Let's be real - nobody enjoys manually adding up endless rows of numbers in Excel. Whether you're tracking monthly expenses, analyzing sales data, or managing inventory, total columns are your secret weapon for faster, more accurate calculations.
At Excelmatic, we've helped thousands of users move beyond basic spreadsheets to AI-powered data analysis. But even in our automated world, knowing these fundamental Excel skills is crucial. Here are five foolproof methods to add totals to your columns, ranked from simplest to most advanced.
Why Total Columns Are a Game-Changer for Business Data
Before we dive into the how-to, let's talk about why this matters. A well-placed total column can:
- Save hours of manual calculation time
- Reduce human error in financial reports
- Provide instant insights into business performance
- Make your spreadsheets more professional and readable
Imagine you're reviewing quarterly sales. Without totals, you're stuck adding numbers manually. With totals? One glance shows which products are crushing it and which need attention.
Method 1: The Classic SUM Function (Perfect for Beginners)
The SUM function is Excel 101 - simple but powerful. Here's how it works:
- Click the cell where you want your total
- Type
=SUM( - Highlight the cells you want to add
- Close with
)and hit Enter
Example: =SUM(B2:B10) adds all values from B2 to B10.
Pro tip: In Excelmatic, our AI can suggest and write these formulas for you automatically - just describe what you need!
Method 2: AutoSum - The One-Click Wonder
For those "I need this done yesterday" moments:
- Click below your data column
- Find the Σ (AutoSum) button on the Home tab
- Press Enter
Excel automatically detects your data range and inserts the SUM formula. It's like having a personal assistant for your spreadsheets.
Method 3: Smart Tables with Built-In Totals
Tables aren't just for pretty formatting. They make your data dynamic and self-updating:
- Select your data and press Ctrl+T
- Check "My table has headers"
- Go to Table Design > check "Total Row"
Now you've got a smart total that automatically adjusts when you add new data. Change the function (SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT) with the dropdown arrow.
Method 4: SUMIF - When You Need Selective Math
Only want to total specific items? SUMIF is your friend:
=SUMIF(range, criteria, sum_range)
Example: =SUMIF(A2:A10,"Product A",B2:B10) totals only Product A sales.
Excelmatic users: Our AI can generate these conditional formulas instantly based on your plain English descriptions.
Method 5: SUMPRODUCT for Advanced Calculations
When you need to multiply and then sum (like calculating total revenue from price × quantity):
=SUMPRODUCT(B2:B10,C2:C10)
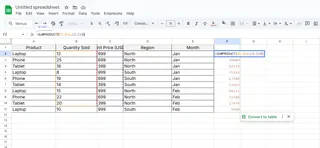
This powerful function handles complex calculations in one step.
Bonus: Avoiding Common Total Column Mistakes
Even pros make these errors:
- Including header cells in your sum range
- Forgetting to update ranges when adding data
- Using SUM when you need SUMIF
Excelmatic's formula checker automatically flags these issues before they cause problems.
From Basic Totals to AI-Powered Analysis
While these Excel methods work, imagine what you could do with AI assistance:
- Automatic formula generation
- Real-time error detection
- Smart suggestions for better data visualization
- Natural language queries like "calculate the total sales volume of all products"
That's exactly what Excelmatic delivers - all these traditional Excel skills, supercharged with artificial intelligence.
Your Next Steps
Try applying these techniques to:
- This month's expense report
- Your sales pipeline spreadsheet
- Inventory tracking
Remember: The goal isn't just adding numbers - it's gaining insights to make better business decisions. And when you're ready to take your data analysis to the next level, Excelmatic is here to help you work smarter, not harder.