Key takeaways:
- Processing lists or tables of data using traditional Excel VBA arrays is powerful but requires significant programming knowledge, is prone to errors, and is difficult to maintain.
- An Excel AI agent like Excelmatic replaces complex VBA code (like
For...Nextloops,ReDim, and multi-dimensional array handling) with simple, natural language prompts. - Using Excelmatic dramatically reduces the time spent on data manipulation, eliminates syntax errors, and empowers non-programmers to perform advanced data processing tasks with ease.
The Challenge: Processing Data Sets in Excel is Tedious
Imagine you're a financial analyst with a spreadsheet of monthly sales figures. Your manager asks you to perform a series of calculations: calculate the total, find the average, apply a 20% growth forecast to each month, and then reorganize the data for a presentation.
If you're an Excel power user, your mind might immediately jump to a powerful but daunting tool: Excel VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) arrays.
VBA arrays are a way to store and manipulate large sets of data in memory, which is much faster than repeatedly reading from and writing to worksheet cells. However, this speed comes at a high cost. You're no longer just working in Excel; you're now a part-time programmer. You have to worry about syntax, data types, loops, and frustrating errors that can bring your work to a halt. For many, this is where a simple task becomes a major roadblock.
The Traditional Method: Wrestling with Excel VBA Arrays
To tackle the sales data task using the traditional method, you'd need to dive into the world of VBA programming. This isn't a simple point-and-click operation.
The Complex Steps of Using VBA Arrays
Let's break down the typical workflow, which quickly reveals why this method is so challenging for most Excel users.
1. Declaring the Array: First, you must open the VBA editor and declare a variable to hold your data. You need to decide:
- Is it a fixed size or dynamic? If you know you'll always have 12 months, you can declare
Dim MonthValues(1 To 12) As Currency. But what if next year you have 15 data points? You'd need a dynamic arrayDim MonthValues() As Currencyand then resize it later withReDim. - What's the data type? Is it
Currency,Integer,String, or aVariantto be safe? Getting this wrong can cause errors.
2. Populating the Array:
Next, you need to get your data from the Excel sheet into the array. This usually involves writing a For...Next loop.
' A loop to read values from Column B into the array
For i = 1 To 12
MonthValues(i) = Cells(i + 1, 2).Value
Next i
This code iterates through each cell in your data range and copies its value into the corresponding position in the array. You have to carefully manage the row and column numbers (Cells(i + 1, 2)) to avoid grabbing the wrong data.
3. Manipulating the Data: Now for the actual work. To increase each value by 20%, you need another loop:
' A loop to process each value in the array
For i = LBound(MonthValues) To UBound(MonthValues)
MonthValues(i) = MonthValues(i) * 1.2
Next i
Notice the use of LBound and UBound—more functions you need to learn to make your code robust. If your data is in two columns (e.g., Month and Sales), you suddenly need a two-dimensional array, and your loops become nested and even more complex.
' A nested loop for a two-dimensional array
For r = 1 To 12 ' Loop through rows
For c = 1 To 2 ' Loop through columns
MonthData(r, c) = Cells(r + 1, c).Value
Next c
Next r
4. Writing the Data Back: Finally, after all the processing, you need to write another loop to paste the results from your array back into the worksheet.
The Limitations of the VBA Approach
While effective for developers, this method is a nightmare for the average business user:
- Steep Learning Curve: You need to understand programming concepts like variables, data types, loops, and array dimensions. This is far beyond the scope of typical Excel training.
- Error-Prone: A simple typo, a wrong cell reference, or an incorrect array index can lead to the dreaded "Subscript out of range" error, which can be difficult to debug.
- Rigid and Inflexible: What if your manager asks a follow-up question? "Great, now can you only show me the months where sales were over $50,000?" You'd have to go back, modify your VBA code, debug it, and run it again. Quick, ad-hoc analysis is nearly impossible.
- Hard to Maintain: If you leave the company, will your replacement be able to understand and update your complex VBA scripts? Often, these custom solutions become "black boxes" that no one dares to touch.
The AI-Powered Solution: Excelmatic
Instead of becoming a programmer, what if you could just tell Excel what you want to do in plain language? This is exactly what Excel AI agents like Excelmatic are designed for. You can perform the same complex data processing tasks without writing a single line of code.

How to Process Data with Excelmatic: A Simple 4-Step Process
Let's solve the same monthly sales data problem using Excelmatic.
1. Upload Your Excel File Drag and drop your Excel or CSV file directly into the Excelmatic chat interface. The AI will instantly read your data and show you a preview. It understands rows, columns, and headers automatically.
2. Describe What You Want in Plain Language Instead of writing loops, just type your request. Start with the first task.
"For the 'Sales' column, create a new column named 'Forecasted Sales' where each value is the original sales multiplied by 1.2."
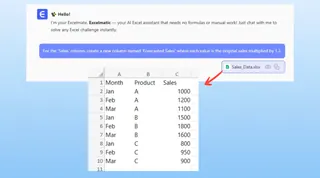
Excelmatic will process this request and generate the new column for you in seconds.
3. Iterate and Refine with Follow-up Questions Now, address your manager's other requests with simple follow-up prompts.
Okay, now filter the table to only show rows where 'Forecasted Sales' are greater than 50000.
Add a new column that calculates the percentage difference between 'Forecasted Sales' and 'Sales'.
Can you generate a pivot table that shows the total sales for each quarter?
Each command is executed instantly. This conversational approach allows for incredible flexibility and speed, turning a 30-minute coding task into a 30-second conversation.
4. Export Your Results Once you're happy with the result, you can download the newly transformed data as a new Excel file. You can also ask Excelmatic to provide the exact Excel formula it used, which you can copy and paste into your original workbook.
User vs. Excelmatic: A Dialogue Example
Here’s how a typical data processing conversation might look in Excelmatic, achieving what would require dozens of lines of VBA code.
User: I've uploaded my sales data. It has 'Month', 'Region', and 'Sales Amount' columns. First, can you create a new column called 'Sales with Tax' that is 'Sales Amount' * 1.08?
Excelmatic: Done. I've added the 'Sales with Tax' column with the calculated values. The updated table is ready. What's next?
User: Great. Now, I only want to see the data for the 'North' and 'West' regions. And please sort the results by 'Sales Amount' in descending order.
Excelmatic: I have filtered the data to include only the 'North' and 'West' regions and sorted the table as you requested. Is there anything else you'd like to do with this data?
User: Yes, please create a pivot table that shows the total 'Sales with Tax' for each region.
Excelmatic: I have generated the pivot table summarizing the total 'Sales with Tax' by region. You can view the pivot table configuration or download the result as a new Excel file.
Traditional VBA vs. Excelmatic: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Excel VBA Arrays | Excelmatic (Excel AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Complete | 30-60 minutes (including coding & debugging) | 1-2 minutes |
| Required Skill | VBA Programming, debugging, logic | Basic language skills, understanding the business need |
| Flexibility | Low. Changes require rewriting code. | High. Easily refine with follow-up questions. |
| Error Rate | High. Prone to syntax and logic errors. | Low. AI handles the logic and syntax. |
| Accessibility | Limited to developers and power users. | Accessible to anyone who can describe their goal. |
FAQ
1. Do I need to know any programming to use Excelmatic? No, not at all. Excelmatic is designed for business users, not programmers. If you can write an email or a text message describing what you need, you can use Excelmatic.
2. Will Excelmatic change my original file? No. Your original file is used for analysis in a secure, read-only environment. Any changes, calculations, or reports you generate can be downloaded as a new Excel file, leaving your original data untouched.
3. Is it safe to upload my company's data to Excelmatic? Excelmatic is built with enterprise-grade security. Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. For specific details on data privacy and security policies, always refer to the official website.
4. What if my data is messy or has inconsistent formatting? Excelmatic includes powerful data cleaning capabilities. You can ask it to "trim leading and trailing spaces," "convert the date column to a standard format," or "fill in the blank cells in the 'Region' column with 'N/A'."
5. Can I get the actual Excel formula from Excelmatic? Yes. In addition to performing the analysis, you can ask Excelmatic to "give me the Excel formula to do this," and it will provide a formula that you can copy and use in your own spreadsheets. This makes it a great tool for learning advanced Excel functions as well.
6. Is this replacing Excel? Not at all. Excelmatic is an AI assistant for Excel. It supercharges your workflow by automating the most tedious and complex parts, allowing you to get to the final result in Excel faster than ever before.
Get Started: Upgrade Your Excel Workflow Today
Stop spending hours trying to remember VBA syntax or debugging complex loops. The era of manual data processing in Excel is over. By embracing an Excel AI agent, you can shift your focus from how to do something in Excel to what you want to achieve.
You can save hours each week, reduce costly errors, and respond to data requests with unprecedented speed and flexibility.
Ready to see it in action? Try Excelmatic for free today and upload one of the spreadsheets you're currently working on. Use the prompts from this article as a starting point and experience the future of data analysis.








