Key Takeaways
- Manually writing and debugging complex Excel formulas like AVERAGEIFS is time-consuming and prone to errors, especially with conditional logic.
- Excelmatic transforms this process by letting you calculate averages using simple, plain English questions, eliminating the need to memorize formula syntax.
- Whether you need a simple average or a multi-condition analysis, Excelmatic delivers instant, accurate results, significantly speeding up your data workflow.
Calculating the average of a set of numbers is a fundamental task in data analysis. Excel offers several powerful ways to do this. The aptly named AVERAGE() function is your starting point, but for more specialized situations, you'll need variations like AVERAGEIF(), AVERAGEIFS(), and AVERAGEA().
While mastering these functions is a valuable skill, modern AI-powered tools provide a more intuitive and often faster alternative. In this guide, we'll explore both methods: the traditional Excel formula approach and the conversational AI method using Excelmatic.
Method 1: The Traditional Formula Approach
Let's start with the classic way of calculating averages using Excel's built-in functions.
How to Use AVERAGE() in Excel
The AVERAGE() function in Excel calculates the arithmetic mean of a range of numbers. To use it, you simply select the range of cells you want to average.
The syntax is straightforward:
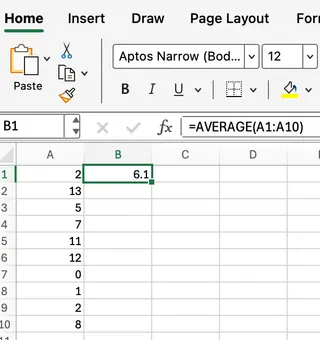
=AVERAGE(A1:A10)
This formula will return the average of the values in cells A1 through A10, as you can see in this screenshot:
Other Useful Excel Average Functions
For more complex scenarios, Excel provides functions that can handle conditions. Here are the most common ones:
AVERAGEIF(): Calculates the average of cells that meet a single condition.AVERAGEIFS(): Calculates the average of cells that meet multiple conditions.AVERAGEA(): Includes logical values (TRUE/FALSE) and text representations of numbers in the calculation.
Let's look at each with a quick example.
AVERAGEIF() in Excel
The AVERAGEIF() function allows you to average only those cells that meet a specific criterion. This is useful when you want to exclude certain values from your calculation.
=AVERAGEIF(B1:B10, ">50")
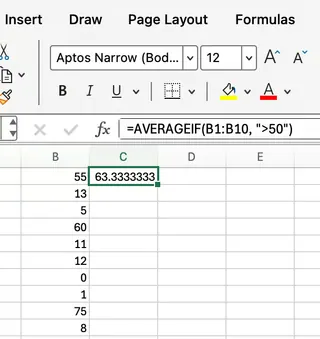
This formula averages only the values in the range B1:B10 that are greater than 50. In this case, 63.3 is the approximate average of 55, 60, and 75.
AVERAGEIFS() in Excel
The AVERAGEIFS() function is similar to AVERAGEIF() but allows for multiple criteria. This is essential when your analysis requires more than one filter.
=AVERAGEIFS(B1:B10, B1:B10, ">50", A1:A10, "Ford")
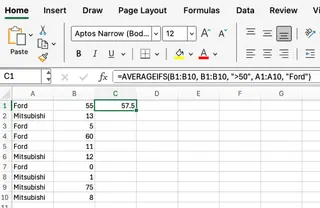
This formula averages the values in B1:B10 only if two conditions are met: the value in B1:B10 is greater than 50, AND the corresponding value in A1:A10 is "Ford". It averages the two values that meet these criteria (55 and 60) to return 57.5.
AVERAGEA() in Excel
The AVERAGEA() function calculates the average of a range, including logical values and text. This can be useful when your data set includes TRUE and FALSE values, which are treated as 1 and 0 respectively.
=AVERAGEA(A1:A10)
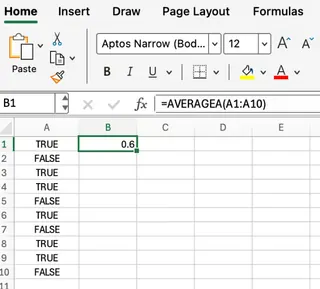
This formula averages all values in A1:A10, treating TRUE as 1 and FALSE as 0.
Method 2: The AI-Powered Alternative with Excelmatic

While formulas are powerful, they require you to remember specific syntax and argument orders. An Excel AI Agent like Excelmatic streamlines this process entirely. You simply upload your file and ask for what you need in plain language.
Let's see how Excelmatic handles the same tasks.
Finding a Simple Average
Instead of writing =AVERAGE(A1:A10), you would upload your spreadsheet to Excelmatic and ask:
What is the average of the values in column A?
Excelmatic instantly processes your request and provides the answer, saving you the time of locating the column and typing the formula.
Finding a Conditional Average (Single Condition)
To replicate the AVERAGEIF() function, you don't need to worry about criteria syntax. Just ask naturally:
Calculate the average for column B, but only for values greater than 50.
The AI understands the condition and applies it automatically, delivering the same result as the AVERAGEIF formula but without the syntax hurdles.
Finding a Conditional Average (Multiple Conditions)
This is where AI tools truly shine. The AVERAGEIFS() formula can become long and confusing. With Excelmatic, the request remains simple and clear:
What is the average in column B for rows where column A is 'Ford' and the value in column B is over 50?
The AI parses the multiple conditions and returns the precise answer (57.5) in seconds. There's no risk of mixing up the average_range and criteria_range arguments.
Traditional Formulas vs. AI: Which Should You Use?
Both methods have their place. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Excel Formulas (AVERAGE, AVERAGEIF) |
Excelmatic (AI Agent) |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Curve | Moderate; requires memorizing syntax. | Minimal; uses plain language. |
| Speed | Fast for simple tasks, slower for complex ones. | Instant for both simple and complex queries. |
| Flexibility | Rigid syntax. A small error breaks the formula. | Highly flexible; understands conversational language. |
| Use Case | Best for building permanent, dynamic calculations within a spreadsheet. | Ideal for quick analysis, reporting, and exploring data without altering the source file. |
Tips for Working with Averages in Excel
Whether you use formulas or an AI tool, keep these tips in mind:
- Know Your Data: Ensure your data range is clean and doesn't include unwanted blank cells or text (unless you intend to use a function like
AVERAGEA()). - Focus Your Analysis: Use conditional averaging to isolate specific subsets of your data for more meaningful insights.
- Choose the Right Tool:
- Use formulas when you need the average to update automatically as data changes within your worksheet.
- Use an AI tool like Excelmatic when you need quick answers, want to analyze data from multiple files, or prefer to avoid writing complex formulas.
Conclusion
The AVERAGE() function and its variants are cornerstones of data analysis in Excel. Mastering them is a worthwhile endeavor. However, the landscape of data analysis is evolving. AI-powered tools like Excelmatic are democratizing data analysis, allowing you to get the insights you need by simply asking questions. By understanding both approaches, you can choose the most efficient method for any task, turning your data into valuable information faster than ever before.
Ready to Simplify Your Excel Workflow?
Try Excelmatic for free today and experience how AI can transform your data analysis. Upload your spreadsheet and start getting answers to questions like "What's the average sales for the last quarter?" or "Show me the average project duration for Team A" in seconds. Focus on the insights, not the syntax.