Key takeaways:
- Traditional Excel loan calculations require memorizing complex functions like PMT, IPMT, and PPMT, and manually adjusting interest rates and periods, which is time-consuming and prone to error.
- Excel AI tools like Excelmatic replace these manual formulas. You can simply ask in natural language, "What's the monthly payment for a $30,000 loan over 5 years at 5% interest?"
- Using Excelmatic not only provides instant, accurate answers but also allows for effortless scenario analysis ("what if the interest rate was 6%?") and can even generate full amortization schedules on command, drastically improving efficiency.
Problem Background & Pain Points
Whether you're planning for a new car, a home mortgage, or a business loan, one of the first questions you'll ask is: "What will my monthly payment be?" Excel is the go-to tool for millions to answer this question. You open a spreadsheet, ready to build a simple calculator.
But this is where the trouble often begins. You need to figure out your payments based on the loan amount (present value), the interest rate, and the number of payment periods. You might vaguely remember there's a function for this, but what is it? PAYMENT? LOAN? After a quick search, you find it: PMT.
Then you're faced with its syntax: =PMT(rate, nper, pv, [fv], [type]). Suddenly, your "simple" task involves deciphering cryptic abbreviations. The biggest trap lies in the details. Your bank quotes an annual interest rate, but you're making monthly payments. Your loan term is in years, but the formula needs the total number of months. You must remember to divide the rate by 12 and multiply the years by 12.
Forgetting this single step can lead to a wildly incorrect payment amount, turning your financial planning into a financial disaster. What if you also want to see how much of each payment goes to interest versus principal? That requires two more functions, IPMT and PPMT, each with its own syntax and quirks. This complexity is frustrating, time-consuming, and a major source of errors for even experienced Excel users.
The Traditional Excel Solution: Steps & Limitations
In the conventional approach, you would set up a small table in Excel to hold your loan parameters and then manually construct the financial formulas.
Let's say you want to calculate the monthly payment for a $12,000 car loan at an annual interest rate of 6.49% over three years.
Step 1: Set Up Input Cells
You would create labels and input your data, perhaps like this:
B1: 12000 (Loan Amount)B2: 3 (Term in Years)B3: 6.49% (Annual Interest Rate)
Step 2: Write the PMT Formula
In another cell, you'd write the PMT formula. Here, you must manually convert the annual rate and yearly term into monthly figures.
The formula would be: =PMT(B3/12, B2*12, B1)
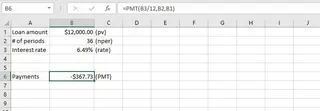
This formula calculates the monthly payment. The result is negative because it represents a cash outflow (a payment you make).
Step 3: Calculate Interest and Principal (IPMT & PPMT)
If you want to know how much of your first payment is interest, you need the IPMT function:
=IPMT(B3/12, 1, B2*12, B1)
The 1 here specifies you're looking at the first period. To find the principal portion, you'd use PPMT:
=PPMT(B3/12, 1, B2*12, B1)
Step 4: Build a Full Amortization Schedule
To see the breakdown for the entire loan, you'd have to create a table with 36 rows (one for each month). You'd write the IPMT and PPMT formulas in the first row, carefully using absolute references (e.g., $B$3/12) for the loan details and a relative reference for the period number. Then, you would drag the formulas down all 36 rows.
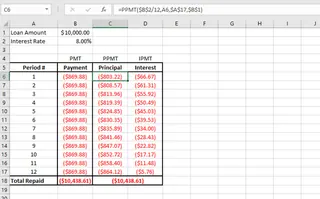
Limitations of the Traditional Method
While powerful, this manual approach is fraught with challenges:
- High Cognitive Load: You must know and remember the syntax for
PMT,IPMT, andPPMT, including the order and meaning of each argument. - Highly Error-Prone: The manual conversion of annual rates and yearly terms to monthly figures (
/12,*12) is the most common point of failure. A simple mistake here invalidates all your calculations. - Rigid and Inflexible: Want to see what happens if the term is 5 years instead of 3? You have to change the input and potentially rebuild your entire amortization table. It’s not built for quick "what-if" analysis.
- Time-Consuming: Building a full amortization schedule with charts is a tedious, multi-step process involving careful formula construction, absolute/relative referencing, and drag-and-fill operations.
- Not Intuitive: The formulas themselves are not self-explanatory. A colleague looking at your sheet might have no idea what
=PMT(B3/12, B2*12, B1)actually represents without dissecting it.
The New Solution: Using an Excel AI Agent (Excelmatic)
Instead of being a formula expert, what if you could just ask Excel for what you need? This is exactly what Excel AI agents like Excelmatic enable. You can describe your financial scenario in plain language, and the AI handles the complex formulas, conversions, and table generation for you.

The Overall Idea
Excelmatic acts as your personal data analyst. You upload your spreadsheet (or even start with a blank canvas), and then begin a conversation. You ask questions, and it provides answers, generates formulas, creates pivot tables, and builds charts directly. It completely removes the need to memorize function syntax.
Step-by-Step: Calculating Loan Payments with Excelmatic
Let's revisit the same car loan scenario: a $12,000 loan, 6.49% annual rate, over 3 years.
1. Upload Your Data (Optional)
You can start by simply opening Excelmatic and asking your question directly. If you have a file with different loan options you're comparing, you can upload that Excel or CSV file.
2. Describe Your Request in Natural Language
This is where the magic happens. Instead of writing a formula, you just type your question in the chat box. Here are a few examples:
To calculate the monthly payment:
What is the monthly payment for a $12,000 loan over 3 years with a 6.49% annual interest rate?
To find the interest portion of a payment:
For that same loan, how much of the first month's payment is interest?
To build a full amortization schedule:
Create a full amortization schedule for a $12,000 loan at 6.49% annual interest over 3 years. Show the interest and principal paid each month.
To work backward (PV function):
If I can afford a $400 monthly payment, what's the maximum loan I can get for 5 years at a 5% annual interest rate?
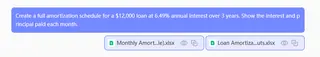
3. Review and Iterate on the Results
Excelmatic will instantly process your request and provide the answer. It will often show you the exact Excel formula it used (=PMT(...)), giving you full transparency. But the real power lies in the conversational follow-up. You can continue to refine your analysis:
- "What if the interest rate was 7.5% instead?"
- "Now show me the same table but for a 5-year term."
- "Create a chart that compares the principal vs. interest payments over the life of the loan."
4. Export Your Results
Once you have the analysis you need—whether it's a single number, a formula, or a full table—you can download it as a new Excel file or copy the results to use in your existing workbooks.
Dialogue Example
Here’s how a typical conversation with Excelmatic might look:
User: I'm considering a mortgage for $350,000. The term is 30 years and the annual interest rate is 6.5%. Can you tell me the estimated monthly payment?
Excelmatic: Certainly. The estimated monthly payment for a $350,000 loan over 30 years at a 6.5% annual rate is approximately $2,212.33. I calculated this using the formula =PMT(6.5%/12, 30*12, 350000).
User: Great. Can you generate a full amortization table for the first 5 years of the loan? I want to see the beginning balance, payment, interest, principal, and ending balance for each month.
Excelmatic: Of course. I have created a table with 60 rows, showing the complete amortization schedule for the first 5 years of your mortgage. The table is ready for you to view or download. Would you like me to visualize how the principal and interest payments change over this period?
User: Yes, add a stacked area chart for that.
Excelmatic: Done. I've added a stacked area chart below the table, visualizing the breakdown of your payments. You can now download the Excel file containing both the schedule and the chart.
Traditional Method vs. Excelmatic: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Excel (Manual) | Excelmatic (Excel AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Write formulas like PMT, IPMT, PPMT |
Ask questions in plain language |
| Time to Result | 5-20 minutes for a full schedule | < 1 minute |
| Error Risk | High (due to manual unit conversions) | Very Low (AI handles conversions automatically) |
| Flexibility | Low (rebuilding required for new scenarios) | High (effortless "what-if" analysis via chat) |
| Learning Curve | Steep (requires memorizing function syntax) | Minimal (if you can ask a question, you can use it) |
FAQ
1. Do I need to know the PMT function to use Excelmatic for loan calculations?
No. You don't need to know any specific Excel function names. Just describe what you want to calculate (e.g., "monthly loan payment"), and Excelmatic will use the correct function behind the scenes.
2. Will Excelmatic automatically handle the conversion from annual rates to monthly payments?
Yes. Excelmatic understands the context of your request. When you mention an "annual interest rate" and ask for a "monthly payment," it automatically performs the necessary conversions (rate/12 and term*12).
3. Can Excelmatic create a full amortization schedule table for me? Absolutely. Simply ask it to "create an amortization schedule" and provide the loan details. It will generate a complete table with all the necessary columns.
4. What if my loan has a down payment? How do I ask that? You can include the down payment directly in your question. For example: "Calculate the monthly payment for a $40,000 car with a $5,000 down payment, over 5 years at 6% interest." The AI will correctly calculate the loan principal as $35,000.
5. Is my financial data safe when I upload it to Excelmatic? Excelmatic is built with security as a priority, employing enterprise-grade security standards to protect your data. For specific details, you can always refer to the official privacy policy and security documentation on the website. Your data is not used for training models.
6. Can I use Excelmatic for investment calculations, not just loans? Yes. The same principles apply. You can ask questions about savings goals, future value of investments, and more. For example: "If I invest $500 a month for 10 years with an average annual return of 8%, how much will I have?"
Take Action: Upgrade Your Excel Workflow Today
Stop wasting time wrestling with complex financial formulas and worrying about manual conversion errors. The hours spent building and debugging loan calculators in Excel could be reduced to mere seconds.
By continuing with the traditional method, you're not just losing time; you're also missing out on the flexibility to quickly explore different financial scenarios and make better-informed decisions.
With an Excel AI agent like Excelmatic, you can turn complex financial analysis into a simple conversation. Get instant, accurate answers and generate complete reports effortlessly.
Ready to see for yourself? Try Excelmatic for free today. Upload a spreadsheet or just start asking questions—you can even copy and paste the prompts from this article to get started.






