Key Takeaways:
- Finding the right input to achieve a specific target in Excel requires complex backward calculations that traditional methods struggle with
- Excelmatic eliminates the need for manual Goal Seek setup by allowing you to simply ask "what input gives me this output?" in plain language
- Compared to Excel's built-in Goal Seek, Excelmatic handles complex formula dependencies automatically and provides instant answers without menu navigation
- For business professionals doing financial modeling or sales forecasting, the AI approach delivers faster, more accessible what-if analysis with minimal Excel expertise required
What-if analysis is a powerful data analysis technique that allows you to test various scenarios and determine a range of possible outcomes. In other words, it lets you see the impact of making a specific change without altering the real data. Such analysis is invaluable in financial modeling, forecasting, and other business applications where backward calculations are required.
This tutorial will focus on one of Excel's core What-If Analysis tools — Goal Seek. We will learn how to use this classic tool in Microsoft Excel with practical examples. We'll also compare this traditional method with modern AI-powered solutions like Excelmatic, which offer a more intuitive and faster way to get the same results.
What is Goal Seek in Excel?
Goal Seek is an Excel What-If Analysis tool that allows users to find the necessary input value in a formula to achieve a specific target output. While other What-If Analysis tools, like Data Tables or Scenario Manager, consider multiple variables, Goal Seek focuses on adjusting a single variable to meet a desired result. It's a foundational feature for anyone looking to master advanced Excel capabilities.
How Goal Seek Works
Goal Seek is used when you know the result you want from a formula but are unsure of the input value needed to achieve it. You essentially work backward by setting the desired outcome and letting Excel iteratively adjust an input variable to find the solution.
Common Applications of Goal Seek
Though Goal Seek is used in different fields, its most common uses are in financial modeling and academic scenarios. Some of these applications are:
- Budget Forecasts: Goal Seek helps determine how much savings or investment is needed to reach a financial goal. For example, if you want to save a certain amount by the end of the year, it can calculate the monthly savings required.
- Loan Payments: It can calculate the loan amount you can afford based on a fixed monthly payment. If you have a specific amount you can pay monthly, Goal Seek can adjust the loan principal to see how much you can borrow.
- Break-Even Analysis: Businesses can use Goal Seek to find the sales volume needed to cover costs and reach a break-even point. By setting the profit to zero, Goal Seek can adjust the sales quantity or price to determine the break-even point.
- Grade Calculations: Students and educators can use Goal Seek to determine the grade needed on a final exam to achieve a desired overall course grade.
- GPA Targets: It can also determine the grades needed in upcoming courses to reach or maintain a specific GPA.
Let’s now explore how to apply this in Microsoft Excel.
How to Use Goal Seek in Excel
Applying Goal Seek for your data models involves a few repeatable steps. We'll cover the traditional method first, then show you a more streamlined AI approach.
The Traditional Method: Using Excel's Built-in Tool
Step 1: Setting up Your Data
Begin by setting up your data and formulas in a way that Excel can interpret them. Ensure the formula you want to solve is correctly linked to the input cell that will be adjusted.
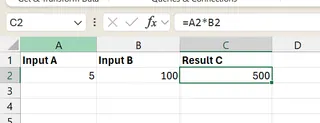
According to the formula in the image above, since Result C depends on Input A and Input B, we can change either Input A or B to reach a target for Result C.
Step 2: Running Goal Seek
First, select the cell with the formula whose result you want to adjust (say, C2). Go to the Data tab, click What-If Analysis in the Forecast group, and choose Goal Seek.
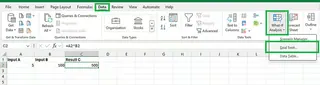
In the Goal Seek dialog box, specify the cell with the formula (Set cell), the desired result (To value), and the input cell to be changed (By changing cell).
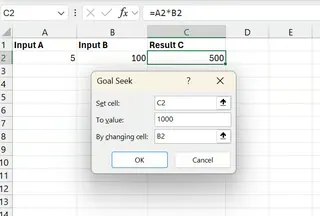
Click OK to allow Excel to find the appropriate input value.
You can click Cancel to discard the change and keep the original values.
Step 3: Analyzing the Result
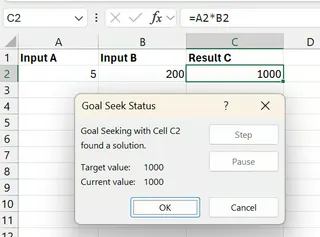
After running Goal Seek, Excel automatically adjusts the selected input cell to reach the target output. The updated value is now in your sheet.
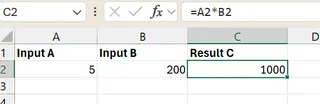
In the image above, by changing Input B to 200 from 100, we have achieved our target Result C of 1000.
The AI Method: Using Excelmatic for Instant Answers

While Goal Seek is effective, it requires navigating menus and understanding specific dialog boxes. An AI agent like Excelmatic simplifies this entire process.
The workflow is straightforward:
- Upload your Excel file to Excelmatic.
- Ask your question in plain language. For the example above, you would simply ask: "To make Result C (cell C2) equal to 1000, what does Input B (cell B2) need to be?"
- Get the answer. Excelmatic analyzes the formula dependencies and provides the correct input value instantly, without you needing to find the right tool or fill in any boxes.
This conversational approach makes complex analysis more accessible and significantly faster.
Excel Goal Seek Examples
Let's explore how these two methods apply to real-world problems.
Example 1: Loan Payment Calculation
Imagine you’re planning to buy a house and want to determine the maximum loan amount you can afford with a monthly payment of $1,000. You have an interest rate and loan term in mind, but you need to figure out the loan principal.
The Traditional Method
Step 1: Setting up Your Data
Open a new Excel worksheet and create the setup as shown below.
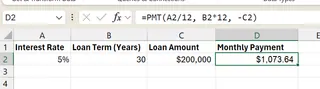
Enter your interest rate (5%) in cell B1, the loan term (30 years) in cell B2, and an initial guess for the loan amount ($200,000) in cell B3. In cell B4, enter the formula for calculating the monthly payment using the PMT function:
=PMT(B1/12, B2*12, -B3)
Step 2: Running Goal Seek
Invoke Goal Seek from the Data > What-If Analysis menu.
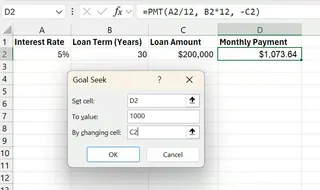
In the dialog box, enter:
- Set Cell:
B4(the monthly payment cell) - To Value:
1000(your desired monthly payment) - By Changing Cell:
B3(the loan amount)
Step 3: Interpreting the Results
After clicking OK, Excel finds the solution.
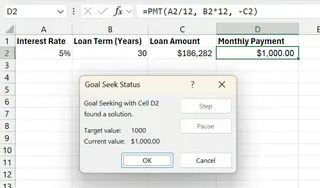
The adjusted loan amount is $186,281.62. This is the maximum loan you can afford with a $1,000 monthly payment under these terms.
Solving with Excelmatic
With Excelmatic, you would simply upload your worksheet and ask:
What should the Loan Amount be to make the Monthly Payment exactly $1000?
Excelmatic would instantly calculate and return the value $186,281.62, saving you the clicks and manual setup.
Example 2: Achieving a Revenue Target
Suppose you’re a sales manager aiming for a revenue target of $500,000. You know the product's price per unit but need to determine how many units to sell.
The Traditional Method
Step 1: Setting up Your Data
Open a new worksheet and enter the data as shown.
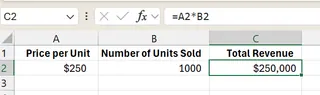
In cell A2, enter the price per unit ($250) and an estimate for units sold in cell B2. In cell C2, enter the formula for total revenue:
=A2 * B2
Step 2: Running Goal Seek
Open the Goal Seek dialog box.
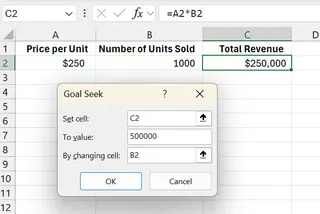
In the dialog box, enter:
- Set Cell:
C2(your total revenue cell) - To Value:
500000(your desired revenue target) - By Changing Cell:
B2(the number of units sold)
Step 3: Interpreting the Results
Excel will adjust the number of units sold in cell B2.
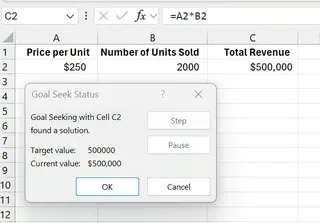
The result shows you need to sell 2,000 units at $250 each to meet your $500,000 revenue target.
Solving with Excelmatic
Using Excelmatic, the process is reduced to a single question:
To get a Total Revenue of $500,000, how many Units to Sell do I need?
Excelmatic processes the request and provides the answer: 2,000.
Common Errors When Using Goal Seek Manually
When using Excel's built-in Goal Seek, you might encounter a few common errors. While AI tools often bypass these issues by handling the logic internally, it's good to know what they are.
1. Excel Goal Seek May Not Have Found a Solution
This is a frequent issue when the tool can’t find a solution. This can happen if the solution is mathematically impossible or if Excel's algorithm can't converge on a solution within its default number of tries.
For example, if the unit price in our sales example was mistakenly set to $0, the revenue would always be $0, no matter how many units are sold. Goal Seek would fail to find a solution to reach $500,000.
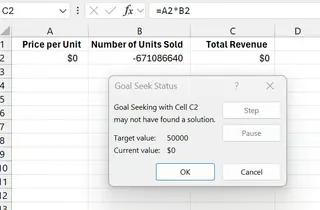
To fix this, first ensure your formula and inputs are logical. If they are, you can increase Excel's maximum iterations (File > Options > Formulas > Max Iterations), but this is rarely necessary for simple models.
2. The "Cell Must Contain a Value" Error
Goal Seek requires the "By changing cell" to contain a hard-coded value, not another formula. If you try to change a cell that is itself calculated from other cells, Excel will show an error.
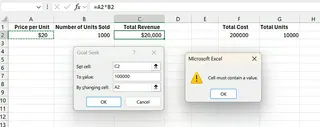
You must ensure the cell you are asking Goal Seek to change is an independent input variable. AI tools like Excelmatic are often better at tracing complex dependencies, reducing the chance of such errors.
Conclusion
This article introduced you to a powerful technique for backward calculations in Excel. We covered the traditional method using the built-in Goal Seek tool, a reliable feature for any analyst to know. Through practical examples, we saw its step-by-step application and potential pitfalls.
We also explored how modern AI agents like Excelmatic are revolutionizing this process. By allowing you to simply ask your question in plain language, they eliminate the need for menu navigation and troubleshooting, delivering instant and accurate answers.
Ready to simplify your what-if analysis? Try Excelmatic today and experience the ease of getting instant answers to your backward calculation questions.
Whether you prefer the hands-on control of Goal Seek or the speed and simplicity of an AI solution, mastering what-if analysis will undoubtedly elevate your data modeling skills.
FAQ
What is Goal Seek in Excel?
Goal Seek is a What-If Analysis tool in Excel. It helps you find the necessary input value to achieve a specific target output in a formula by adjusting a single variable.
When should I use Goal Seek?
Use Goal Seek when you know the desired outcome of a formula and need to determine the specific input value that will achieve that result.
How do I run Goal Seek in Excel?
Select the cell with the formula, go to the Data tab, click What-If Analysis, choose Goal Seek, and then specify the target value and the input cell to change. Alternatively, use an AI tool like Excelmatic to ask the question directly in plain language.
What happens if I cancel a Goal Seek operation midway?
If you cancel a Goal Seek operation, Excel will revert to the original values before the operation began.
Why does Goal Seek sometimes fail to find a solution?
Goal Seek may fail if the target value is unrealistic or mathematically impossible given the constraints, or if the input value can't converge within the allowed iterations.






