Key takeaways:
- Traditional two-way and approximate lookups in Excel require complex, nested formulas like
VLOOKUP(INDEX(MATCH(...), MATCH(...)), ...)which are difficult to build, read, and debug. - Excel AI tools like Excelmatic replace these convoluted formulas with simple, natural language questions, allowing you to ask directly for the information you need from multiple tables.
- Using Excelmatic dramatically reduces the time spent on lookup tasks from minutes or hours to seconds, eliminates formula errors, and makes data analysis more flexible and accessible to all users.
Problem Background & Pain Points
Imagine you're an analyst managing a simple dashboard. You have two tables in your Excel sheet. The first is a 5-day temperature forecast for several international cities. The rows are cities (London, Paris, Tokyo) and the columns are days (Day 1, Day 2, etc.). The second table is a simple "outlook key" that translates a temperature range into a descriptive text, like 0-10°C is "Cold", 11-20°C is "Mild", and so on.
The request from your manager seems simple: "Create a tool where I can select a city and a day, and it instantly tells me the weather outlook."
This "simple" request is the start of a classic Excel headache. You immediately realize it's a two-step problem:
- First, you need to find the specific temperature by looking up a value in both a row and a column simultaneously (a two-way lookup).
- Second, you need to take that temperature and find where it falls within the ranges of your outlook key (an approximate match lookup).
For anyone who's spent time in Excel, the words "nested formulas," "INDEX/MATCH," and "VLOOKUP with approximate match" start flashing in your mind. It's doable, but it's tedious, error-prone, and creates a formula that is nearly impossible for a colleague to understand without a detailed explanation. What if a city is added? What if the day format changes? The formula breaks. This is where the manual Excel approach shows its limits.
The Traditional Excel Solution: Steps and Limitations
To solve this problem manually, you need to master and combine several advanced Excel functions. The final formula is a testament to Excel's power, but also its complexity.
Here's the typical step-by-step process:
Step 1: Perform the Two-Way Lookup with INDEX/MATCH
First, you need to retrieve the correct temperature from the forecast matrix. VLOOKUP alone can't do this, as it only looks up based on a single column. The standard solution is a combination of INDEX and MATCH.
INDEX(array, row_num, [column_num]): This function returns a value from a table or range (thearray) at a specified row and column number.MATCH(lookup_value, lookup_array, 0): This function finds the position of alookup_valuewithin a range (lookup_array). The0ensures an exact match.
You use MATCH twice: once to find the row number for the selected city, and a second time to find the column number for the selected day.
In the worksheet shown, the temperature forecast table is in B2:F8, with city names in A2:A8 and days in B1:F1. An "Outlook Key" table in H2:I7. To retrieve a temperature, you would set up input cells for city and day selection—for example, in cells J11 and J12 (or another available cell within columns A-J). The formula would be:
=INDEX(B2:F8, MATCH(J11, A2:A8, 0), MATCH(J12, B1:F1, 0))
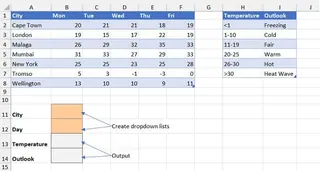
This formula correctly finds the temperature, but we're only halfway there.
Step 2: Perform the Approximate Match Lookup with VLOOKUP
Now you have the temperature (e.g., 22°C). You need to find its corresponding outlook from the "Outlook Key" table in H2:I7. For this, use VLOOKUP with its range_lookup argument set to TRUE for an approximate match:
=VLOOKUP(temperature, H2:I7, 2, TRUE)
Important: For this to work, the first column of your lookup table (the temperature thresholds in column H) must be sorted in ascending order.
Step 3: Nest the Formulas and Face the Complexity
To get the final answer in one cell, nest the INDEX/MATCH formula from Step 1 inside the VLOOKUP formula from Step 2:
=VLOOKUP(INDEX(B2:F8, MATCH(J11, A2:A8, 0), MATCH(J12, B1:F1, 0)), H2:I7, 2, TRUE)
This formula works. But it has significant limitations:
- Hard to Read and Debug: If you get a
#N/Aor#REF!error, good luck finding the source. Is it the rowMATCH? The columnMATCH? TheVLOOKUPrange? - Fragile: If someone inserts a row or column, or if the lookup table isn't sorted correctly, the formula breaks silently, often giving a wrong answer instead of an error.
- High Learning Curve: Explaining this to a junior team member or a non-technical manager is a challenge in itself. It creates a knowledge silo.
- Inflexible: What if your manager now asks, "Which city is the hottest on Day 3?" or "Show me the outlook for all cities on Friday." Your carefully constructed formula is useless for these ad-hoc questions. You have to start over.
The New Solution: Using Excel AI (Excelmatic)
Instead of building a complex chain of functions, what if you could just describe the outcome you want in plain language? This is exactly what Excel AI Agents like Excelmatic are designed for. You upload your file and start a conversation with your data.

Here’s how you’d solve the exact same problem in a fraction of the time with Excelmatic.
Step 1: Upload Your Data File
First, you simply upload your Excel workbook containing the two tables—the temperature forecast and the outlook key—to Excelmatic. It accepts .xlsx, .csv, and other common formats. The AI will instantly read and understand the structure of your data.
Step 2: Describe Your Desired Result in Natural Language
Instead of writing a formula, you type your question into the chat interface. You can be as specific or as broad as you like.
For the original problem, you could ask:
I have a forecast table and an outlook key. For Paris on Day 4, what is the weather outlook?
Or, to get both pieces of information:
Using both tables, find the temperature for London on Day 3 and then tell me its corresponding outlook.
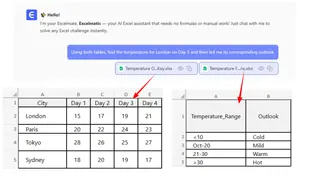
Step 3: Get an Instant Answer and Iterate
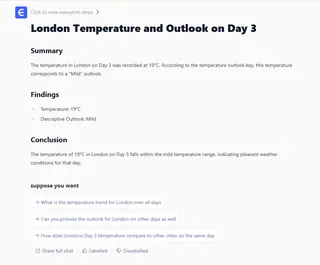
Excelmatic's AI doesn't just spit out a number. It understands the two-step logic of your request, performs the two-way lookup, finds the approximate match, and gives you the final, human-readable answer.
It might respond with: "The weather outlook for Paris on Day 4 is 'Pleasant'."
The real power comes from iteration. You can continue the conversation to explore your data further, something that is incredibly cumbersome with static formulas.
- "What is the outlook for every city on Day 5?"
- "Which city has the highest temperature on Day 2?"
- "Create a new table that shows the outlook, not the temperature, for all cities across all 5 days."
Excelmatic will generate these results—whether it's a simple text answer, a new summary table, or a chart—on the fly.
Step 4: Export Your Results
Once you have the answer or the new table you need, you can download it as a new Excel file with a single click. The generated data is clean, accurate, and ready to be shared or used in a report. You can also ask Excelmatic to generate a formula for you if you need to place it in an existing workbook.
Dialogue Example
Here’s how a typical conversation with Excelmatic might look to solve this problem:
User: I've uploaded my file with a temperature forecast grid and an outlook reference table. Can you help me figure out the outlook for a specific city and day?
Excelmatic: Of course. Which city and day are you interested in?
User: Let's start with Tokyo on Day 5.
Excelmatic: The forecasted temperature for Tokyo on Day 5 is 28°C. Based on your outlook reference table, this corresponds to a "Hot" outlook.
User: Perfect! Now, could you create a new table that replaces all the temperatures in the original forecast with their corresponding outlooks? I want to see the full week's outlook for all cities.
Excelmatic: Done. I have generated a new table with cities as rows and days as columns, where each cell contains the correct weather outlook. You can view it now or download it as an Excel file.
Traditional Formulas vs. Excelmatic: A Quick Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Excel (INDEX/MATCH/VLOOKUP) | Excelmatic (AI Agent) |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Solve | 10-20 minutes (for an expert) | < 1 minute |
| Required Skill | Expert-level knowledge of nested functions | Ability to describe the problem in language |
| Flexibility | Very low. Formula is rigid and single-purpose. | Very high. Ask follow-up questions easily. |
| Error Rate | High risk of syntax, range, or logic errors. | Low. AI handles the complex logic internally. |
| Maintainability | Difficult. Hard to understand and update. | Effortless. Just ask a new question. |
FAQ
1. Do I need to know INDEX/MATCH to use Excelmatic for this kind of lookup? No, not at all. You only need to describe what you're trying to find. The AI handles the complex lookup logic for you, whether it's a two-way, approximate, or even multi-table lookup.
2. Is my company's data secure when I upload it to Excelmatic? Data privacy and security are top priorities. Excelmatic uses secure protocols for data transfer and processing. For specific details on data handling and encryption, always refer to the official privacy policy on the website. Your data is not used for training models.
3. What if my table headers or data aren't perfectly clean? Excelmatic's AI is designed to be robust and can often interpret messy or inconsistent headers (e.g., "Day 1" vs. "Day_1"). However, for best results, it's always good practice to have clear and descriptive column names.
4. Can Excelmatic generate the complex formula for me to use in my own sheet?
Yes. While Excelmatic can perform the analysis directly, you can also ask it to "write an Excel formula to do this." It can generate the INDEX/MATCH or XLOOKUP formula for you to copy and paste into your own workbook, acting as an expert formula-writing assistant.
5. How is this different from just using XLOOKUP?
XLOOKUP is a fantastic and powerful function that simplifies many lookup scenarios compared to VLOOKUP or INDEX/MATCH. However, it's still a formula. You need to understand its syntax and how to nest it for two-way lookups. Excelmatic removes the need to write any formula, making the process faster and accessible to users of all skill levels.
Take Action: Upgrade Your Excel Workflow Today
Every minute you spend wrestling with a complex, nested formula is a minute you're not spending on actual analysis and decision-making. The INDEX/MATCH combination is a powerful tool, but it represents an older, more manual way of working with data.
By embracing an Excel AI agent like Excelmatic, you can offload the tedious mechanics of data retrieval and focus on the "what" and "why" behind your data. Instead of debugging a formula, you can be asking your next critical business question.
Ready to stop memorizing formulas and start having a conversation with your data? Try Excelmatic for free today. Upload the very spreadsheet you're struggling with and ask it the question you're trying to answer. You might be surprised at how simple your most complex problems can be.






