Key Takeaways
- Data entry errors and inconsistencies disrupt business analysis, leading to poor decision-making and wasted resources
- Excel's traditional Data Validation requires complex setup and technical knowledge that most business users don't have
- Excelmatic's AI instantly validates and cleans data with simple language commands, eliminating complex rule setup and technical barriers
- Combining proactive validation with Excelmatic's AI auditing provides the most comprehensive approach for ensuring data quality in business workflows
Understanding and implementing data validation principles is essential for junior data analysts and seasoned specialists alike. Ensuring your data is accurate and consistent is the bedrock of reliable analysis. In this guide, we'll explore two powerful approaches to achieving this in Excel: the classic, rule-based Data Validation feature and Excelmatic's modern, AI-powered method for instant auditing.
What Is Data Validation?
Data validation is the process of checking the accuracy and consistency of data. The goal is to ensure that any data entered into a spreadsheet conforms to specific, predefined criteria. These criteria can include the correct data type (e.g., number, text, date), values within a specified range, or elements with an appropriate length.
Essentially, it's about maintaining data quality from the very beginning or cleaning it up after the fact.
Why Is Data Validation So Important?
Robust data validation is a must for many reasons. It safeguards against data entry errors and ensures that the information used in analyses is reliable and valid. Let's take a closer look at the main reasons for data validation.
Data quality
Data validation prevents inaccurate or inconsistent values from being stored. This reduces eventual errors, increases overall data quality, and enhances the meaningfulness of data analysis.
The importance of high-quality data is perfectly encapsulated in the GIGO concept, which is popular in computer science and stands for garbage-in, garbage-out. Essentially, analyzing flawed data leads to erroneous and misleading results.
Let's see some examples where a lack of validation could lead to weird values:
- University Records: A university can't have a decimal number of students; only whole numbers are valid.
- Medical Records: A person's maximum body temperature can't be higher than 50°C.
- Age Entries: An age field should only accept realistic values, typically between 0 and 120.
- Email Addresses: An email field should follow a specific format, which includes an '@' symbol.
- Inventory Counts: Product quantities in an inventory system should not be negative.
Remember that while data validation ensures data integrity, it doesn't guarantee absolute correctness. For example, a validation rule can ensure only "cat" or "dog" entries are allowed, but it can't prevent a cat from being labeled as a dog by mistake.
Data integrity and compliance
Data validation is crucial for maintaining data integrity and ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards.
In healthcare, compliance with HIPAA is mandatory to protect patient information. Similarly, businesses operating in the EU must adhere to GDPR, ensuring data privacy and security for individuals.
Data cleaning and preprocessing
A famous principle states that data analysts spend approximately 80% of their time on getting data ready for use and only 20% on the analysis itself. Because data analysts often spend a disproportionate amount of their time cleaning and preprocessing data, effective validation methods applied early in the workflow can save countless hours.
Decision making
Analyzing validated data leads to reliable and insightful findings that, in turn, help make more informed data-driven decisions. In the long run, data validation saves the time and money of the company and results in a healthier, more cost-efficient, and profitable business.
Ensuring Data Quality: Two Modern Approaches
There are two primary ways to tackle data validation in Excel: proactively preventing errors with built-in rules, or reactively auditing existing data with powerful tools.
Method 1: Proactive Control with Excel's Built-in Data Validation
This is the traditional method. Excel's Data Validation feature allows you to set up rules that control what users can enter into a cell. It's perfect for creating templates or shared worksheets where you want to enforce standards from the start.
You can find this feature under the Data tab in the Data Tools group.
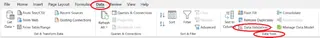
This opens the Data Validation pop-up window, where you can define your rules.

Here are the main techniques you can use:
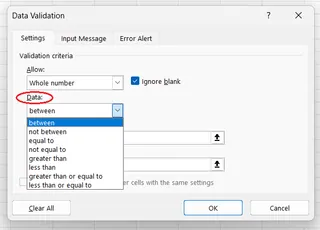
Restricting Data Type and Range/Length
This is the most common use case. You can restrict entries to Whole number, Decimal, Date, Time, or Text of a specific length. For each type, you can apply logical conditions like between, greater than, or equal to.
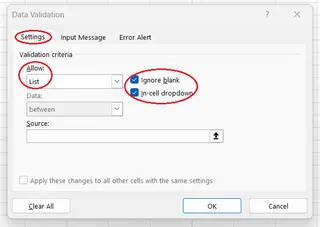
Creating Drop-down Lists
To limit choices to a predefined set of values (e.g., "Cat", "Dog"), a drop-down list is the best solution. You simply create your list of options in a range of cells, then point the Data Validation rule to that list.
- Enter your list items and optionally convert them to an Excel Table (Ctrl+T) so the list updates automatically.
- Select the cell(s) where you want the drop-down.
- Open Data Validation, choose List from the Allow dropdown, and select your list range as the Source.
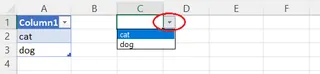
The result is a clean, user-friendly drop-down menu in your cell.
Applying Custom Formulas
For more complex rules, you can use a custom formula. This gives you ultimate flexibility. Here are a few examples:
- No Duplicates:
=COUNTIF(range, uppermost_cell)<=1 - Past Dates Only:
=uppermost_cell<TODAY() - No Extra Spaces:
=uppermost_cell=TRIM(uppermost_cell)
While powerful, this method requires you to know the right formulas and apply them correctly, which can be a steep learning curve.
Method 2: Instant Auditing with Excelmatic
What if the data is already in your spreadsheet? Or what if the rules are too complex to write as a formula? This is where Excelmatic changes the game.

Instead of building rules cell-by-cell, you upload your file and ask questions in plain language. Excelmatic does the heavy lifting, delivering instant answers, charts, and insights. This is a reactive, or auditing, approach to data validation that's perfect for business users.
Let's see how this compares to the custom formulas above:
Finding Duplicates:
- Traditional: Carefully write and apply the formula
=COUNTIF(A:A, A2)<=1to the entire column. - Excelmatic: Upload the file and ask: "Find all duplicate entries in the Customer ID column." Excelmatic instantly identifies and can even list them for you.
- Traditional: Carefully write and apply the formula
Validating Dates:
- Traditional: Set a validation rule with the formula
=B2<TODAY(). - Excelmatic: Simply ask: "Are there any order dates in the future? Show me which ones."
- Traditional: Set a validation rule with the formula
Checking for Proper Formatting (e.g., no extra spaces):
- Traditional: Use the formula
=A2=TRIM(A2)and then filter forFALSEresults. - Excelmatic: Ask: "Identify any cells in the 'Product Name' column with leading or trailing spaces."
- Traditional: Use the formula
The Excelmatic approach is not about preventing errors during entry but about finding them with incredible speed and ease in existing datasets—perfect for business analysis and reporting.
Finding Invalid Data: A Clear Contrast
Excel has a feature to find data that violates existing rules. After setting a rule, you can go to Data Validation -> Circle Invalid Data.
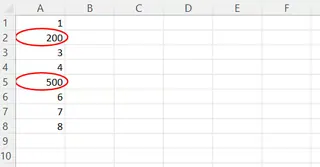
This is helpful, but it's still a manual process.
With Excelmatic, the process is much more direct. You ask your question, and the tool doesn't just circle the data; it can filter it, list it in a new table, or even create a chart summarizing the errors. This is data cleaning and validation on demand.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Task
Both methods are valuable, but they serve different purposes.
| Use Case | Best Method | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Creating a data entry template for a team | Excel's Data Validation | Proactively prevents errors at the source, ensuring consistency. |
| Auditing a large, existing dataset for errors | Excelmatic | Incredibly fast and intuitive. No need to write complex formulas. |
| Enforcing simple, fixed rules (e.g., a list of states) | Excel's Data Validation | Simple to set up a drop-down list for permanent rules. |
| Finding complex or ad-hoc errors | Excelmatic | Flexible enough to handle any question you can ask in plain language. |
How to Manage Traditional Data Validation Rules
If you're using Excel's built-in feature, here's how to edit or remove your rules.
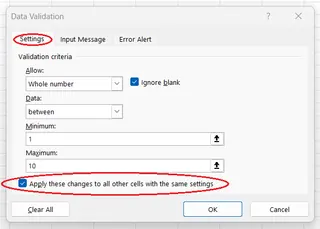
How to Edit Data Validation
- Select a cell that has the data validation rule you want to edit.
- Open the Data Validation window (Data > Data Tools > Data Validation).
- Make your changes in the Settings, Input Message, or Error Alert tabs.
- Crucially, check the box that says Apply these changes to all other cells with the same settings.
- Press OK.
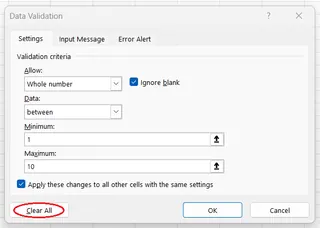
How to Remove Data Validation
- Select the cell(s) from which you want to remove validation.
- Open the Data Validation window.
- If you want to remove it from all similar cells, check Apply these changes....
- Click the Clear All button at the bottom left.
- Press OK.
Conclusion
Ensuring data accuracy is non-negotiable for quality analysis. Excel provides a robust, proactive system through its Data Validation feature, which is perfect for building structured templates and enforcing rules during data entry.
However, for the common task of auditing and cleaning existing data, Excelmatic offers a faster, more intuitive, and more powerful alternative for business users. By simply asking questions in plain language, you can perform complex validation checks in seconds, not hours—eliminating technical barriers and accelerating your data analysis workflow.
Whether you're validating sales data, cleaning customer records, or ensuring compliance in financial reports, Excelmatic makes data quality assurance accessible to everyone, regardless of technical expertise.
Ready to transform how you validate and clean data in Excel? Start using Excelmatic today and experience instant, AI-powered data validation and cleaning.
FAQ
What is data validation?
Data validation is the process of checking the accuracy and consistency of data to ensure it meets predefined conditions, such as data type, range, or length.
What are the advantages of data validation?
Data validation improves data quality, helps maintain data integrity and compliance, speeds up data cleaning, and leads to more reliable findings and better data-driven decisions.
What are the main data validation techniques in Excel?
The traditional method involves using the Data Validation feature to restrict data type and range, create drop-down lists, or apply custom formulas. The modern approach uses Excelmatic to audit data using natural language queries.
What is the fastest way to find invalid data in an existing spreadsheet?
While Excel's "Circle Invalid Data" feature works for pre-defined rules, the fastest and most flexible method is to use Excelmatic. You can ask a direct question like "Find all rows where the quantity is negative" and get an instant, actionable list of errors.
How to prevent entering duplicates in Excel?
You can use a custom Data Validation formula like =COUNTIF(range, uppermost_cell)<=1. Alternatively, after data is entered, you can ask Excelmatic to "find all duplicate values" in a specific column for a quick audit.
How to set a customized error message for invalid data in Excel?
In the Data Validation window, use the Error Alert tab to set a style (Stop, Warning, Information), title, and custom message that appears when a user enters invalid data.
How to delete data validation in Excel?
Select the relevant cells, open the Data Validation window, click the Clear All button, and then press OK.






