Key takeaways:
- Predictive analytics with Excel AI hinges on three things: what to predict, the data you have, and the output you need.
- The article provides 10 ready-to-use templates (trend, causal, classification, demand, growth, scenario, risk, seasonal, rolling, model selection) to cover common forecasting tasks.
- Each template includes a clear command structure and expected outputs (forecasts, confidence intervals, charts, factor importance, scenario tables).
- Start simple: pick the template that matches your business question, then iterate and combine templates for complex plans.
- Practical workflows (e.g., using Excelmatic) reduce manual cleaning, enable conversational instructions, and produce fast reports, charts, and dashboards.
- Action step: pick one metric, choose a template, type one command, and start iterating---early forecasts teach you about your data and improve over time.
In this data-driven era, predictive analytics has become a core capability for business decision-making. With the Excel AI assistant, anyone can turn historical data into forward-looking insights. This article gives you a ready-to-use set of predictive analytics commands to help you see the future in your data.
Understanding the Core Logic of AI Forecasting
Getting AI to make useful forecasts comes down to three clear points: what you want to predict, what data you have, and what output you need. AI doesn't need you to spell out every column name, but it does need a clear task definition. Forecasting is essentially about finding patterns — time patterns, causal patterns, classification patterns — and your instruction serves as the navigation that guides the AI to the right pattern.
10 Excel AI Predictive Analytics Templates
1. Trend extrapolation commands
Scenario: Predicting the future based on historical trends
- Template: "Based on [historical data column], use [time-series method] to forecast the next [number of periods], provide confidence intervals and a trend chart."
- Example: "Based on column B monthly sales, use exponential smoothing to forecast sales for the next 6 months, provide 95% confidence intervals and a line chart with the forecast."
Output: forecast table + trend chart + confidence band
2. Causal forecasting commands
Scenario: Understanding how factors affect outcomes
- Template: "Build a [model] to analyze the impact of [factors] on [outcome], and predict how [outcome] will change when [conditions change]."
- Example: "Build a linear regression model to analyze the impact of ad spend and promotions on sales, and predict the sales growth rate when ad budget increases by 20%."
Output: regression equation + factor importance ranking + scenario predictions
3. Classification forecasting commands
Scenario: Automatically classifying new data points
- Template: "Predict which [category] a new [object] is most likely to belong to, and provide a probability ranking."
- Example: "Predict which value tier (high/medium/low) a new customer is most likely to belong to, and list probabilities for all tiers in order."
Output: classification result + probability distribution + key decision factors
4. Demand planning commands
Scenario: Data-driven planning for the supply chain
- Template: "Forecast demand for each [item] over the next [period] and calculate recommended [replenishment amounts]."
- Example: "Forecast weekly demand for each SKU for the next 8 weeks and calculate recommended reorder quantities using a 2-week safety stock."
Output: demand forecast table + replenishment plan + inventory alerts
5. Growth assessment commands
Scenario: Assessing the health of business growth
- Template: "Calculate the growth rate of [metric], fit the best trend line, forecast the value at [future date], and evaluate sustainability."
- Example: "Calculate the monthly compound growth rate of users, fit an exponential trend line, forecast year-end users and assess whether growth is sustainable."
Output: growth rate figures + trend-fit chart + health score
6. Scenario simulation commands
Scenario: Evaluating the impact of different decisions
- Template: "Simulate the effect on [target metric] when [variable A] changes by [X%] and [variable B] changes by [Y%]."
- Example: "Simulate the impact on gross margin if raw material costs rise 15% while production efficiency improves 8%."
Output: scenario comparison table + sensitivity analysis chart + recommended optimal plan
7. Risk alert commands
Scenario: Detecting potential problems in advance
- Template: "Identify the Top [N] [objects] with the highest probability of [risk event], and list the key risk features."
- Example: "Identify the top 50 customers with the highest churn probability and list their common traits (e.g., low activity, high complaint counts)."
Output: high-risk list + risk scores + alert signals checklist
8. Seasonal decomposition commands
Scenario: Understanding and leveraging business cycles
- Template: "Decompose [data] into seasonal and trend components, forecast the next [period], and mark peak periods."
- Example: "Decompose quarterly revenue seasonality, forecast revenue for the four quarters next year, and mark expected peak quarters."
Output: seasonal component chart + annual forecast curve + peak period markers
9. Rolling forecast commands
Scenario: Dynamically managing cash and finances
- Template: "Based on [assumptions], produce a rolling forecast of [financial metric] for the next [period] and flag anomalies."
- Example: "Based on a monthly revenue increase of 5% and a 60-day receivable cycle, create a rolling 12-month cash flow forecast and flag months with cash shortfalls."
Output: monthly cash flow table + shortfall alert chart + improvement suggestions
10. Model selection commands
Scenario: Choosing the best algorithm for your data
- Template: "Use [method A] and [method B] to forecast [data], compare which performs better and explain why."
- Example: "Use a 12-period moving average and Holt-Winters to forecast monthly sales, compare RMSE and recommend the better method."
Output: method comparison chart + error metrics table + recommendation
Your Forecasting Skill Path: From Quick Start to Advanced AI Models
Start by choosing the template that most closely matches your scenario and substitute the specific parameters. For example, to forecast next quarter's sales, use template 1: "Based on quarterly sales data, forecast the trend for the next three quarters."
Once you're comfortable with the basics, try combining templates. For an annual operations plan you might: decompose historical seasonality (template 8), forecast annual trends (template 1), then create an inventory plan based on those forecasts (template 4). Combining templates lets you handle more complex analyses.
As you become an expert, tweak technical parameters in the templates — change confidence intervals, adjust forecast horizons, modify algorithm settings, or add business constraints — to make forecasts better reflect reality.
How to Ensure Your Excel AI Forecasts Are Accurate & Reliable
Forecast accuracy starts with data quality. Ensure your data is complete and consistent, and remove outliers. Also question your assumptions — will historical trends really continue? Has the external environment changed? AI forecasts are advisory, not absolute truths; combine them with your business judgment and market knowledge.
Regularly validate forecasts against actual data, and update models and parameters when business patterns change. Forecast models need ongoing care — like plants, they require regular watering and pruning to keep producing valuable results.
Full Practical Example with Excelmatic
Recently, I came across a tool called Excelmatic that completely transformed my view of data analysis. The whole process feels as simple as conversing with an expert assistant, eliminating all the tedious steps of traditional workflows.
1. Step 1: Upload your data
You don't need to prepare formulas or format anything — just organize your raw sales data (for example, a CSV or Excel file with fields like "Date," "Product," "Sales," "Channel") and drag it into the tool's upload area.
Why is this simple? In traditional workflows you first have to clean the data, standardize formats, and handle missing values — steps that can easily take half an hour. These AI tools typically perform initial cleaning and recognition automatically in the background.
2. Step 2: Give it instructions
This is the core step. It's like talking to a senior data analyst: type your request into the chat box. For example: "Analyze last month's sales for me. Focus on: which product sold best? Which channel had the fastest sales growth? How do weekend sales patterns differ from weekdays?"
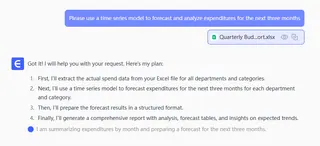
Why is this powerful? In Excel you'd need to create separate pivot tables, calculate period-over-period growth, and group by date — tedious and time-consuming. Here, you simply ask the question.
3. Step 3: Generate the report
Within seconds, the AI produces a well-structured report that might include:
- Core summary: Text that directly tells you "Product A is the top seller, Channel B shows the fastest month-over-month growth."
- Key charts: Automatically attached visuals like a "product sales ranking bar chart" and "channel trend line chart."
- Data snapshots: Top-10 tables for key metrics.
Why is this efficient? It's like the AI instantly does pivoting, charting, and report writing for you — compressing hours of analysis into tens of seconds.
4. Step 4: Drill deeper based on the report
This is how analysis becomes deeper. Based on the report, you can follow up with natural, consecutive questions. For example:
So Product A sold the most. Is its sales evenly distributed across different cities? Please show that on a map.
Last month's final week had a promotion — can you separately analyze sales and average order value before, during, and after the promotion? Present it with a combined chart."

Why is this intelligent? It means the analysis isn't one-off; it supports contextual, continuous interaction and layered drill-downs. In traditional tools, each new question often requires redoing the analysis.
5. Step 5: Create a dashboard
After all Q&A is complete, give the final instruction to dashbord.
The AI will automatically lay out the previously scattered insights into a single-page dashboard containing metric cards, trend charts, distribution charts, and data tables.
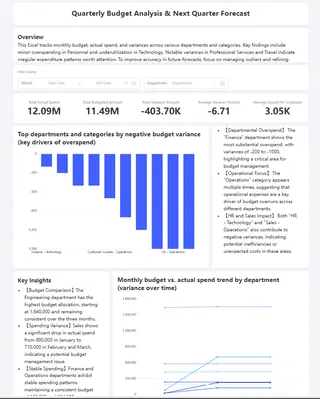
Who Needs This? Identify Your Perfect Use Case for Excel AI Forecasting
Situations where time is especially tight are perfect use cases for tools like this. For example:
- Before a meeting: Your boss or client suddenly asks for insight and you need a chart-backed brief in 10 minutes.
- Weekly/monthly reporting: Quickly distill highlights and issues from massive data instead of spending a whole day on spreadsheets.
- Exploring unfamiliar data: You receive a new or unfamiliar dataset and need a fast overview of its structure, key dimensions, and potential problems.
- Non-analyst roles: Marketing, operations, and sales people who want to do their own analysis without learning complex formulas or coding.
The core value of this "conversational analytics" tool is that it translates your business thinking directly into analytical results, skipping the tedious technical steps and letting you focus on what questions to ask and how to act on the answers.
Ready to Predict? Your 5-Minute Action Plan to Apply AI Forecasting Today
Pick the one business metric you care about most — sales, users, or cost. Choose the most relevant template, adjust the parameters, and enter the command. Don't chase a perfect forecast on the first try; the important thing is to start. Early forecasts will have errors, but you'll learn about your business, your data, and how to work effectively with AI.
Remember: the goal of forecasting isn't to know the future with 100% certainty, but to make today's decisions better informed and reduce tomorrow's surprises. Every forecast is an intentional act of thinking about your business's future.
The best time to start Excelmatic for predictive analytics is now. Pick a template, type one command, and begin your data-driven forecasting journey.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is an Excel AI predictive analytics template and how do I use one? A: A template is a ready-made command pattern you paste into Excel AI to perform a forecasting task (e.g., trend extrapolation, demand planning). Pick the template matching your question, swap in your columns and periods, and run — the AI returns forecasts, charts, and tables.
Q: Which template should I start with?
A: Start with the simplest match to your business metric — e.g., use the Trend Extrapolation template for straightforward time-series sales forecasts or the Demand Planning template for inventory SKUs.
Q: How do I choose between trend, causal, and classification templates?
A: Use trend for pure time-series forecasting, causal when you have explanatory variables (marketing, price), and classification when you need to assign categories (churn risk tiers, value segments).
Q: How reliable are the AI forecasts and confidence intervals?
A: AI forecasts are advisory and depend on data quality and chosen model. Confidence intervals give statistical bounds but should be validated against historical holdout data and combined with business judgment.






