Key Takeaways:
- Excel's Flash Fill requires clear patterns and manual examples, often failing with inconsistent data that business professionals frequently encounter
- Excelmatic eliminates the need for pattern recognition by allowing you to clean and transform data using simple language commands
- Unlike Flash Fill that produces static results, Excelmatic can easily regenerate updated outputs and handle complex multi-column operations with precise instructions
- For marketing, sales, and operations teams dealing with messy data, Excelmatic provides a more reliable and intuitive solution that adapts to varying data formats
Wrangling messy data in Excel can feel like a chore. Thankfully, features like Flash Fill can automate repetitive tasks, saving you from writing complex formulas. Flash Fill is a smart feature in Excel that spots patterns in your data and completes the work for you. It’s brilliant for cleaning up names, formatting numbers, or sorting data in just a few keystrokes.
In this article, we’ll show you how Flash Fill works and how to get the most out of it. We'll also explore how modern AI tools like Excelmatic are taking data manipulation to the next level, offering a more intuitive and powerful alternative.
What Is Flash Fill in Excel?
Flash Fill helps clean and reformat data automatically. If you provide an example, like pulling a first name from a full name, Excel spots the pattern and fills in the rest of the column. It’s a fantastic tool for tasks like separating dates, reordering text, or combining columns without writing a single formula.
The idea came from a real moment of head-scratching. Back in 2009, a Microsoft researcher, Sumit Gulwani, was asked how to combine first and last names in Excel. He didn’t have a good answer then, but that question stuck with him. A few years (and a lot of thinking) later, Flash Fill was rolled out in Excel 2013.
How to Turn Flash Fill On and Off
Flash Fill is usually turned on by default in Excel 2013 and later. If it isn’t, or if you want to switch it off, here’s how:
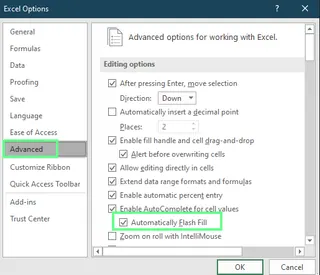
- Go to File > Options.
- In the Excel Options window, select Advanced.
- Under Editing Options, find Automatically Flash Fill and tick (or untick) the box.
- Click OK to save.
On/off Flash Fill. Image by Author.
How to Use Flash Fill in Excel
Now let's see how Flash Fill works. You can use it in two main ways.
Automatic Activation
As you start typing in an adjacent column, Excel watches what you're doing. If it detects a clear pattern, it will offer to complete the rest of the column for you.
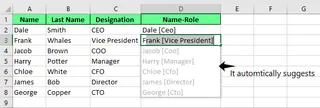
For example, imagine one column has names and another has job titles. We want to combine them so the title appears in brackets next to the name. In the first cell, type: Dale [Ceo]. As you begin typing in the next cell, Excel suggests the rest of the entries. If you like the suggestions, just hit Enter to accept.
Flash Fill automatic suggestion. Image by Author.
Notice how Flash Fill intelligently adapts to the pattern, even if the initial example has minor inconsistencies, like the lowercase "eo" in "Ceo".
Manual Activation
Sometimes, Excel won’t suggest anything automatically. In that case, you can trigger Flash Fill manually.
After entering your pattern in the first cell, use one of these shortcuts:
- On Windows: Press
Ctrl + E - On Mac: Press
Cmd + E
Alternatively, you can click the Data tab in the ribbon and then select Flash Fill.

Flash Fill button on the ribbon. Image by Author.
Flash Fill Options and Settings
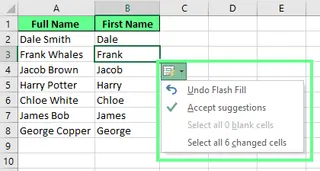
After Flash Fill runs, a small options button appears. This menu gives you quick tools to manage the results:
- Undo Flash Fill: Reverts the fill if the pattern was wrong.
- Select blank cells: Highlights any cells Flash Fill skipped, often due to inconsistent data.
- Select changed cells: Quickly shows which cells were filled so you can review them.
Flash Fill options. Image by Author.
Practical Examples of Flash Fill in Action
Flash Fill can handle a wide variety of real-world tasks. Here are some practical ways to use it, along with a look at how an AI-powered tool can offer an even simpler solution.
Extracting Parts of Data
You can easily pull specific information from a cell. For example, to split full names into first and last names, just type the first name in a new column, press Ctrl + E, and Flash Fill does the rest.
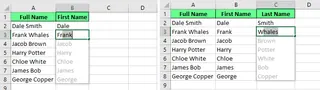
Extract the last and first name from the full name using Flash Fill. Image by Author.
Similarly, you can extract a zip code from a full address. Type the zip code once, and Flash Fill will handle the rest.
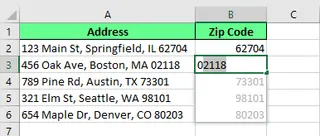
Extract a zip code from a full address. Image by Author.
The AI-Powered Alternative: Excelmatic

For these tasks, you can also use an AI agent like Excelmatic. Instead of providing an example, you simply state your goal in plain language. After uploading your file, you could ask:
Create two new columns, 'First Name' and 'Last Name', by splitting the 'Full Name' column.
Or for the address example:
Extract the zip code from the 'Address' column and put it in a new column named 'Zip Code'.
Excelmatic understands the request and performs the extraction, which can be faster and more intuitive than setting up examples, especially for complex data.
Combining Data
Flash Fill also works in reverse. You can merge data from separate cells. If you have first names, last names, and ages in different columns, you can combine them into a single, formatted string. Flash Fill will recognize separators like spaces, commas, or dashes.
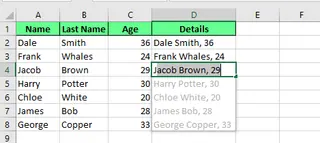
Combine multiple cells into one using Flash Fill. Image by Author.
The AI-Powered Alternative: Excelmatic
With Excelmatic, combining data is just as straightforward. You would upload your worksheet and ask:
Combine 'First Name', 'Last Name', and 'Age' into a new column called 'Summary'. The format should be 'FirstName LastName (Age)'.
This method gives you precise control over the final output without relying on pattern detection, reducing the chance of errors.
Cleaning and Formatting Data
Flash Fill is excellent for standardizing data. For example, it can remove leading spaces and apply proper case capitalization. Type the corrected data in the first cell, and Flash Fill will clean the rest.
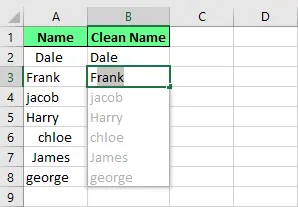
Remove the unnecessary spaces using Flash Fill. Image by Author.
You can also reformat phone numbers. If your data is in the 1234567890 format, you can convert it to (123) 456-7890 with a single example.
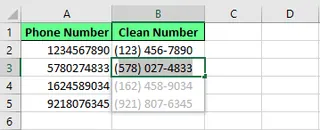
Format the numbers using Flash Fill. Image by Author.
The AI-Powered Alternative: Excelmatic
AI tools excel at these cleaning tasks. In Excelmatic, you could simply instruct:
Clean the 'Name' column by removing extra spaces and capitalizing the first letter of each name.
Or for the phone numbers:
Reformat all numbers in the 'Phone' column to the format (XXX) XXX-XXXX.
Excelmatic understands the intent behind the command ("clean," "reformat"), making it a more robust solution for tidying up entire datasets.
Advanced Uses: Rearranging, Modifying, and Creating Data
Flash Fill can handle more complex transformations once you get the hang of it. You can rearrange product codes, mask sensitive information, or even generate email addresses from names and domains.
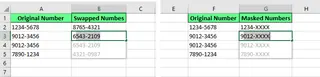
Swap and hide the data using Flash Fill. Image by Author.
To create email addresses, you can combine a first initial, last name, and domain. Type one example, like [email protected], and Flash Fill will generate the rest.
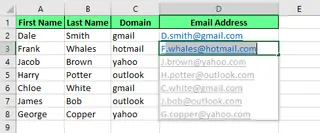
Generate an email address using Flash Fill. Image by Author.
With Excelmatic, these advanced tasks become even easier. You could say:
Create email addresses in a new column using the first initial from 'First Name', a period, the full 'Last Name', and the '@' symbol followed by the 'Domain'.
The natural language command allows for complex, rule-based generations that Flash Fill might struggle with if the pattern isn't perfectly consistent.
What Flash Fill Might Miss or Misinterpret
Flash Fill saves time, but it isn’t perfect. Here are some common limitations:
- Static Data: Flash Fill creates static values. If you change the original data, the filled results will not update. You must run Flash Fill again. While AI tools like Excelmatic also produce static output, regenerating the results is as simple as re-running your language prompt.
- Inconsistent Patterns: If your data is inconsistent, Flash Fill might get confused. For example, if some names have a middle name and others don't, Flash Fill may return incorrect or mismatched values when trying to extract last names.
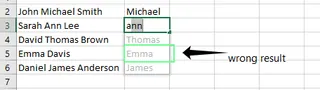
Flash Fill gives the wrong result. Image by Author.
This is where Excelmatic shines. You can give a more specific instruction: "Extract the last word from the 'Full Name' column to create the 'Last Name' column." The AI can interpret the rule ("last word") instead of just a visual pattern, leading to more accurate results.
- Hidden Characters: Flash Fill can be tripped up by non-printable characters like line breaks or extra spaces, which are common in data copied from the web. This can cause it to skip cells or produce errors. AI tools are often designed to automatically identify and clean these invisible characters during processing.
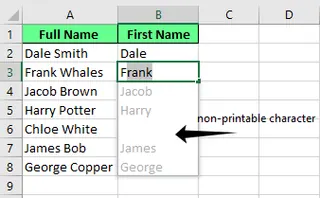
A blank cell due to a non-printable character. Image by Author.
- Number Formatting: When Flash Fill handles numbers, it may convert them to text. This can cause issues with calculations. You may need to manually re-apply number formatting after using Flash Fill.
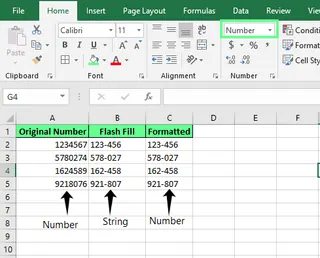
Flash fill changes the formatting. Image by Author.
Troubleshooting Flash Fill Issues
If Flash Fill isn’t working, here are a few things to try:
- Provide More Examples: If Excel doesn’t detect the pattern after one entry, try giving two or three examples.
- Trigger it Manually: Press
Ctrl + E(Windows) orCmd + E(Mac), or use the button on the Data tab. - Check Your Settings: Make sure Flash Fill is enabled by going to File > Options > Advanced and checking Automatically Flash Fill.
- Start Fresh: Clear the column, enter a clearer example, and try again.
If these steps fail, your data may be too inconsistent for Flash Fill. At this point, consider using Excel formulas or an Excelmatic that can handle more complex logic.
Final Thoughts
Flash Fill is an indispensable Excel shortcut for quick and simple data manipulation. It excels at cleaning, reformatting, and combining data when a clear pattern exists. However, remember that it's a one-time operation and can struggle with inconsistent data.
For more complex, nuanced, or repetitive tasks, Excelmatic offers a more powerful and flexible solution. By understanding language commands, it moves beyond pattern-matching to interpret your intent, delivering faster and more accurate results for business professionals.
Whether you stick with the classic or embrace Excelmatic's AI-powered approach, mastering these tools will transform your data cleaning workflow and save valuable time.
Ready to upgrade your data cleaning capabilities? Try Excelmatic today and experience the power of AI-driven data transformation - no pattern recognition needed, just simple commands that work.
Flash Fill Excel FAQs
Can Flash Fill handle data from multiple columns at once?
No, Flash Fill works by creating a pattern in a single column adjacent to your source data. However, it can use data from multiple nearby columns to detect a pattern. For true multi-column operations based on specific rules, an AI tool is more effective, as you can instruct it to, for example, "Combine columns A, C, and F."
Can Flash Fill create abbreviations?
Yes. For example, if you type "HR" for "Human Resources," Flash Fill will likely understand you want initials and apply that pattern to the rest of the column.
Can I use Flash Fill with Excel tables?
Yes, Flash Fill works perfectly well with data structured in an Excel Table.
Can I use Flash Fill with PivotTables in Excel?
You can’t use Flash Fill inside a PivotTable, as its structure is dynamic. However, you can use it in a column right next to a PivotTable, and it can use the PivotTable data to recognize patterns.
Why isn’t Flash Fill working when I try to reformat dates in Excel?
Flash Fill is based on text patterns, not data types. It doesn't understand date logic. If you try to turn 1/3/2025 into 3-Jan-25, it will just copy the text pattern. For true date formatting, you should use Excel's cell formatting options or the TEXT() function.






