no need to write VBA scripts or configure connection properties. If you can ask a question, you can get an updated report.
This approach is perfect for fast-paced environments where you need accurate answers from new data immediately, without getting bogged down in the technical steps of refreshing.
A Quick Note on Google Sheets
It's worth mentioning that Google Sheets handles this differently. Pivot tables (Google writes this with a space) update automatically whenever the source data changes. You don't have to click "Refresh" or do anything special. As long as your data is within the range the pivot table is looking at, any changes will be reflected instantly.
Troubleshooting: Old vs. New Methods
Traditional methods are powerful, but they can sometimes lead to frustrating errors. Here’s a look at common issues and how different approaches solve them.
Issue 1: New Data Not Appearing
- Traditional Fix: The most common cause is that the new data is outside the PivotTable's defined source range. You need to click on the PivotTable, go to PivotTable Analyze > Change Data Source, and manually adjust the range. A better long-term fix is to format your source data as an Excel Table (
Ctrl + T), which expands automatically. - AI Agent Fix: This problem is eliminated. By uploading the new file, you ensure all data is analyzed from scratch, so you never have to worry about a data range again.
Issue 2: Broken External Data Connections
- Traditional Fix: If a source file was moved or renamed, the connection will break. You have to go to Data > Queries & Connections, find the broken link, and manually update the file path in its properties.
- AI Agent Fix: Not applicable. You simply upload the latest version of the file, completely bypassing connection management.
Issue 3: Slow Refresh on Large Datasets
- Traditional Fix: Huge datasets can make Excel lag or freeze during a refresh. The common workarounds are to turn off automatic calculations, split large PivotTables into smaller ones, or remove unnecessary fields.
- AI Agent Fix: The heavy lifting is done by the AI's powerful backend servers, not your local machine. This means analysis of large files is often much faster and doesn't slow down your computer.
Final Thoughts
Keeping your reports accurate is non-negotiable, and knowing how to get updated data is a critical skill.
- Manual refreshing is great for quick, one-off updates.
- Advanced automation (VBA, Power Query) is a robust solution for complex, established workflows.
- AI agents like Excelmatic offer a new level of speed and simplicity, giving you immediate insights without the technical overhead.
Choosing the right method depends on your specific needs, but by adding these techniques to your toolkit, you can ensure your numbers are always current and reliable.
Ready to eliminate PivotTable refresh headaches forever? Try Excelmatic today and experience instant data analysis with just a simple question.
What is the difference between a PivotTable and regular tables in Excel?
Regular tables organize raw data, while PivotTables allow you to group, filter, and calculate data interactively without altering the original dataset.
What is a PivotChart, and how is it related to a PivotTable?
A PivotChart is a visual representation of a PivotTable. When you update or filter the PivotTable, the PivotChart automatically reflects those changes. It provides a dynamic and visual summary of your data.
Why do my PivotTable fields disappear after refreshing?
If the source data range changes drastically (columns removed or renamed), fields may no longer exist. So make sure that all original field names still exist in your dataset before refreshing.
Can I connect a PivotTable to a live database?
Yes. You can connect directly to databases such as SQL Server, Access, or external APIs through Data > Get Data. Once connected, you can refresh the PivotTable to pull updated records automatically.
How can I add calculated fields in a PivotTable?
You can create a calculated field to perform custom formulas within your PivotTable. Go to Analyze > Fields, Items & Sets > Calculated Field, then define your formula. This helps add metrics like profit margins or growth rates.






