Key Takeaways
- Timestamps are essential for tracking sales, monitoring project progress, and logging data updates, but manual methods are time-consuming
- Excelmatic's AI approach lets you generate dates, times, and complex calculations using simple language commands instead of memorizing formulas
- Compared to traditional functions, Excelmatic handles both simple timestamps and advanced time-based logic with greater speed and accuracy
- For business users, adopting AI tools means focusing on data insights rather than technical Excel complexities
Working with dates and times is a fundamental part of many spreadsheets, from project plans to sales logs. You might need to timestamp new entries, calculate deadlines, or simply display the current time on a dashboard. In this guide, we'll explore two powerful ways to accomplish this: the traditional formula-based approach and a modern, AI-powered solution.
We'll start with Excel's classic NOW() function, then show you how an AI tool like Excelmatic can achieve the same results faster and more intuitively.
Method 1: The Traditional Approach with the Excel NOW() Function
The NOW() function in Excel is designed to return the current date and time based on your system clock. It's a go-to tool for time-stamping data, tracking changes, or creating dynamic reports that update automatically.
How Excel NOW() works
When you enter the NOW() function in a cell, Excel displays the current date and time. The value updates every time the worksheet recalculates. Because it's always recalculating, NOW() is best for cases where real-time values are useful or required, like in dashboards, clocks, or in combination with other time-sensitive formulas.
Syntax for Excel NOW()
The syntax for the NOW() function is straightforward as it does not require any arguments.
=NOW()
After entering the formula, press Enter to display the current date and time.
Formatting the Result of Excel NOW()
By default, Excel may display the result as a date and time or just a date, depending on your cell formatting. You can always see how it looks and then change the display format if you want something different.
To format the cell:
- Select the cell with the
NOW()formula - Press Ctrl+1 to open the Format Cells dialog box
- Choose Date, Time, or Custom to get the exact format you need.
Combining Excel NOW() with Other Functions
The real power of NOW() comes from combining it with other Excel functions. For example, to calculate the number of days between now and a future date in cell A2, you can subtract NOW() from the future date.
=A2 - NOW()
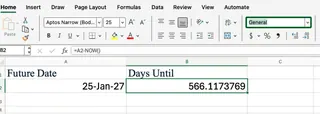
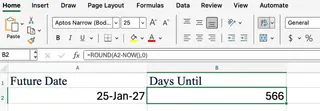
This formula returns the difference in days (and fractions of days). You can use the Excel ROUND() function to clean this up and show only the whole number of days.
You can also combine NOW() with the IF() function to create alerts. For instance, if you have a due date in cell A2, you can check if it's overdue with this formula:
=IF(NOW()>A2, "Past Due", "On Time")
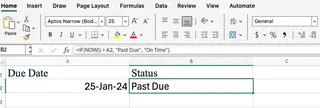
This formula compares the current date and time to the value in A2. If the due date has passed, it returns "Past Due"; otherwise, it shows "On Time."
Method 2: The AI-Powered Approach with Excelmatic
Remembering function names, syntax, and how to nest them correctly can be time-consuming. This is where an AI Excel Agent like Excelmatic changes the game. Instead of writing formulas, you simply describe what you want in plain language.

Excelmatic handles a wide range of tasks, from data analysis and charting to formula generation. For date and time calculations, it acts as your personal Excel expert.
Let's see how Excelmatic handles the same tasks we just performed with NOW(). After uploading your file, you could simply ask:
- To insert the current time: "Put the current date and time in cell B2."
- To calculate remaining days: "In column C, calculate the number of days between the date in column A and today."
- To create a status alert: "In column D, if the date in column A is before today, write 'Past Due'. Otherwise, write 'On Time'."
Excelmatic interprets your request and instantly applies the correct formulas or values to your sheet, saving you the effort of writing and debugging them yourself.
Comparing the Methods: NOW() vs. Excelmatic
| Feature | Excel NOW() Function |
Excelmatic (AI Agent) |
|---|---|---|
| How it Works | Manual formula entry (=NOW()). |
Natural language prompt (e.g., "add a timestamp"). |
| Ease of Use | Requires knowledge of function syntax and how to combine it with others. | Highly intuitive. Just describe your goal in plain language. |
| Speed | Fast for simple tasks, but complex nested formulas can be slow to write. | Extremely fast for both simple and complex requests. |
| Use Cases | Great for users comfortable with formulas who need dynamic, auto-updating cells. | Ideal for users who want to get results quickly without memorizing functions. |
| Flexibility | Full control over the formula, but limited by user's knowledge. | Handles a wide range of tasks beyond just dates, including analysis and charts. |
Updating, Recalculating, and Limitations
Both methods have unique characteristics you should be aware of.
The NOW() Function
- Volatility:
NOW()is a volatile function, meaning it updates every time the worksheet recalculates (e.g., when you open the file or enter new data). This is great for a live clock but problematic if you need a static timestamp. For a fixed date or time, use the shortcuts Ctrl + ; (date) or Ctrl + Shift + ; (time). - System Clock Dependency: The function relies on your computer's system clock. If your system time is incorrect, the output will be too.
Excelmatic
- Clarity over Volatility: When you ask Excelmatic to insert a timestamp, it can either insert a static value or generate the
NOW()function, depending on your request. You can be specific: "Insert a static timestamp in C2" versus "Make C2 always show the current time." This gives you direct control over volatility. - System Clock Dependency: Like the
NOW()function, Excelmatic's time-based calculations will rely on the underlying system clock.
Conclusion
The Excel NOW() function is a reliable and powerful tool for adding dynamic date and time information to your spreadsheets, especially if you enjoy working with formulas. It gives you precise control and is built directly into Excel.
However, for those who want to work faster and more intuitively, an AI agent like Excelmatic offers a clear advantage. By translating plain English requests into accurate results, it eliminates the need to memorize formulas and lets you focus on your data, not on the technicalities.
The best method depends on your workflow. For quick, dynamic updates, NOW() is excellent. For complex tasks or a more streamlined, conversation-driven experience, Excelmatic's AI-powered approach is the modern way forward.
Ready to transform how you work with Excel? Try Excelmatic today and experience the power of AI-driven spreadsheet management.






