Key Takeaways:
- Manually splitting data from single cells (like full names or addresses) into multiple columns is time-consuming and prone to errors, especially with inconsistent formatting.
- Excelmatic eliminates the need to memorize complex formula syntax by allowing you to split text using simple language commands like "split column A into first and last names".
- Compared to TEXTSPLIT, Excelmatic handles advanced scenarios like multiple delimiters and row splitting effortlessly, without requiring technical Excel expertise.
- For business professionals who need quick, accurate data cleaning for reports and analysis, AI tools provide a faster, more accessible alternative to manual formula writing.
When working with data, we often encounter information crammed into single cells—like names, addresses, and zip codes combined. Knowing how to efficiently split this data into multiple cells is an essential skill for every Excel user.
While this once required complex formula combinations, we now have more powerful tools available. This article introduces you to two approaches: Excel's built-in TEXTSPLIT() function, and a smarter, faster AI-powered solution.
Method 1: Using the Excel TEXTSPLIT() Function
The TEXTSPLIT() function is a powerful text processing tool in Excel that splits text strings into multiple cells based on specified delimiters. This makes it remarkably easy to extract specific information from single cells and distribute it across different columns or rows.
Understanding the TEXTSPLIT() Syntax
The TEXTSPLIT() function uses the following syntax:
=TEXTSPLIT(text, col_delimiter, [row_delimiter], [ignore_empty], [pad_with])
text: The text you want to split.col_delimiter: The character that separates columns.row_delimiter: (Optional) The character that separates rows.ignore_empty: (Optional) Set toTRUEto ignore empty values resulting from consecutive delimiters.pad_with: (Optional) The value to use for padding missing values.
Basic Splitting: Text to Columns
Let's start with the most common scenario: splitting a cell containing a full name into first and last names.
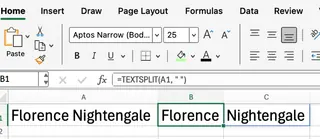
Suppose cell A2 contains the name "Florence Nightingale," and you want to place "Florence" and "Nightingale" into separate cells.
Use this formula:
=TEXTSPLIT(A2, " ")
Advanced Splitting: Text to Rows
Beyond column splitting, TEXTSPLIT() can also split text across multiple rows using the row_delimiter parameter.
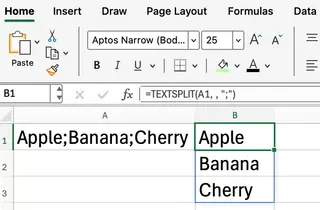
Suppose cell A1 contains a fruit list: "Apple;Banana;Cherry" and you want each fruit in a new row. Use this formula:
=TEXTSPLIT(A1, , ";")
Note that the second parameter (column delimiter) is left blank, while the semicolon serves as the row delimiter.
Complex Splitting: Handling Multiple Delimiters
Sometimes your data might use mixed delimiters. TEXTSPLIT() allows you to specify an array containing multiple delimiters.
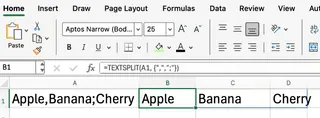
For example, if cell A4 contains text using both commas and semicolons as separators, you would write:
=TEXTSPLIT(A4, {",",";"})
Handling Empty Values
When text contains consecutive delimiters, TEXTSPLIT() might produce empty cells in the results. You can control this behavior using the ignore_empty parameter.
=TEXTSPLIT("A,,B", ",", , TRUE)
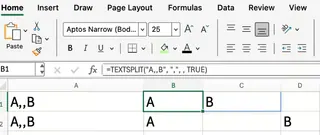
In the figure above, the formula in the first row has ignore_empty set to TRUE, skipping empty values, while the second row has it set to FALSE (or omitted), preserving empty cells.
Method 2: Using AI Tools Like Excelmatic

While the TEXTSPLIT() function is powerful, it requires remembering syntax and parameter usage. For users who prefer natural language interaction or want to handle complex tasks faster, AI tools offer a more intuitive solution.
Excelmatic is an Excel AI Agent that allows you to give instructions in everyday language, then automatically completes your data processing tasks.
Text Splitting with Excelmatic
Using Excelmatic for all the scenarios above is remarkably simple. You don't need to write any formulas—just tell it what you want.
Workflow:
- Upload your Excel file to Excelmatic.
- Type your request in plain language.
- Excelmatic delivers the results instantly.
Comparison with TEXTSPLIT()
Basic Splitting (Name Separation):
TEXTSPLIT():=TEXTSPLIT(A2, " ")- Excelmatic Instruction: "Split the full names in column A into first and last names in separate columns"
Splitting to Rows (Fruit List):
TEXTSPLIT():=TEXTSPLIT(A1, , ";")- Excelmatic Instruction: "Split cell A1 content by semicolons into separate rows"
Handling Multiple Delimiters:
TEXTSPLIT():=TEXTSPLIT(A4, {",",";"})- Excelmatic Instruction: "Split text in cell A4 using both commas and semicolons as delimiters"
Handling Empty Values:
TEXTSPLIT():=TEXTSPLIT("A,,B", ",", , TRUE)- Excelmatic Instruction: "Split the text in this column and ignore empty results"
The advantages of Excelmatic are clear:
- No Formula Memorization: You don't need to remember
TEXTSPLIT's complex syntax and parameters. - Natural Language Interaction: Complete tasks as if you're talking to an assistant, significantly reducing the learning curve.
- Intelligent Processing: The AI better understands your intent and can deliver ideal results even with inconsistently formatted data.
- Greater Efficiency: For users unfamiliar with formulas, typing a sentence is much faster than repeatedly debugging formulas.
More Advanced Usage Tips
Whichever method you choose, you can handle more complex scenarios by combining other functions:
TRIM(): Combine withTRIM()(or add "remove extra spaces" to your Excelmatic instruction) to clean up unnecessary spaces in split results.SEQUENCE(): Combine withSEQUENCE()to dynamically reference split results.TEXTJOIN(): UseTEXTJOIN()to recombine split data.
For Excelmatic users, these multi-step operations can often be completed with one more complex instruction, such as: "Split the names in column A into two columns, then join them with '-' and remove all spaces."
Conclusion
In Excel, the TEXTSPLIT() function is a powerful native tool for text splitting tasks, especially suitable for users comfortable with Excel formulas.
However, with advances in AI technology, tools like Excelmatic offer a faster, more intuitive solution. By allowing you to use plain language, it removes the need to memorize syntax and debug complex formulas.
Ready to simplify your data cleaning? Try Excelmatic today and experience the ease of splitting text with simple language commands.
Next time you need to split cell text, choose the method that best suits your habits and the complexity of your task.