Key Takeaways
- Business professionals waste hours manually formatting Excel data types and debugging errors, slowing down analysis and reporting.
- Excelmatic's AI-powered approach automates data type identification, conversion, and error checking through simple natural language commands.
- What traditionally requires complex formulas and manual clicks can now be done in seconds with plain language instructions to Excelmatic.
- For market, sales, and operations teams, mastering data types with Excelmatic ensures faster, more accurate data analysis without technical Excel expertise.
If you work with data, understanding the different data types in Excel is fundamental. This knowledge helps you input data correctly, perform the right operations, and avoid frustrating errors.
In this article, we will explore essential data types such as Number, Text, Dates, and more. We'll explain how to identify and convert them using traditional Excel methods. More importantly, we'll show you how Excelmatic's AI tools can handle these tasks in seconds, transforming your workflow.
Whether your work involves complex calculations or organizing information, mastering data types will help you format your spreadsheet correctly and dramatically increase the efficiency of your data operations.
How to Identify Data Types in Excel
Correctly identifying a cell's data type is the first step toward accurate data management.
The Traditional Method
To determine the data type in Excel, right-click on any cell or a range of cells and choose Format Cells. The Number tab here will display the available data types, such as Number, Date, or Text.
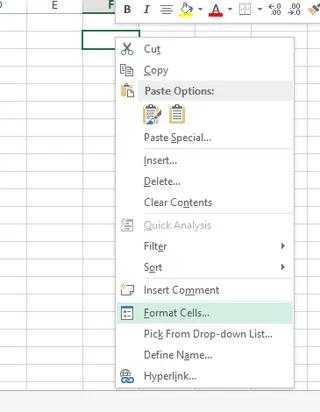
Selecting the Format Cell option. Source: Image by author
This opens a dialog box showing a list of all available data types.
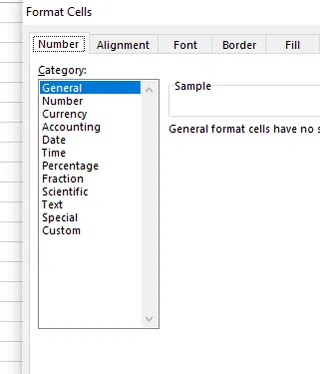
List of data types in Excel. Source: Image by author
Alternatively, you can go to the Number group on the Home tab to see and change the data type.
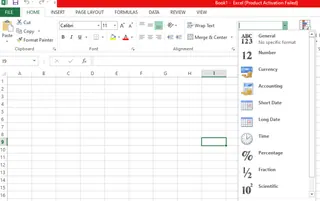
Different data types as displayed in the Home tab. Source: Image by author
The AI-Powered Method
While manual checks are useful, an AI agent like Excelmatic can identify and correct data types automatically. Instead of clicking through menus, you can simply upload your file and ask a question in plain English, like, "Are there any text values in the 'Sales' column?" The AI will instantly analyze the data and give you a clear answer, saving you the trouble of manual verification.

Different Data Types in Excel
Using the correct data type is crucial. An incorrect format can misrepresent your data and lead to calculation errors. Let's explore the most common data types and see how to manage them both manually and with AI.
Number Data
Number data encompasses a wide range of values, from currency and dates to percentages and fractions. Excel often treats these as Numeric, but their specific formatting is key to their function.
Currency
If you work with financial data, the Currency data type is essential. It formats monetary values with the correct symbols and decimal places.
Traditional Method:
- Select the range of cells you want to change.
- Right-click and select the Format Cells option.
- In the Number tab, select Currency and choose your desired symbol and decimal places.
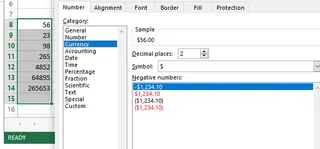
Converting numbers into Currency Format. Source: Image by author
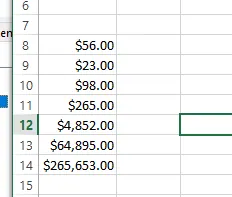
Numbers converted to Currency values. Source: Image by author
A Faster Way with Excelmatic:
Forget the clicks. With Excelmatic, you just upload your sheet and type your request:
Format the 'Sales' column as US dollars with two decimal places.
Excelmatic instantly applies the correct formatting across the entire column.
Date and Time
The Date and Time data types are critical for chronological analysis, scheduling, and time-based calculations.
Traditional Method:
- Select the cell(s) to format.
- Right-click and choose Format Cells.
- Go to the Number tab and select Date or Time.
- Choose the specific format you need (e.g., MM/DD/YYYY, H:MM AM/PM).
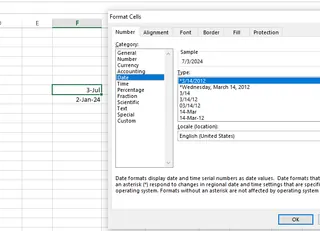
Changing the text to the Date and Time data types. Source: Image by author
A Faster Way with Excelmatic:
Handling date formats is notoriously tricky. Excelmatic simplifies it. Just ask:
Ensure all dates in the 'Order Date' column are in the format YYYY-MM-DD.
Or even perform calculations directly:
Calculate the number of days between 'Start Date' and 'End Date' for each row.
Percentage
The Percentage data type is used to display ratios and proportional values in an easy-to-read format.
Traditional Method:
- Select the cells.
- Right-click and open Format Cells.
- Choose Percentage from the Number tab and set the decimal places.
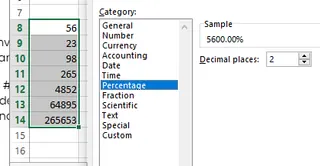
Converting numbers into percentages. Source: Image by author
A Faster Way with Excelmatic:
Simply tell Excelmatic what you need:
Convert the 'Growth Rate' column to percentages.
Fractions
The Fraction data type displays decimal values as fractions, which can be useful in specific contexts like measurements or recipes.
Traditional Method:
- Select the decimal values.
- Right-click, choose Format Cells.
- In the Number tab, select Fraction and pick the desired fraction type.
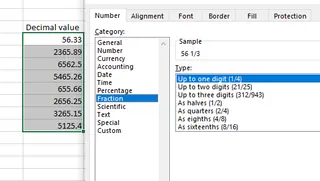
Converting decimal values to Fractions. Source: Image by author
A Faster Way with Excelmatic:
A simple command is all it takes:
Display the values in column C as fractions.
Scientific
The Scientific data type uses exponential notation (e.g., 1.23E+04) to display very large or very small numbers concisely.
Traditional Method:
The process is the same: select cells, right-click, open Format Cells, and choose Scientific.
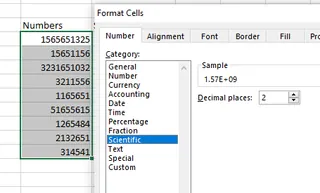
Changing to scientific data type. Source: Image by author
A Faster Way with Excelmatic:
Just ask:
Change the 'Measurement' column to scientific notation with 3 decimal places.
Special
Excel's Special data type is pre-formatted for common identifiers like Zip Codes, Phone Numbers, and Social Security Numbers, ensuring they are displayed correctly (e.g., preserving leading zeros in a zip code).
Traditional Method:
In the Format Cells dialog, select Special and choose the appropriate type.
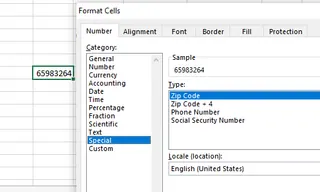
The dialog box of Special cells. Source: Image by author
A Faster Way with Excelmatic:
This is a classic data cleaning task where AI excels.
Format column B as a 5-digit zip code.
Custom
The Custom data type gives you complete control to create your own format codes, like combining text with numbers (e.g., 0.00 "units").
Traditional Method:
Select Custom in the Format Cells window and enter your desired format code in the "Type" box.
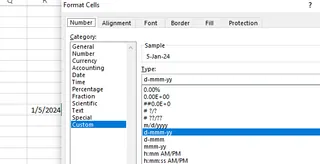
Selecting the Custom data type. Source: Image by author
A Faster Way with Excelmatic:
Describe the format you want, and let the AI figure out the code.
Format the date in column A to show as 'd-mmm-yy'.
Text Data
Text is the most basic data type, allowing you to input any combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. A key distinction is that numbers formatted as Text cannot be used in calculations. This is useful for identifiers like employee IDs or zip codes with leading zeros.
Traditional Method:
To convert numbers to text, select the cells, open Format Cells, and choose the Text data type.
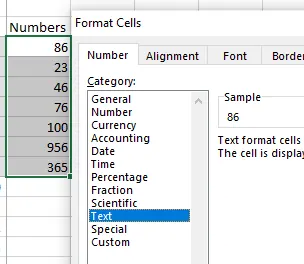
Converting numbers into Text Format. Source: Image by author
A Faster Way with Excelmatic:
Preventing Excel from auto-formatting numbers is a common challenge. Excelmatic makes it easy.
Treat the 'Employee ID' column as text to keep the leading zeros.
Boolean Data
Boolean data represents the logical values TRUE and FALSE. These are the foundation of logical functions that help you perform decision-making tasks in your spreadsheet.
You typically generate Boolean values by making a comparison, like =A1=B1.
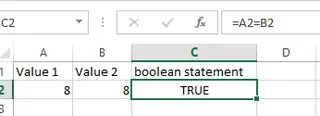
Applying a boolean operator on equal values. Source: Image by author
Excel's logical functions like IF(), AND(), OR(), and NOT() use these TRUE/FALSE results to perform actions.

Lists of all the logical operators in Excel. Source: Image by author
While writing formulas like IF(AND(A2>50, B2="Shipped"), "TRUE", "FALSE") is powerful, it can get complicated.
A Faster Way with Excelmatic:
Instead of building complex logical formulas, you can just state the condition you want to analyze.
Show me all records where 'Sales' are greater than 1000 and 'Region' is 'North'.
Excelmatic handles the underlying IF, AND, and OR logic for you, providing the answer directly.
Error Data
Error values (all starting with #) are Excel's way of telling you something is wrong with a formula or data.
- #NAME?: A typo in a function name or text in a formula that isn't in quotes.
- #DIV/0!: A formula is trying to divide a number by zero.
- #REF!: A formula refers to a cell that is no longer valid (e.g., it was deleted).
- #NUM!: An invalid number is used in a formula, or the result is too large/small for Excel.
- #N/A: A value is "not available" for a function (common with lookups).
- #VALUE!: The wrong type of argument is used (e.g., adding text to a number).
- #NULL!: Two ranges in a formula do not intersect.
How an AI Agent Can Help:
When you see an error, instead of debugging the formula yourself, you can ask Excelmatic:
Why am I getting a #DIV/0! error in column G? How can I fix it?
The AI can diagnose the problem and suggest a solution, such as using an IFERROR function or correcting the source data.
Verifying Data Types in Excel
You can use functions to verify data types. For example, ISNUMBER() returns TRUE if a cell contains a number, and ISTEXT() does the same for text. ISBLANK() checks if a cell is empty.
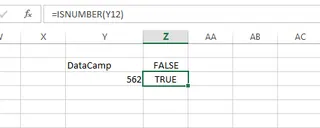
Checking if a cell contains a number. Source: Image by author
With Excelmatic, verification is conversational. Just ask: "Check for any non-numeric values in the 'Quantity' column."
What Are Linked Data Types in Excel?
Linked data types are an advanced feature that connects your cells to live, online data sources like stocks, geography, and currencies. This allows you to pull rich, automatically updating information directly into your worksheet. This is one of Excel's steps toward a more dynamic, connected spreadsheet experience, similar to the intelligence offered by Excelmatic.
Summary Table
Here’s a quick comparison of managing data types manually versus with Excelmatic.
| Data Type | Description | How to Verify (Manual) | AI-Powered Method (Example Prompt) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | General numeric values. | ISNUMBER() |
"Ensure column B contains only numbers." |
| Currency | Monetary values with symbols. | Check for currency symbols. | "Format column C as Euros." |
| Date and Time | Chronological values. | Check the format in Format Cells. | "Convert 'Order Date' to DD-MM-YYYY format." |
| Percentage | Ratios and proportions. | Check for the % symbol. | "Show 'Discount' column as percentages." |
| Fraction | Decimal values as fractions. | Check the format in Format Cells. | "Display column F as fractions." |
| Scientific | Exponential notation for large/small numbers. | Check for E+n notation. | "Convert 'Particle Size' to scientific notation." |
| Special | Pre-formatted for IDs like Zip Codes. | Check the special format. | "Format column H as a phone number." |
| Custom | User-defined formats. | Check the custom code in Format Cells. | "Format column D as '0.00 units'." |
| Text | Alphanumeric characters; not for calculation. | ISTEXT() |
"Treat 'Zip Code' column as text." |
| Boolean | Logical TRUE or FALSE values. |
Use logical tests (e.g., =A1=B1). |
"Is it true that Sales > Budget?" |
| Error | Indicates a problem in a formula. | Identify messages starting with #. |
"Why am I getting a #REF! error?" |
| Linked Data | Connects to live web data. | Check for data cards and web icons. | N/A (Similar concept to AI data enrichment) |
Final Thoughts
Understanding Excel's data types is essential for anyone serious about data accuracy and analysis. The traditional methods of right-clicking and navigating menus are the building blocks of spreadsheet knowledge.
However, the landscape is changing. Excelmatic now offers a faster, more intuitive path to the same results. By handling tedious formatting and complex logic through simple language commands, these tools free you up to focus on what truly matters: gaining insights from your data.
Stop wasting time on manual data type formatting and error debugging. Try Excelmatic for free today and experience how AI can transform your Excel workflow from tedious to effortless.
Embracing both the fundamentals and modern tools will make you a more powerful and efficient Excel user.