Key Takeaways
- Manual Excel formulas for CAGR can be complex and error-prone, requiring precise syntax and cell references that slow down business analysis
- Excelmatic's AI-powered approach delivers instant CAGR calculations without formulas - simply ask in plain language and get accurate results
- You can eliminate formula memorization and focus on decision-making by adopting AI tools that handle the calculations for you
- Get faster insights for investment analysis, business planning, and performance tracking
The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is one of the most valuable metrics for analyzing performance over time. Understanding how to calculate CAGR in Excel can significantly enhance your analytical capabilities for common use cases such as tracking investment returns, assessing business growth, or forecasting future trends.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything from basic formula-based calculations to advanced techniques. We'll also introduce a modern, AI-powered approach that can deliver the same results in a fraction of the time, ensuring you can confidently apply CAGR analysis to your professional work.
What Is the CAGR Formula?
Compound annual growth rate represents the mean annual growth rate of an investment or business metric over a specified time period longer than one year.
Unlike simple growth rates that can fluctuate dramatically from year to year, CAGR provides a smoothed rate that accounts for compounding effects, offering a clearer picture of steady growth over time.
The mathematical formula for CAGR is:
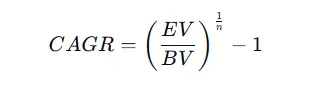
CAGR equation. Image by Author
Where:
- EV (ending value) is the final value of your asset or metric
- BV (beginning value) is the initial value
- n is the number of years in the period
Now that we’ve understood the equation, let’s dive into the different ways to calculate it in Excel.
How to Calculate CAGR in Excel
Before calculating CAGR, it's essential to organize your data correctly. Let’s start by setting up an effective spreadsheet structure as the foundation for all our CAGR analyses.
Setting up the data
Create three essential columns: Initial Value, Final Value, and Time Period (Years). In our example, these are columns B, C, and D. Format the cells appropriately. Typically, you’ll want to format the values as currency or numbers, and the time period as a number.
In Excel, it will look like this:
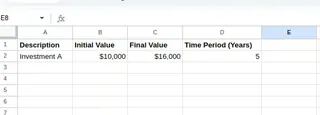 Setting up the data. Image by Author.
Setting up the data. Image by Author.
Now that we have our data organized, let’s explore the different methods of calculating CAGR in Excel.
Method 1: Using the 'POWER()' function
The most straightforward approach uses Excel’s POWER() function, which calculates the result of a number raised to a specified power. You can also use the caret symbol (^) as an alternative to the POWER() function.
In our example, in cell C8, type the following equation:
=((C2/B2)^(1/D2))-1
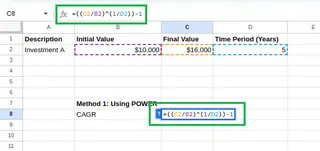 Calculating CAGR using POWER() function. Image by Author.
Calculating CAGR using POWER() function. Image by Author.
You will see the result:
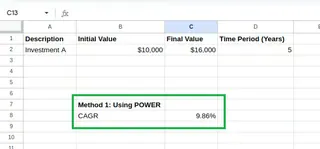 Calculated CAGR. Image by Author.
Calculated CAGR. Image by Author.
Method 2: Using the 'RATE()' function
We could also use Excel’s RATE function instead. The RATE() function calculates the interest rate per period for a loan or investment. We can adapt it for CAGR as follows:
=RATE(D2,0,-B2,C2)
where:
D2is the number of periods (years)- The second parameter (periodic payment) is set to
0 -B2is the negative of the initial value (required for theRATE()function)C2is the final value
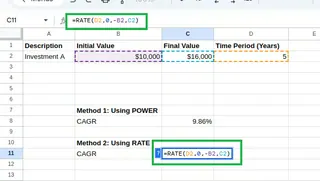 Calculating CAGR using RATE() function. Image by Author.
Calculating CAGR using RATE() function. Image by Author.
You will see the same value as above:
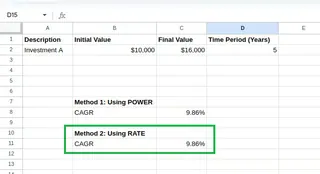 Calculated CAGR. Image by Author.
Calculated CAGR. Image by Author.
Method 3: The AI-Powered Way with Excelmatic

While mastering Excel formulas is a valuable skill, modern tools offer a faster and more intuitive path to the same answer. Excelmatic is an AI Excel Agent that lets you get insights from your data by simply asking questions in plain language.
Instead of memorizing formulas or worrying about correct cell references, you can get your CAGR calculation done in seconds - perfect for busy professionals who need accurate answers fast.
Here’s how it compares:
| Method | Your Action | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Excel | Type =((C2/B2)^(1/D2))-1 or =RATE(D2,0,-B2,C2) |
Full control and understanding of the calculation. |
| Excelmatic | Upload your file and ask: "Calculate the CAGR using the initial value in B2, final value in C2, and time period in D2." | Instant, error-free results without needing to remember any formulas. |

With Excelmatic, you eliminate the risk of typos in your formulas and can focus on interpreting the results rather than building the calculation. It's the perfect solution for busy professionals who need accurate answers, fast.
Now that we have covered the basic calculation methods, let’s explore some advanced techniques for handling more complex scenarios.
More Advanced Excel CAGR Techniques
While the basic CAGR example we saw above works well for standard situations, real-world scenarios often require more advanced approaches. Let’s explore some advanced techniques to handle these scenarios. While these manual functions are powerful, it's worth noting that modern AI tools like Excelmatic can often interpret these complex needs from a simple question, saving you the effort of learning specific functions like YEARFRAC() or XIRR().
Handling irregular time periods
What if your data is irregular, with investments starting mid-year or sales figures spanning unusual time frames?
Imagine you’re analyzing a product launch that began in March 2023 and has performance data through September 2024. Using a standard CAGR calculation with “2 years” would be inaccurate.
In cases like these, leveraging Excel’s date functions becomes essential. One effective method is using the YEARFRAC() function to compute the exact fraction of the year between the start and end dates.
=(EV/BV)^(1/YEARFRAC(start_date, end_date))-1
This approach calculates the exact time period as a fraction of a year, ensuring that the growth rate reflects the true duration of the investment.
Incorporating additional variables
Beyond irregular time periods, real-world CAGR calculations may require adjustments for external factors or additional cash flows. Here are some advanced techniques:
Inflation-adjusted CAGR
Inflation can erode the real value of returns. Adjusting the CAGR to account for inflation yields a more realistic view of growth. The formula is modified as follows:
=((EV/BV)^(1/n)-1) - InflationRate
CAGR with irregular cash flows
When cash flows are not uniform, due to additional investments or withdrawals, the standard CAGR formula may not capture the true growth. In these cases, the XIRR() function is ideal because it accounts for the exact dates of each cash flow:
=XIRR(cash_flows, dates)
Weighted CAGR
Sometimes, different periods contribute unequally to overall performance. By applying a weighted approach, you can assign more significance to periods with higher investments or returns. While Excel does not have a built-in weighted CAGR function, combining functions like SUMPRODUCT() and SUM() allows for a custom calculation.
=SUMPRODUCT(Values, Weights)/SUM(Weights)
By incorporating these equations and techniques, your Excel CAGR calculations become more robust and adaptable to real-world scenarios.
Practical Applications of the Excel CAGR Formula
CAGR is a widely used calculation across multiple domains. It provides valuable insights into growth patterns and performance over time and can be applied in various fields, including:
- Investment analysis: CAGR enables investors to evaluate and compare the performance of different investments over varying time periods.
- Business growth planning: Companies use CAGR to analyze historical growth trends and establish realistic future targets for revenue, profit margins, or customer acquisition.
- Market research: Analysts use CAGR to assess market growth rates, identify emerging opportunities, and compare performance across different market sectors.
- Sales performance evaluation: Sales teams utilize CAGR to measure the effectiveness of long-term sales strategies, smoothing out quarter-to-quarter fluctuations.
- Economic analysis: Economists apply CAGR when analyzing macroeconomic indicators like GDP, employment rates, or housing prices over extended periods.
CAGR’s ability to normalize growth rates across different time periods makes it particularly valuable for comparative analysis and long-term planning.
Excel CAGR Formula vs. Other Growth Rate Calculations
While CAGR is an extremely useful metric, it’s essential to understand how it compares to other growth measurements and when each is most appropriate.
Let's compare CAGR with other standard metrics, such as the average annual growth rate (AAGR), year-over-year growth (YoY), and total growth rate.
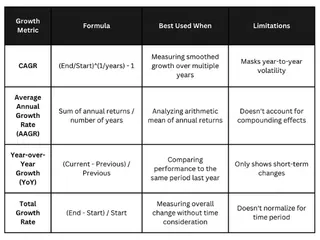 Comparing CAGR with other growth rates. Image by Author.
Comparing CAGR with other growth rates. Image by Author.
As seen in the table above, CAGR’s main advantage is its ability to smooth out volatility and provide a “steady growth rate” equivalent.
However, this same feature can sometimes mask critical year-to-year fluctuations. For instance, a business that experienced explosive growth followed by a plateau would show a moderate CAGR that fails to highlight this pattern. In such cases, supplementing CAGR with year-by-year growth rates provides a more complete picture.
Similarly, while AAGR is more straightforward to calculate, it typically overestimates growth compared to CAGR because it doesn’t account for the compound effect. CAGR is often the preferred metric for long-term forecasting.
Conclusion
This article introduced you to the concept of CAGR and its practical applications. We discussed multiple methods for calculating it in Excel, from traditional formulas like POWER() and RATE() to a modern, AI-powered approach with tools like Excelmatic. We also learned how to handle irregular time periods and incorporate additional variables for more complex scenarios.
Understanding how to calculate and interpret CAGR will significantly enhance your analytical capabilities. While knowing the underlying formulas is valuable, embracing AI tools can make your workflow faster, more accurate, and more efficient. The concepts and techniques covered in this guide provide a solid foundation for applying CAGR in your professional work, whichever method you choose.
Ready to simplify your CAGR calculations and focus on strategic decisions rather than complex formulas?
Try Excelmatic today and experience the power of AI-driven data analysis - get instant answers to your growth rate questions without memorizing a single formula.
FAQ
What is CAGR?
CAGR calculates the compound annual growth rate, providing a smoothed annual rate of growth over a specified time period.
How do you calculate CAGR in Excel?
You can calculate CAGR in Excel using formulas like =((End/Start)^(1/Years))-1 or the RATE function. Alternatively, you can use an AI tool like Excelmatic to get the answer instantly by asking a question in plain English.
What is the difference between CAGR and simple annual growth rate?
CAGR accounts for the compounding effect over multiple years, providing a smoothed growth rate representing steady year-over-year growth. A simple annual growth rate only measures the percentage change between two points without accounting for compounding.
Why is my CAGR calculation showing #NUM! error in Excel?
This error typically occurs when your ending value is negative or when your starting value is zero. CAGR calculations require a positive starting value and either a positive or zero ending value.
When should I use XIRR instead of the standard CAGR formula?
Use XIRR instead of standard CAGR when you have irregular cash flows or investments made at different time intervals.






