Key Takeaways
- Manual counting and complex Excel formulas are time-consuming and error-prone, especially for business users who need quick insights
- Excel's COUNT functions require technical syntax knowledge that creates barriers for marketing, sales, and operations professionals
- Excelmatic's AI delivers instant counting results with simple language commands, eliminating formula memorization and errors
- Combining Excel knowledge with Excelmatic provides the most efficient workflow for accurate data analysis and decision-making
Counting cells is a fundamental task in any data analysis workflow. In Excel, a family of COUNT() functions can save you time, reduce errors, and make your data analysis a whole lot smoother. But what if you could achieve the same results without memorizing any formulas at all?
In this guide, we’ll walk you through Excel’s powerful count functions in a practical, easy-to-follow way. We'll also compare the traditional formula-based approach with a modern AI-powered solution, Excelmatic, to show you how you can get answers faster than ever.
What Is the COUNT() Formula in Excel?
The COUNT() function in Excel counts the number of cells that contain numeric values within a specified range. Its primary purpose is to quickly determine how many cells contain numbers, ignoring text, errors, and blank cells.
For example, if you're managing a sales report or tracking test scores, COUNT() helps you identify how many valid numerical entries are present.
You can use this function when you need to:
- Count how many items have a price entered
- Identify how many students submitted numeric grades
- Summarize the number of responses in a survey containing numeric data
By automating the counting process, COUNT() saves time and reduces the risk of manual errors.
The Traditional Way: COUNT() Formula Syntax
The syntax for using the COUNT() formula is straightforward:
COUNT(value1, [value2], ...)
Let’s understand this:
| Argument | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
value1 |
Required | Cell reference or range in which numbers need to be counted. |
[value2] |
Optional | Additional cell references or ranges. You can include up to 255 additional items. |
The COUNT() function only includes numbers, dates, and numeric text (like 1 if entered directly as an argument). It ignores text, logical values (TRUE or FALSE), error values, and empty cells within a range.
How to Count in Excel: Formulas vs. AI
Let’s see how you can use both traditional formulas and AI for real-world work.
Example 1: Counting Simple Numeric Data
First, we’ll cover how to count numeric values in a simple range. Suppose we have two columns: Roll No and Marks. Some cells in the Marks column are empty.
The Formula Approach
To count how many numeric entries are in the Marks column, you would use this formula:
=COUNT(B2:B11)

Since 2 out of 10 cells are empty, the formula correctly returns 8.
You can also include additional numeric values outside the range directly in the formula:
=COUNT(B2:B11, 20)
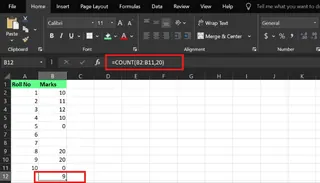
This formula counts the eight numeric values in the range B2:B11 plus the extra number 20, returning 9.
The AI-Powered Way with Excelmatic
With an AI tool like Excelmatic, you skip the formulas entirely.

- Upload your Excel file.
- Ask a simple question in plain language: "How many numeric entries are in the Marks column?"
Excelmatic understands your request, analyzes the data, and gives you the answer: 8. You don't need to remember the function name or specify the cell range.
Example 2: Counting Dates and Times
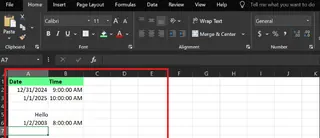
Let’s say you’re managing an employee attendance sheet. In Excel, dates and times are stored as numbers, so COUNT() can tally them. However, the data might contain notes or be empty.
The Formula Approach
To count valid dates and times, you'd apply COUNT() to each column:
For the date column:
=COUNT(A2:A6)
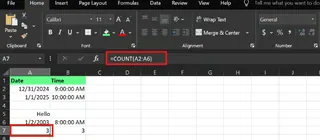
For the time column:
=COUNT(B2:B6)
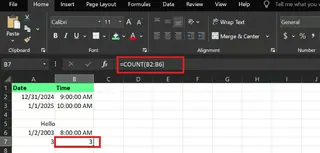
Both formulas return 3, correctly ignoring the blank cells and the text note "Hello."
The AI-Powered Way with Excelmatic
Instead of writing two separate formulas, you can just ask:
- "Count the valid check-in dates in column A."
- "How many valid check-in times were recorded in column B?"
Excelmatic interprets your intent and provides the correct count for each, without you needing to worry about whether dates and times are treated as numbers.
Example 3: Using Named Ranges
Named ranges make formulas more readable. For example, you can name the range C2:C6 as SalesData.

The Formula Approach
After defining the named range SalesData (via Formulas > Define Name), you can use it in your formula:
=COUNT(SalesData)
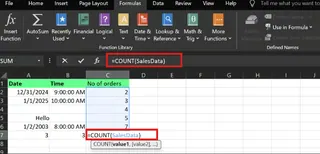
This is more readable than =COUNT(C2:C6), but it requires an initial setup step.
The AI-Powered Way with Excelmatic
Excelmatic makes named ranges obsolete. It automatically recognizes column headers.
You can simply ask: "Count the entries in the Sales column."
Excelmatic understands that "Sales" refers to the data in that column, delivering the result without any manual setup. This is a huge time-saver and makes your analysis more fluid.
Example 4: Combining COUNT() with Other Functions
The real power of formulas comes from nesting them. For instance, you can calculate an average by combining SUM() and COUNT().
The Formula Approach
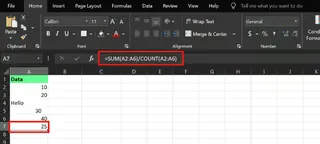
To calculate the average, ignoring text and blanks:
=SUM(A2:A6)/COUNT(A2:A6)
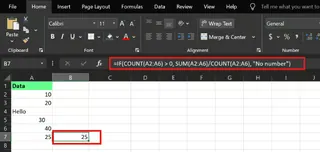
You can also create conditional logic with IF():
=IF(COUNT(C2:C7)>0, SUM(C2:C7)/COUNT(C2:C7), "No numbers")
And you can embed the count in a text string for reporting:
="There are " & COUNT(C2:C7) & " numeric values."

The AI-Powered Way with Excelmatic
These complex tasks become incredibly simple with AI.
- To get the average: "What is the average of the values in column A?" Excelmatic automatically calculates it, ignoring non-numeric cells.
- To handle the conditional logic: "Calculate the average of column C. If there are no numbers, tell me."
- For a summary report: "Create a sentence that says how many numeric values are in column C."
Excelmatic handles the multi-step logic behind the scenes, giving you the final result directly.
Avoiding Errors: Formulas vs. AI
Even simple functions can lead to errors if you're not careful.
Common Formula Errors: #NAME? and #VALUE!
- #NAME? Error: This usually means a typo in the function name (e.g.,
COUUNT()instead ofCOUNT()) or a non-existent named range. - #VALUE! Error: This occurs when the function receives an argument of the wrong type, like
=COUNT("text").
Fixing these requires careful proofreading of your formulas and data.
How Excelmatic Eliminates These Errors
With Excelmatic, these errors become a thing of the past. Since you are not writing the formula yourself, you cannot make a syntax or typo error. The AI interprets your natural language request, which eliminates the primary cause of #NAME? and #VALUE! errors, ensuring a smoother, error-free workflow for business analysis.
Other Count Functions: The Expanded Toolkit
Beyond COUNT(), Excel offers more specialized counting functions.
COUNTA(): Counting All Non-Empty Cells
The COUNTA() function counts all cells that are not empty, including numbers, text, and error values.
The Formula Approach
=COUNTA(A2:A6)

This returns 4, counting everything except the one empty cell.
The AI-Powered Way with Excelmatic
Simply ask: "How many non-empty cells are in column A?"
COUNTBLANK(): Identifying Empty Cells
As the name suggests, COUNTBLANK() counts the number of empty cells in a range.
The Formula Approach
=COUNTBLANK(A2:A6)

This returns 2, as there are two blank cells in the range.
The AI-Powered Way with Excelmatic
Ask: "Count the number of blank cells from A2 to A6."
COUNTIF(): Conditional Counting
COUNTIF() is one of the most useful functions, allowing you to count cells that meet a specific condition.
Its syntax is: =COUNTIF(range, criteria)
The Formula Approach
Example 1: Numbers above a threshold To count sales values above 100:
=COUNTIF(B2:B6, ">100")

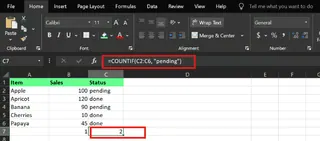
Example 2: Specific text To count how many orders are "pending":
=COUNTIF(C2:C6, "pending")
Example 3: Using wildcards To count items starting with the letter "A":
=COUNTIF(A2:A6, "A*")

The AI-Powered Way with Excelmatic
Conditional counting is where AI truly shines. You can ask complex questions naturally:
- For numbers: "How many sales were over 100?"
- For text: "Count the number of orders with 'pending' status."
- For wildcards: "Count how many items start with the letter A."
Excelmatic translates these questions into the correct logic, saving you from having to remember the exact syntax for criteria like ">100" or "A*".
Conclusion
Excel’s counting functions are undeniably powerful. Mastering them is a key step toward becoming proficient in data analysis. They provide the control and precision needed to clean up spreadsheets, spot gaps, and create reliable reports.
At the same time, Excelmatic offers a revolutionary approach for business professionals. By allowing you to simply ask questions in plain language, it eliminates the learning curve of formulas, reduces errors, and accelerates your data analysis workflow.
Whether you're counting sales figures, analyzing customer data, or preparing reports, Excelmatic makes complex counting tasks accessible to everyone—regardless of technical expertise.
Ready to transform how you count and analyze data in Excel?
Start using Excelmatic today and experience instant, accurate counting with AI-powered efficiency.