Key Takeaways:
- Manually combining text in Excel with
&orCONCATENATEis time-consuming and error-prone, especially when dealing with delimiters and blank cells across multiple cells. - Excelmatic eliminates the need to learn complex formula syntax by allowing you to combine text using simple language commands like "join columns A, B, and C with commas".
- Compared to TEXTJOIN, Excelmatic handles advanced scenarios like conditional joining and unique value listing without requiring nested functions or technical expertise.
- For business professionals who need quick, accurate text merging for reports and data cleaning, AI tools provide a faster, more accessible alternative to manual formula writing.
Building well-formatted text from Excel data is a common need, but stringing values together can get messy. Manually adding delimiters and dealing with empty cells is time-consuming and error-prone. Fortunately, modern solutions have made this task much easier.
In this guide, we'll explore two powerful approaches to combining text in Excel. First, we'll dive into the TEXTJOIN() function, a huge leap forward from older methods. Then, we'll introduce an even simpler, AI-powered alternative, Excelmatic, which lets you accomplish the same tasks using plain language. By the end, you'll have a clear picture of which method best suits your workflow.
Method 1: The Modern Formula Approach with TEXTJOIN()
Let's start with Excel's best built-in tool for the job: the TEXTJOIN() function. It's flexible, powerful, and a massive upgrade over its predecessors.
How Excel TEXTJOIN() Works
At its core, TEXTJOIN() lets you join text values from multiple cells, inserting a consistent delimiter (like a comma or space) between them. Unlike older functions, it can process a full range at once and gives you the option to ignore blank cells.
Here’s the syntax:
=TEXTJOIN(delimiter, ignore_empty, text1, [text2], ...)
delimiter: The character(s) you want between each piece of text (e.g., ", ", " | ", etc.).ignore_empty:TRUEto skip blank cells,FALSEto include them.text1, [text2], …: The cells, ranges, or text values you want to combine.
For example, suppose you have values in A1, B1, and C1. You want to join them with commas while skipping any blanks:
=TEXTJOIN(",", TRUE, A1:C1)
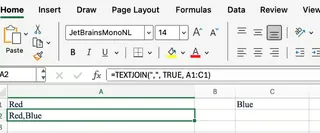
If B1 is empty, the result will be the values from A1 and C1, separated by a single comma. This simple feature is a game-changer.
TEXTJOIN() vs. CONCATENATE() vs. CONCAT()
If you've used CONCATENATE() or CONCAT(), you might wonder why you’d switch. Here's a quick comparison:
TEXTJOIN(): The most advanced. Lets you specify a delimiter for an entire range and can automatically skip blanks.CONCAT(): A newer function that can join ranges, but you can’t specify a delimiter automatically and it doesn't skip blanks.CONCATENATE(): The oldest option. It forces you to select each cell individually and has no built-in delimiter or blank-skipping features.
Let’s join values in B1, C1, and D1 with a semicolon. See how the formulas differ:
=TEXTJOIN(";", TRUE, B1:D1)
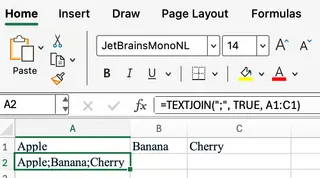
With CONCAT() or CONCATENATE(), you have to add the delimiter manually between each cell reference, making the formula long and cumbersome:
=B1 & ";" & C1 & ";" & D1
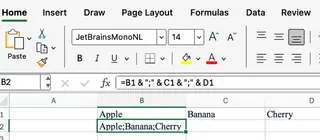
The advantage of TEXTJOIN() is clear: it’s cleaner, shorter, and far more efficient, especially when dealing with many cells or potential blanks.
Method 2: The AI-Powered Approach with Excelmatic

While TEXTJOIN() is a fantastic formula, what if you could skip formulas altogether? This is where AI tools like Excelmatic come in. Excelmatic is an AI agent that understands plain language commands, allowing you to perform complex tasks without writing a single formula.
The process is simple:
- Upload your Excel file to Excelmatic.
- Type your request in plain language.
- Excelmatic delivers the results instantly.
Let's revisit the same scenarios and see how Excelmatic handles them.
Basic Text Joining with Excelmatic
Remember our first example of joining A1, B1, and C1 with a comma, skipping blanks? Instead of writing =TEXTJOIN(",", TRUE, A1:C1), you would simply tell Excelmatic:
For each row, combine the text from columns A, B, and C into a new column named 'Combined'. Use a comma and a space as the separator. Ignore any empty cells.
Excelmatic processes this request and generates the new column for you, perfectly formatted. There's no syntax to remember and no risk of a #VALUE! error.
Handling Custom Delimiters and Complex Logic
What about more complex scenarios? Let's look at building dynamic summaries. In the original article, we used a combination of TEXTJOIN and FILTER to list survey responses:
Formula Method: =TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, FILTER(F2:J2, F1:J1="Yes"))
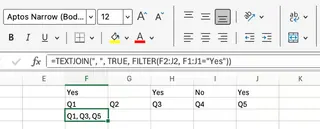
This formula is powerful but requires knowledge of dynamic arrays and nested functions.
Excelmatic Method: The instruction is far more intuitive.
Create a summary column. For each row, list the column headers from F to J where the cell value is 'Yes'. Separate the headers with a comma and a space.
Excelmatic understands the conditional logic and generates the summary without you needing to figure out how to nest FILTER inside TEXTJOIN.
Similarly, for creating clean shipping address labels from data with potential blanks:
Formula Method: =TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, H1:L1)
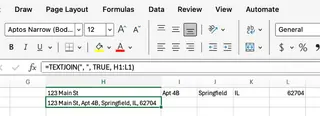
Excelmatic Method:
Combine columns H through L into a single address line. Separate each part with a comma and a space, and make sure to skip any blank cells.
The AI handles the "ignore empty" logic automatically based on the natural language instruction.
Head-to-Head: TEXTJOIN() vs. Excelmatic
| Feature | TEXTJOIN() Function |
Excelmatic (AI Agent) |
|---|---|---|
| How it Works | Formula-based; requires learning syntax and arguments. | Prompt-based; uses natural language instructions. |
| Learning Curve | Moderate. Need to remember argument order and how to nest with other functions. | Minimal. If you can describe what you want, you can use it. |
| Complexity | Becomes complex quickly. Requires nesting FILTER, UNIQUE, SORT for advanced tasks. |
Handles complex logic with simple sentences. No nesting required. |
| Flexibility | Limited to the function's defined parameters. | Highly flexible. Can combine joining with sorting, filtering, and other data transformations in one step. |
| Best For | Users comfortable with Excel formulas who need dynamic, in-cell results that update automatically. | Users who want fast, accurate results without writing or debugging formulas, especially for data cleaning and reporting. |
Advanced Scenarios Made Simple
As you get more comfortable with either method, you can tackle more advanced tasks. With formulas, this often means combining TEXTJOIN with UNIQUE, FILTER, or SORT.
For example, to create a comma-separated list of unique product categories from a range:
Formula Method: =TEXTJOIN(", ", TRUE, UNIQUE(TRANSPOSE(A1:E1)))
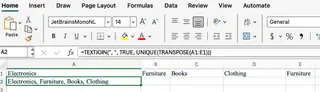 Note: This formula requires
Note: This formula requires TRANSPOSE because UNIQUE works on columns by default.
Excelmatic Method: This complexity disappears.
From the range A1:E1, find all the unique values, and list them in a single cell, separated by a comma and a space.
The AI handles the orientation, uniqueness, and joining all in one go.
Conclusion: Choose the Right Tool for the Job
If you're still using CONCATENATE() or manually stringing cells together with &, switching to the TEXTJOIN() function will save you a significant amount of time and frustration. It’s a powerful, modern function that is essential for anyone serious about mastering Excel formulas. Learning it helps you think in ranges, a skill that pays off across all of Excel's newer features.
However, if your goal is to get from question to answer as quickly as possible, an AI tool like Excelmatic represents the next frontier. It removes the burden of remembering syntax and debugging formulas, allowing you to focus on your data, not on the mechanics of Excel. By simply describing what you need, you can perform text combinations and other complex data manipulations with unparalleled speed and ease.
Ready to streamline your text combining workflow? Try Excelmatic today and experience the ease of merging data with simple language commands—no formulas required.
Both are excellent solutions. The best one for you depends on your comfort with formulas and the complexity of your task. Why not give both a try and see how they can revolutionize your workflow?