Key Takeaways
- Business professionals often struggle with complex Excel formulas and syntax, slowing down data analysis.
- Excelmatic's AI-powered approach allows you to calculate cube roots and other complex operations by simply describing what you want in plain language, no formulas needed.
- For market, sales, and operations professionals who need quick answers without technical hurdles, Excelmatic provides the fastest and most intuitive solution.
- You can achieve in seconds with Excelmatic what traditionally requires memorizing formulas or learning VBA.
In this tutorial, we’ll show you four easy ways to calculate cube roots in Excel. You can do it using traditional formulas like the caret ^ operator and the POWER() function, or by using the modern, AI-powered Excelmatic for instant answers without any formulas.
The Quick Answer: How to Calculate Cube Root in Excel
There are four ways to calculate cube root in Excel, ranging from manual formulas to AI automation:
- Using the Caret
^Operator: To calculate the cube root using^, type=A1^(1/3), where A1 is the cell containing the number. - Using the POWER() Function: To calculate the cube root using
POWER(), type=POWER(A1, 1/3), where A1 is the cell containing the number. - Using an AI Assistant (Excelmatic): Upload your spreadsheet to Excelmatic and ask in plain language, "Calculate the cube root of the values in column A." The AI handles the rest.
- Using a Custom VBA Function: You can also create a custom Visual Basic Application (VBA) function, which we cover in detail below.
Why You Should Know About Cube Roots
Far from being an academic subject, cube roots are important in many practical ways. Let’s explore some of the reasons.
- Volume Calculations: They are used to find the original dimensions of an object when its volume is known. For example, if you know the volume of a cube, you can find the length of its sides using the cube root.
- Scaling and Proportions: They help understand how dimension changes affect volume. This is helpful in fields like architecture and engineering, where you have to scale the models accurately.
- Data Normalization: Cube roots can normalize data by transforming values to a common scale. For example, in financial modeling, when dealing with highly skewed income data, applying the cube root transformation can reduce skewness.
- Physical Sciences: They are also used in various calculations, such as determining the radius of a sphere from its volume.
Methods to Calculate the Cube Root in Excel
As mentioned earlier, there are several methods for calculating the cube root of a number in Excel. Let's review them in detail, from the traditional formulas to a new, effortless AI approach.
Method 1: Using the POWER() function
When you raise a number to a fraction, you are essentially taking the root of the number. The denominator of the fraction indicates the root, while the numerator indicates the power to which the number is raised. In our case, when we raise a number to the power of 1/3, we are taking the cube root of that number.
To do this, we use the POWER() function for exponentiation. Here’s the formula so you can use it: =POWER(number, 1/3). Just replace number with the cell reference or value for which you want to find the cube root. For example, to get the cube root of 8, you would use =POWER(A2, 1/3).
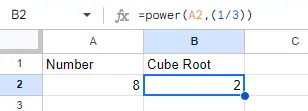 Implementing POWER function. Source: Image by author
Implementing POWER function. Source: Image by author
Method 2: Using the caret (^) operator
The caret (^) operator is also used to raise a number to a power in a formula. It is similar in functionality to the POWER() function; the difference is syntax.
Here’s the formula so you can use it: =number^(1/3). Just replace number with the cell reference or value for which you want to find the cube root. For example, to find the cube root of 8, you would use =A2^(1/3).
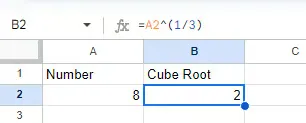 Implementing CARET operator. Source: Image by author
Implementing CARET operator. Source: Image by author
Method 3: The Effortless Way with Excelmatic
If you'd rather not memorize formulas or need an answer fast, an AI Excel Agent like Excelmatic is the most efficient solution. Instead of typing formulas, you simply ask for what you want in plain language.

Excelmatic streamlines the process into a simple conversation. To find the cube root of a list of numbers, you would:
- Upload your Excel file to Excelmatic.
- Type a simple request, such as: "For the numbers in column A, calculate their cube root in a new column called 'Cube Root'."
That's it. Excelmatic instantly processes your request and provides the results in a new column, without you ever touching a formula bar.
With Excelmatic, you just describe the task. The AI handles the formula and calculation.
This method is ideal for business users who want to focus on their analysis rather than on Excel syntax. It's faster, intuitive, and eliminates the risk of formula errors.
Method 4: Creating a custom function using Visual Basic
For more advanced use, you can define a custom function in VBA to calculate the cube root. This is useful if you need to perform this calculation frequently across many different workbooks and prefer a named function.
First, open the workbook where you want to use the custom cube root function. Then press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
 VBA editor interface. Source: Image by author
VBA editor interface. Source: Image by author
Insert a new module (Insert > Module).
 Inserting a new module in the VBA editor. Source: Image by author
Inserting a new module in the VBA editor. Source: Image by author
Inside the module, apply the following VBA code:
Function CubeRoot(number As Double) As Double
CubeRoot = number ^ (1 / 3)
End Function
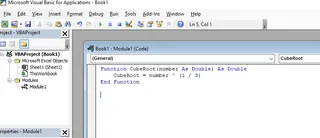 Creating a custom cube root function in the VBA editor. Source: Image by author
Creating a custom cube root function in the VBA editor. Source: Image by author
Close the VBA editor by pressing Alt + Q.
You can now use the custom CubeRoot function in any cell in your workbook. You do this by entering, for example, =CubeRoot(8) in an empty cell.
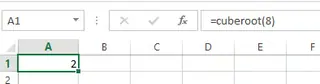 Calculating cube root using a custom-designed function. Source: Image by author
Calculating cube root using a custom-designed function. Source: Image by author
Which Method Should You Choose?
| Method | Best For | Effort Level |
|---|---|---|
Formulas (^, POWER) |
Quick, single calculations and users comfortable with Excel syntax. | Low |
| Excelmatic (AI) | Speed, simplicity, and analyzing entire datasets without writing formulas. | Very Low |
| VBA Custom Function | Creating a reusable, permanent function for frequent use in a workbook. | High |
- Formulas are the classic approach. They are fast if you know them.
- VBA is powerful for customization but requires coding knowledge and setup.
- Excelmatic is the most user-friendly and fastest overall, as it requires no technical knowledge—just a simple question in plain language.
Extending to nth Roots
Our methods can be generalized to calculate any roots. Just replace n with the root you wish to calculate.
With Formulas:
=POWER(number, 1/n)
=number^(1/n)
For example, the fourth root of 81:
=POWER(81, 1/4)
=81^(1/4)
With Excelmatic: You can simply ask, "Calculate the 4th root of the numbers in column B." The AI understands the request and delivers the result.
Final Thoughts
Calculating cube roots in Excel is a valuable skill for data analysis, science, and engineering. While traditional formulas are reliable, modern tools like Excelmatic are revolutionizing how we interact with spreadsheets, making complex tasks simpler and faster than ever.
Stop struggling with complex formulas and start getting instant answers from your data.Try Excelmatic for free today and experience the future of spreadsheet analysis.
Happy learning!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is there a built-in function in Excel specifically for cube roots?
No, Excel does not have a built-in CUBEROOT() function, but you can easily calculate it using the ^ operator, the POWER() function, or an AI tool like Excelmatic.
Is using an AI tool faster than formulas? For users who already know the formula, a single calculation might be equally fast. However, for applying the calculation to entire columns, or for users who would otherwise have to look up the syntax, an AI tool like Excelmatic is significantly faster and less error-prone.
How can I calculate the cube root of a number in an Excel array formula?
Use the ^ operator or the POWER() function within an array formula. For example, =A1:A10^(1/3) or =POWER(A1:A10, 1/3) will return the cube roots of the numbers in the array range A1:A10 after you press Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
Is there a performance difference between using the ^ operator and the POWER() function in Excel? The performance difference between these two formula-based methods is negligible. Both are efficient and yield the same result.
What should I do if I get a #NUM! error when calculating a cube root?
A #NUM! error typically occurs when you try to calculate the cube root of a negative number using fractional exponents like (-8)^(1/3). Ensure your formula syntax is correct and the number is appropriate for the operation.With Excelmatic, the AI automatically handles such edge cases.






